Table Of Contents
Estimated Tax Definition
Estimated tax refers to the tax arrangement that makes individuals pay taxes in proportion to the income they generate from their self-employed ventures. These taxes apply to freelancers and any independent artisan or contractor whose earnings are not subject to withholding. It allows self-employed taxpayers to pay a portion of their earnings as tax to the government.
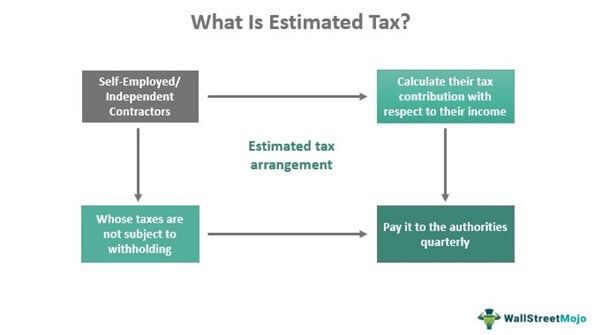
The individuals or firms determine estimated tax with respect to what the taxpayers earn over a period. Individuals and firms pay these taxes quarterly, helping the government authorities generate significant revenue. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) expects the independent business operators to pay these taxes every quarter within the due date.
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Estimated tax refers to the tax system for self-employed and independently working individuals.
- Based on their earnings, they calculate the tax based on the tax brackets for the current fiscal year and pay their part as tax.
- In the United States, individuals use Form 1040(ES) to calculate their taxes, while corporations use Form 1120-W.
- Individuals/companies are subject to paying penalties for underpayment of the taxes. However, these can be avoided under certain circumstances.
How Do Estimated Taxes Work?
The estimated tax applies to those individuals whose income is not subject to withholding. In a regular tax structure, employers deduct the income from employees' payroll at regular intervals to serve their local, state, and national tax payment responsibilities. However, self-employed people who work independently have no specific tax structure to follow. As there are no higher authorities to deduct or withhold their taxes from the payroll, these individuals pay a portion of their earnings as taxes through estimated tax payments.
The IRS expects self-employed individuals to pay these taxes if they incur a tax liability worth $1,000 for that year. Moreover, if it's a partnership business, the individuals are subject to paying taxes worth over $500.
Regular employees have to fill up a W-4 tax form to help employers know how much tax to withhold. The recruiters take the details at the time of hiring to deduct the tax amount from their earnings before they issue the paychecks.
The IRS further assesses the payable estimated tax to check whether the amount paid as tax is accurate, less or too much. While filing the estimated tax return at the end of the financial year, if the taxpayers find that the payment was too much, they can apply for an estimated tax refund.
The proof of income may include salary receipts, capital tax gains, interest income dividends, coupon receipts, self-occupation, or any other form which adds to the net amount available with the individual or company. In addition, individuals or companies with unequal monthly income may annualize their income to calculate the total income received during the year.
Applicability
In the United States, individuals use Form 1040(ES) to calculate their taxes, while corporations use Form 1120-W. While filling up the form, taxpayers disclose all incomes and deductions and calculate this amount accurately. In the case of excess tax payments, the amount can be recovered after the end of the current fiscal year through return filing.
Individuals or companies are exempted from paying the estimated tax for a particular year if they meet all the below-mentioned conditions:
Examples
Let us consider the following estimated tax examples for an in-depth understanding of the concept:
Example #1
John works for ABC Corp and earns $100,000 annually. He has been paying $1,000 as withheld taxes each month to his company. His child has expenses worth $5000. He has invested in T-bills securities, which are projected to earn him an income of $2,000 during the year. Let us calculate the estimated tax for the current year for John.

Based on his income, John falls under the bracket of 24%.

John has to pay a tax of $20,400 annually (or $5,100 quarterly).
Example #2
In the above example, consider the below-added information for John and re-estimate the taxes he owes:
- Education loan of $30,000.
- Interest expenses of $30,000
- Medical Expenses: $5,000

John falls into the bracket of 12%.

John has to pay a tax of $2,400 annually (or $600 quarterly).
Estimated Tax Penalty
If individuals or firms do not pay the estimated tax properly throughout the year, they are subject to paying the penalty for underpayment. Most of them try to avoid paying the penalty by presenting documents to prove their tax liability is less than $1,000.
In addition, if taxpayers pay around 90% of what they owe or 100% of the tax as indicated on the return for the previous year, they can still avoid the penalty based on whichever is lower. One can avoid the penalty if the estimated tax payments become due because of a casualty or unusual circumstances. If a taxpayer retires at the age of 62 and above or becomes disabled during the tax year, the penalty remains inapplicable.
Advantages
Through these taxes, self-employed individuals remain accountable for their tax liabilities and get an opportunity to contribute their part in maintaining the nation's economic ecosystem. Here is a list of advantages of such taxes:
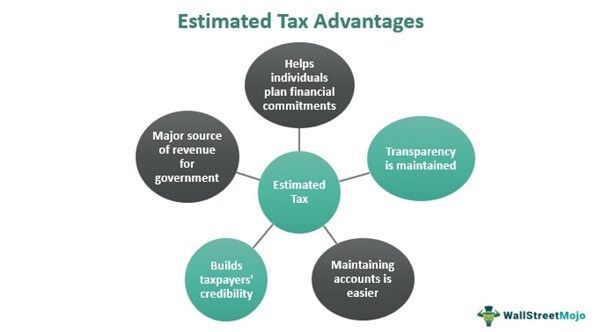
- It forms a major source of revenue for the government. If this element of financial returns from the nation goes missing, it will major impact planning and development.
- It helps individuals plan for their future financial commitments by identifying their actual expenditures and saving.
- These quarterly payments help the government frame strategies and prepare estimates to grow the economy, letting them make major planning and execution decisions.
- Maintaining accounts gets easier as taxpayers pay these taxes at regular intervals. It enhances the productivity and transparency of individuals and companies.
- Paying such taxes strengthens the credibility of a taxpayer. It may further help them in opting for debt or other investments.
Disadvantages
While the estimated tax has numerous advantages, it does have a few limitations, which include:
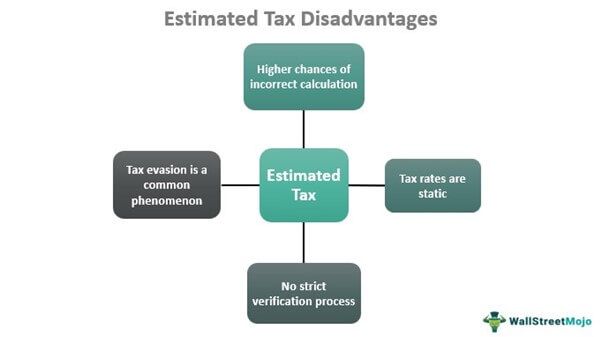
- Tax evasion is quite common when it comes to paying these taxes. As there is a possibility of the actual income proof being hidden, companies and individuals might skip paying taxes, distorting the supposed returns from the nation for the government.
- In the process, taxpayers might unintentionally miss out on counting on many incomes generated from a few sources. As a result, it is difficult to calculate the exact tax amount as the income might not always be accurately computed.
- There is no verification system to check if the taxpayers pay accurate taxes. Though the proof of income is checked to see if the tax paid is accurate, the process is time-consuming.
- Income tax rates are static for the year. If the annual income changes during the year, the taxes do not change for the year. The taxpayer still pays the same amount as he did in the beginning.
