Table Of Contents
What Is Equal Weighted Index?
The equal-weighted index is one of the stock indices that assign or give equal value to all the stocks in the index. Therefore, the index's total value is determined by the value of each stock as if all of them carry equal importance or value in the calculation of the index.
No preference is given to the stocks’ market capitalization; all stocks are assigned equal weightage. It is useful for small businesses because they get equal importance in the index as large companies, thus removing the bias towards market capitalization while investing. This also offers less risk and better opportunity towards value investing.
Key Takeaways
- The equal-weighted index assigns equal value or importance to all the stocks in the index, regardless of their market capitalization.
- Unlike other indices that favor larger stocks, the equal-weighted index does not give preference based on market size. It treats each stock equally in terms of contribution to the index value.
- When recalculating a new index using the old equal-weighted index, the arithmetic mean of returns or the percentage change in the index value for each stock in the fund must be determined.
- This ensures an accurate representation of the overall performance of the index constituents.
Equal Weighted Index Explained
The majority of the stock indexes are either market capitalization index or price-weighted index. The market capitalization index gives more importance to stocks with high market capitalization. On the other hand, as the name suggests, the price-weighted index provides significance to the stocks according to their prices, i.e., price is the only consideration in calculating the price-weighted index.
The equal weighted index funds assign the same value to all the stocks and considers investment equally in each stock making up the index. Thus, if the price of a stock in an index fund goes down, this fund will buy more shares. If the price goes up, it will sell shares to balance the fund equally in the index. Due to more buying and selling activity, trading cost remains high in the equal-weighted index funds.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Features
- The equal dollar weighted index assigns the same value to each stock, making up the index irrespective of market capitalization, firm size, or share price.
- They are more diversified.
- Due to buying and selling, the trading cost of funds based on an equal-weighted index remains high.
- Funds based on this index indicate a less risky option.
Formula
The formula mentioned below states how to calculate equal weighted index.
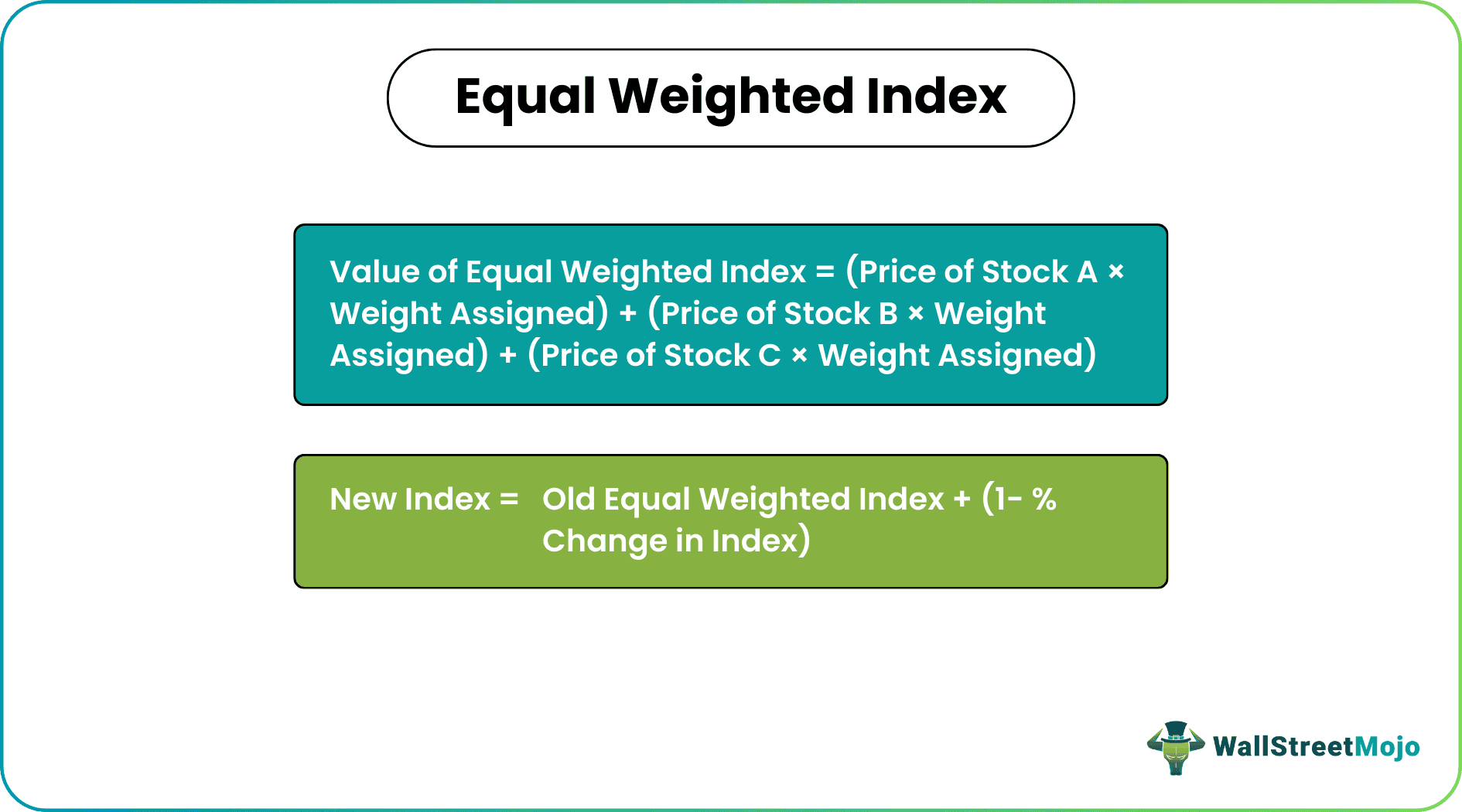
The world equal weighted index is calculated by assigning the same weight to each stock in the index. For example, suppose there are only three stocks in the market. It will give each a weightage of 33.3% (100/3). The formula for calculation of this index in simple terms would be as follows: -
Value of Equal Weighted Index = (Price of Stock A * Weight Assigned) + (Price of Stock B * Weight Assigned) + (P of Stock C * Weight Assigned)
To calculate the new index using the old equal-weighted index, we will have to calculate the arithmetic mean of the return on each stock in the fund or the percentage change in the index value. The formula for the new weighted index from the old index is as follows: -
New Index = Old Equal Weighted Index + (1- % Change in Index)
Thus the above formula shows how to calculate equal weighted index.
Example
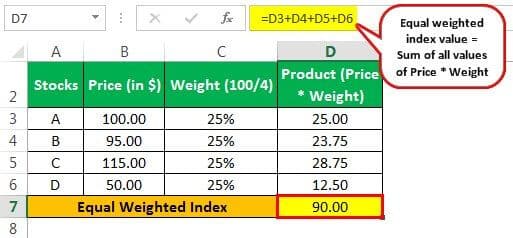
Let’s take an example of world equal weighted index calculation.
Let us assume there are four stocks in the equal-weighted index- Stock A, Stock B, Stock C, and Stock D and the prices of each stock are as follows: -

Solution:
The calculation of the Equal Weighted Index will be -

The above equal weighted index example clearly explains the concept.
Equal Weighted Index and Small Business
The equal dollar weighted index give importance to each stock equally. It favors smaller companies since they are weighted equally to large firms irrespective of market capitalization or share price. They do not get such an advantage in the market-capitalization-weighted index, where the weight of each stock is given according to its market capitalization in the economy.
Advantages
- The long-term performance of this index is better than other indices.
- This index is not concentrated only on the largest company stocks. Thus, it is more diversified.
- Since the index is diversified, it carries a lesser risk.
- This index does not give over importance to overpriced stocks.
Disadvantages
- Due to a large amount of buying and selling to keep the index fund balanced, there is a high transactional cost or portfolio turnover rate.
- The index is more volatile in the event of a recession.
- The underperforming companies are given the same weight in the index.
- Due to the high transaction cost and portfolio turnover rate, it may have tax implications.
Equal Weighted Index Vs Capitalization Weighted Index
Market capitalization gives value to top stocks according to their market capitalization. Therefore, the largest companies with huge market capitalization will get more value than small or mid-cap stocks.
On the contrary, they give equal value to each stock irrespective of the company's market capitalization size. So, to balance the fund, it will have to buy more securities for stocks whose price has decreased and sell the securities for those whose prices have increased.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.