Table Of Contents
What Is Equity Beta?
Equity Beta measures the volatility of the stock to the market, i.e., how sensitive is the stock price to a change in the overall market. It compares the volatility associated with the change in prices of a security. Equity Beta is commonly referred to as levered beta, i.e., a beta of the firm, which has financial leverage.
Equity beta is one of the major components of the CAPM model for evaluating the expected return of the stock. Thus it is a measure of the systematic risk of the entity and compares the risk of the stocks relative to the market risk. It helps in assessing the volatility of the stock returns against the broader market.
Equity Beta Explained
Hence, the company's equity beta calculation is a measure of how sensitive the stock price is to changes in the market and the macroeconomic factors in the industry. It's a number describing how a benchmark set predicts the return of an asset compared to it.
It helps us to analyze in a broad way how the stock returns can deviate due to changes in the micro & macro environment.
It also has some criticism since the company's past performance does not predict future performance, and therefore beta is not the only measure of risk. However, it can be used as a component while analyzing the company's business performance and future strategic plans & policies that will impact its growth prospects.
Interpretations
Below are some of the scenarios in which beta can be interpreted to analyze the company's performance compared to its peers and the sensitivity analysis of the same with reference to the benchmark index used in its calculation.
- Beta < 0 - The underlying asset moves in the opposite direction to a change in the benchmark index. Example: an inverse exchange-traded fund.
- Beta = 0 - The movement of the underlying asset is not correlated to the movement of the benchmark. example: fixed yield assets like government bonds, treasury bills, etc.
- 0<Beta<1 - The movement of the underlying asset is in the same direction but less than the benchmark. example: stable stocks like FMCG industries or consumer goods
- Beta =1 -The underlying asset's movement exactly matches the benchmark index. It is a representative stock of the benchmark index showing correct returns compared to the market volatility.
- Beta >1 - The underlying asset's movement is in the same direction but more than the movement in the benchmark index. For example, such stocks are very much influenced by the daily market news and swing very fast due to heavy stock trading, making them volatile and attractive to traders.
Formula
Below are the equity beta formula.
Equity Beta Formula = Asset Beta ( 1 + D/E( 1-Tax )
Equity Beta Formula = Covariance ( Rs,Rm) / Variance (Rm)
where
- Rs is the return on a stock,
- Rm is a return on market and cov (rs, rm) is the covariance
- Return on stock = risk-free rate + equity beta (market rate – risk-free rate)
How To Calculate?
The equity beta formula can be used in the following three methods.

Method #1 - Using the CAPM Model
An asset is expected to generate at least the risk-free rate of return from the market. If the beta of the stock equals to 1, this means the returns are with a par of the average market returns.
Steps to calculate Equity Beta using the CAPM Model:
Step 1: Find out the risk-free return. It is the rate of return where the investor's money is not at Risk-like treasury bills or the government bonds. Let's assume its 2%
Step 2: Determine the expected rate of return for the stock and the market/index to be considered.
Step 3: Input the above numbers in the CAPM Model, as mentioned above, to derive at the beta of the stock.
Method #2 - Using Slope Tool
Let's understand the equity beta calculation of Infosys stock using the slope.
Steps to calculate Equity Beta using Slope -
Step 1: Download the historical data for Infosys from the stock exchange website for the past 365 days and plot the same in an excel sheet in column b with dates mentioned in column a.
Step 2: Download the nifty 50 index data from the stock exchange website and plot the same in next column c.
Step 3: Take only the closing prices for both the data as above
Step 4: Calculate the daily returns in % for Infosys and nifty both till the last day in column d and column e.
Step 5: Apply the formula: =slope (d2:d365,e2:e365) to get the beta value.
Method #3 - Using Unlevered Beta
Equity Beta is also known as a levered beta since it determines the level of a firm's debt to equity. It's a financial calculation that indicates the systematic risk of a stock used in the CAPM model.
Example
Mr. A analyses a stock whose unlevered beta is 1.5, debt-equity ratio of 4%, and a tax rate =30%. Calculate the levered equity beta.
- Beta: 1.5
- Debt-Equity Ratio: 4%
- Tax Rate: 30%
Solution:
Calculation of levered beta is as follows -
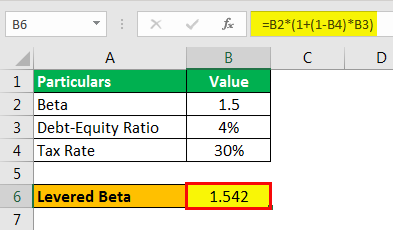
- Levered Beta Formula= Unlevered Beta ( 1+ (1-Tax)*D/E Ratio)
- = 1.5(1+(1-0.30)*4%
- = 1.542
Example
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept.
Example#1
Calculate levered equity beta by regression and slope tool both using the below-mentioned table.
| Date | Stock Price | Nifty | % change in Stock Price | % change in Nifty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27-May-19 | 708.1 | 11,924.75 | -0.16% | 0.68% |
| 24-May-19 | 709.2 | 11,844.00 | 1.16% | 1.60% |
| 23-May-19 | 701.05 | 11,657.00 | -1.23% | -0.68% |
| 22-May-19 | 709.75 | 11,737.00 | 0.06% | 0.24% |
| 21-May-19 | 709.3 | 11,709.00 | 1.33% | 0.08% |
Beta by regression method -

- Beta = COVAR(D2:D6,E2:E6)/VAR(E2:E6)
- =0.64
By Slope Method -

- Beta = Slope(D2:D6, E2:E6)
- =0.80
Example #2
We have the following data as: exp rate of return = 7% , market rate of return = 8% & risk free rate of return = 2%. calculate beta using the CAPM model.
- Exp Rate of Return: 7%
- Market Rate of Return: 8%
- Risk Free Rate of Return: 2%
Solution:
As per CAPM Model, exp rate of return on stock = risk-free rate + beta (market rate – risk-free rate). Therefore, beta = (exp rate of return on stock - risk-free rate)/(market rate–risk-free rate). So, the calculation of beta is as follows -
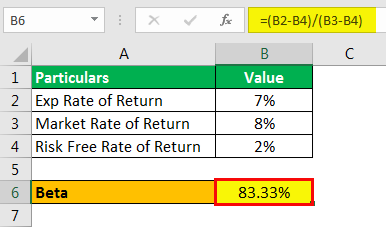
Hence Beta = (7%-2%)/ (8%-2%) = 0.833.
Equity Beta Vs Asset Beta
Both the above method measures the systematic risk of the business but they measure different aspects of the risk profile.
- The market equity beta measures the risk of the sticks of a company with relation to the markets, whereas the latter measures risk of the assets of the company, both debt and equity with relation to the markets.
- The former is also called levered beta whereas the latter is also called unlevered beta.
- The asset beta tends to be lower than market equity beta since asset beta includes the risk of both equity and debt, thus lowering the overall risk of the company.
- The former calculates the cost of equity of the business whereas the latter calculates the cost of capital of the whole enterprize.
- It is different from the asset beta of the firm as the same changes with the company's capital structure, which includes the debt portion.
- If the firm has zero debt, the asset beta and equity beta are the same. As the debt burden of the company increases, equity beta increases.
Thus, both measures are equally crucial for decision making purpose, evaluating the company’s risk profile and calculating the cost of capital.

