Table Of Contents
Equity Dilution Meaning
Equity Dilution is a method companies use to raise capital for their business and projects by offering ownership in exchange. This process, therefore, reduces or dilutes the ownership of existing owners. New equity is held by more individuals which dilute the ownership of the company. However, the expertise of new investors could improve the overall performance of the company.
Equity dilution can have a significant effect on the company’s portfolio, especially when an individual or a company whose expertise would solve issues in the company such as supply chain management, manufacturing, or marketing. Their advice or opinions help start-ups raise the bar of their performance in the areas they lack experience.
Equity Dilution Explained
Equity dilution is when the ownership of the existing owners decreases due to new investors or issuing of new shares. These events occur after a fundraise or employee option pool is launched.
Dilution is usually carried out when a huge capital requirement for the company arises for growth plans or infrastructural development. For companies, it is important to understand that dilution beyond a point could lead to a decrease in their control over the decisions of the company.
However, capital-intensive businesses such as energy, iron, steel, and automobile industries require capital from time to time for their manufacturing process for which equity dilution might be one of the simpler and cost-efficient sources to raise funds.
Formula
Let us understand the formula which can be applied to the equity dilution formula.
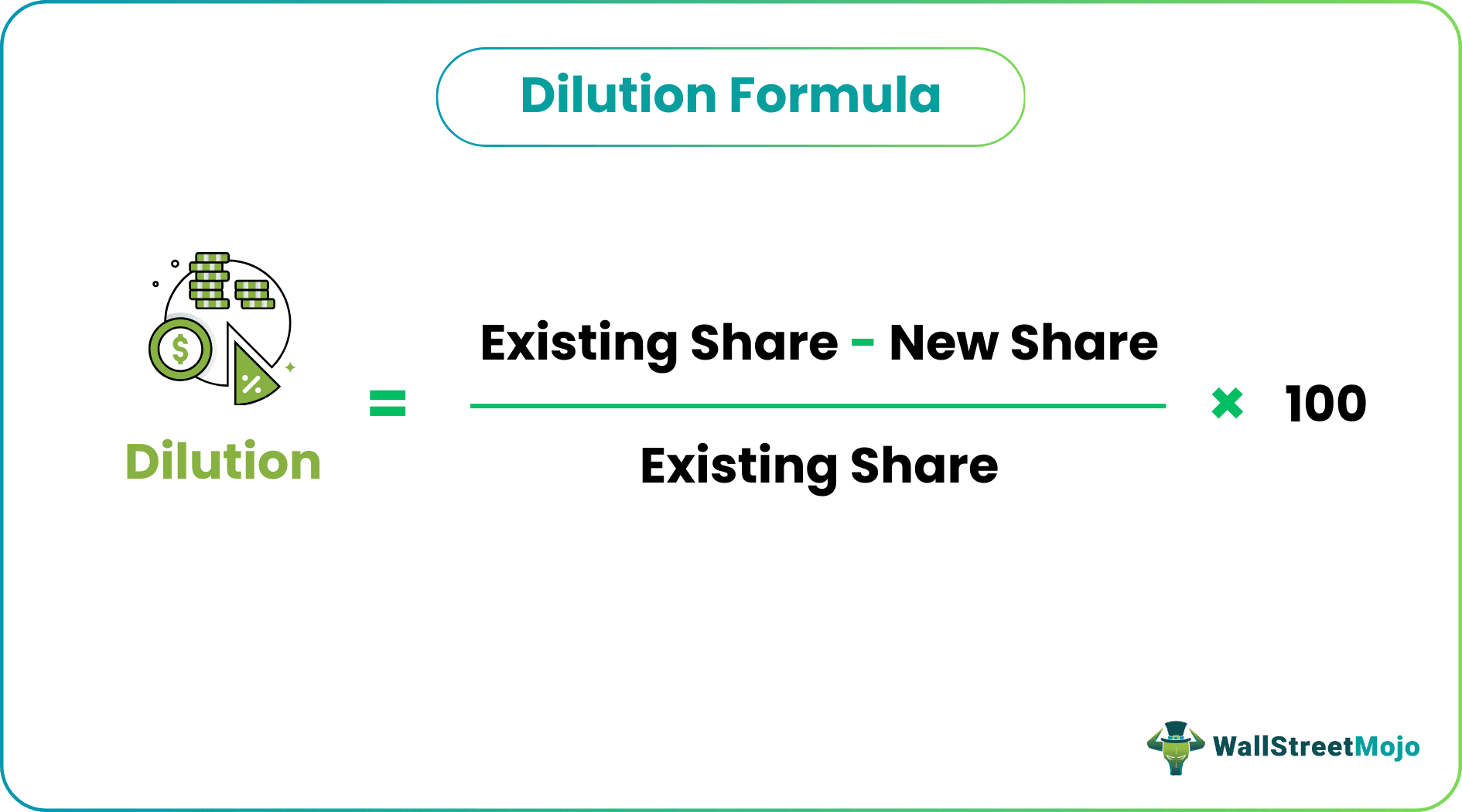
Equity Dilution = (Existing Share - New Share) / Existing Share ×100
Examples
Let us understand the concept in depth through applying the equity dilutor calculator to a couple of examples.
Example #1
There is a partnership firm of lawyers. In that firm, there are four partners, named A, B, C, and D. Partners have equal profit-sharing ratios, i.e., 25% each. Now, the firm wants to introduce a new partner name E. After the admission of E into the firm, the partnership deed was changed, and now, the new profit-sharing ratio is 20% each. Calculate equity dilution.
Solution
Below is the given information –

Calculation of change in the ratio can be done as follows,

- =(25% - 20%) / 25%*100%
Change in Ratio will be -

- Change in Ratio = 20%
Similarly, we can calculate the change in ratio for old partners –

Explanation
A, B, C & D share an equal ratio in partnership, i.e., 25% each partner. Now the partnership firm has brought a new partner into the firm. Because of his admission to a firm, the existing partners must sacrifice 20% of their existing ratios. Now each partner shares 20% of the profit & loss of the firm.
Example #2
RHS Inc. is a private company, and all the shares have been held by its promoters only. Promoters of the company decided to list RHS Inc. in the stock exchange. Promoters want to issue an initial public offer to the public. Promoters are holding 70000 million common stocks at $1 each. Promoters want to issue 33600 million common stocks in the initial public offer, and they will hold remaining stock. Calculate dilution of ownership.
Solution
Below is the given information -

Calculation of after dilution holding of promoters –

- =7000 - 33600
- =36400
Calculation of Dilution of Ownership can be done as follows –

- =(70000 - 33600) / 7000*100%
Dilution of Ownership will be –

- =52%
Calculation of New Holdings

- =100% - 52%
- =8%
Explanation
Promoters of RHS Inc. want to make an initial public offer. They are offering 33600 million stocks in an initial public offer out of 70000 million. Due to this offer, their ownership will be diluted. Before the offer, they are 100% owners of the company, but after the offer, they will be the 52%-part owner of a company, and 48% of the stock will be held by the public and a few financial institutions. Through the initial public offer, they have diluted their ownership.
Example #3
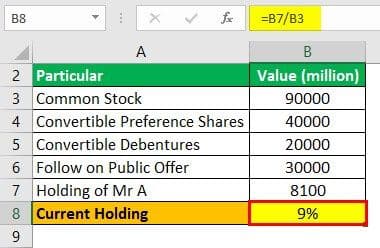
HNR Inc. is a public corporation. The company is listed on the US stock exchange (NYSE). The company has common equity of 90000 million stocks. The company has 40000 million convertible preference shares. Also, the company wants to issue follow on public offer (FPO) to raise funds from the public. The company is issuing 30000 million stocks following the public offer. The company had issued 20,000 million convertible debentures to the public five years ago. These debentures will need to be converted into common stock in the current year. One shareholder of the company is currently holding 8100 million stocks. Calculate equity dilution.
Solution
Below is the given information –

Current Holding

- =8100/90000
- =9%
Calculation of Common Stock & Current holding after conversion of preference share -

- =90000 + 40000
- Common Stock = 130000
- =8100/130000
- Current Holding = 6.23%
Calculation of Common Stock & Current holding after conversion of debentures -

- =130000 + 20000
- Common Stock = 150000
- =8100/150000
- Current Holding = 5.40%
Calculation of Common Stock & Current holding after follow on public offer –

- =150000 + 30000
- Common Stock = 180000
- =8100/180000
- Current Holding = 4.50%
Calculation of Dilution of Holding after Conversion of Preference Shares –

- =(9% - 6.23%) / 9%*100%
Dilution of Holding after Conversion of Preference Shares –

- =30.77%
Calculation of Dilution of Holding after Conversion of Debentures –

- =(6.23% - 5.40) / 6.23%*100%
- =13.33%
Calculation of Equity Dilution after Follow on Public Offer –

- =(5.40% - 4.50%) / 5.40%*100%
- =16.7%