Table Of Contents
What is Enterprise Value Formula?
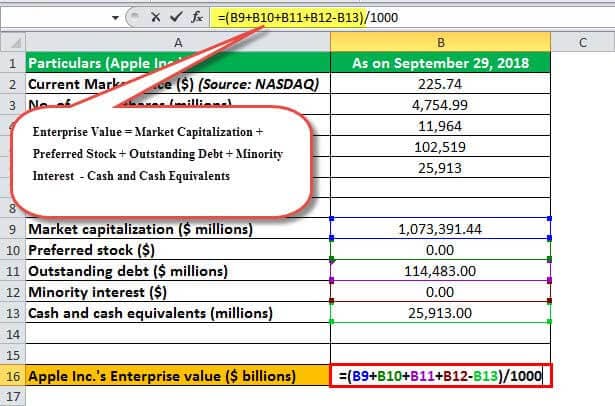
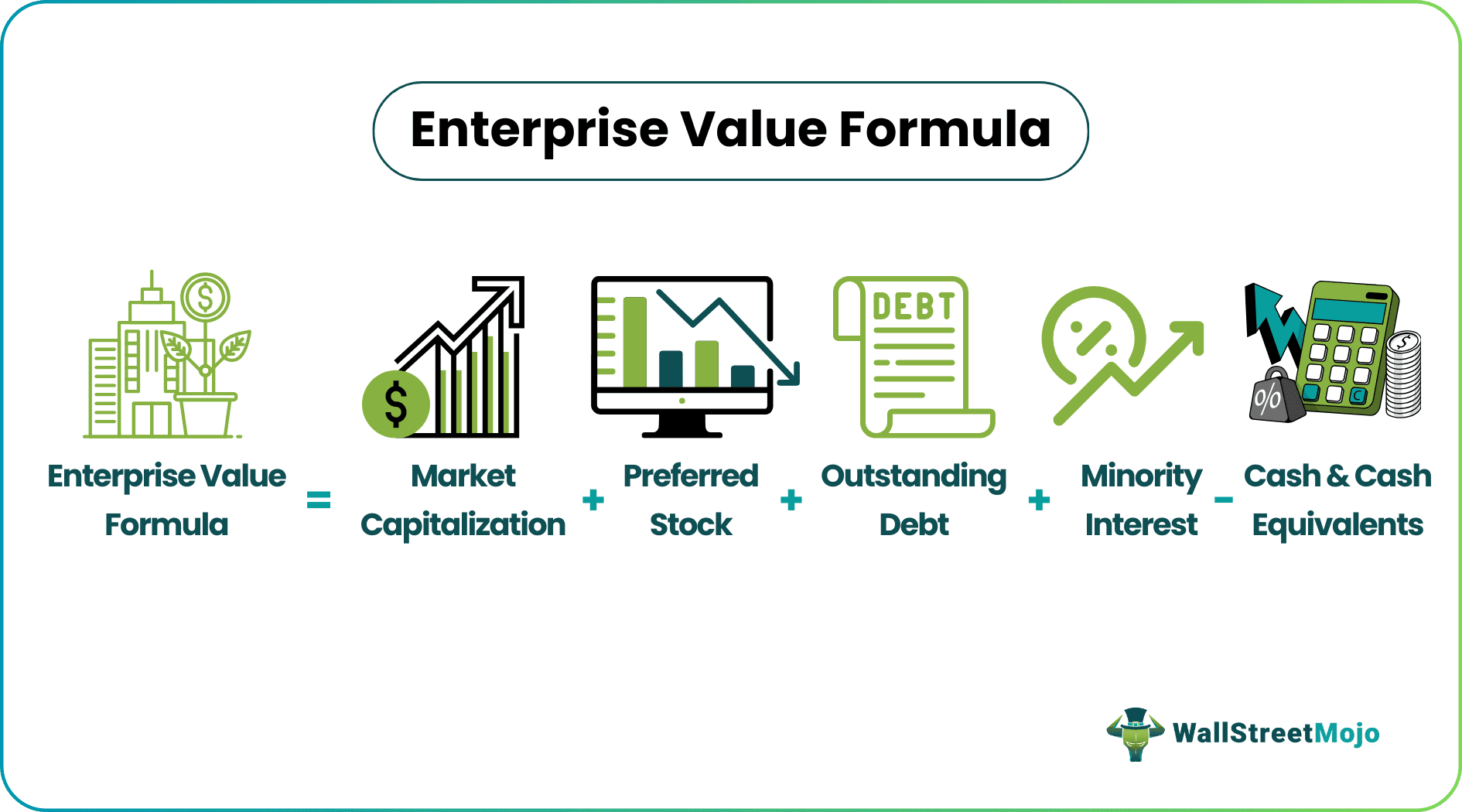
The enterprise value of a company can be ideally defined as an amount that represents the entire cost of the company in case some investor intends to acquire 100% of it. The formula for enterprise value is calculated by adding the company market capitalization, preferred stock, outstanding debt, and minority interest together, and then deducting the cash and cash equivalents obtained from the balance sheet. The cash and cash equivalents are deducted from the enterprise value since the post-acquisition of the complete ownership of the company; the cash balance belongs to the new owner. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Enterprise value Formula = Market Capitalization + Preferred stock + Outstanding Debt + Minority Interest - Cash & Cash Equivalents
Step by Step Application of Enterprise Value Formula
The Calculation of Enterprise Value equation can be done in the following six simple steps:
Firstly, the current price per share of the company has to be found out from the stock market, and then the number of paid-up equity shares has to be collected from the balance sheet. Now, the current market capitalization of the stock can be derived by multiplying the current price per share with the great number of paid-up equity shares.
Market Capitalization = Current Price Per Share x Outstanding Number of Paid-up Equity Shares
Now, the current value of the preferred stock is computed by multiplying the stock's per value by the number of outstanding preference shares, which are both available on the balance sheet.
Preferred Stock = Par Value x Outstanding Number of Preference Shares
The current outstanding debt balance is calculated by adding financial liabilities like bank loans and corporate bonds, again available on the balance sheet.
Outstanding Debt = Bank Loans + Corporate Bonds
Now, the minority interest is captured, as reported in the balance sheet.
The cash and cash equivalents are computed by adding the cash balance and fixed deposits and current account deposits with banks, which are again mentioned in the balance sheet under the current asset section.
Cash and Cash Equivalents = Cash Balance + Fixed Deposits and Current Account Deposits with Banks
Finally, the enterprise value is arrived at by adding the values derived in Step1-4 and deducting the value in Step 5 as shown below,
Enterprise Value = Market Capitalization + Preferred Stock + Outstanding Debt + Minority Interest - Cash and Cash Equivalents
Video Explanation Of Enterprise Value
Examples of Enterprise Value Formula
Let's take a few simple to advanced examples to understand Enterprise Value.
Example #1
Let us assume that a company ABC Limited has the following financial information:
- Shares Outstanding: 2,000,000
- Current Share Price: $3
- Total Debt: $3,000,000
- Total Cash: $1,000,000
Therefore, given
- Market capitalization = 2,000,000 * $3 = $6,000,000
- Preferred stock = $0
- Outstanding debt = $3,000,000
- Minority interest = $0
- Cash and cash equivalents = $1,000,000
Based on the above formula, the calculation of the enterprise value of ABC Limited can be as follows:
- EV Formula = Market capitalization + Preferred stock + Outstanding debt + Minority interest - Cash and cash equivalents
- Enterprise value = $6,000,000 + $0 + $3,000,000 + $0 - $1,000,000
- Enterprise value = $8,000,000 or $8 million
Example #2
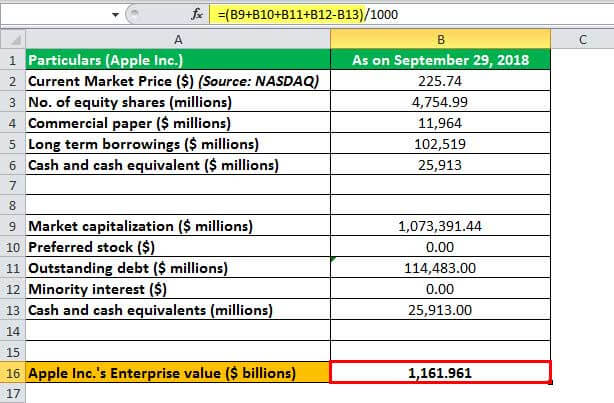
Let us take the real-life example of Apple Inc.'s annual report as on September 29, 2018. The following information is available:
Given
- Market capitalization (millions) = 4,754.99 * $225.74 = $1,073,391
- Preferred stock = $0
- Outstanding debt (millions) = $11,964 + $102,519 = $114,483
- Minority interest = $0
- Cash and cash equivalents (millions) = $25,913
Based on the above formula, the calculation of the enterprise value of Apple Inc. can be as follows:
- EV Formula = Market capitalization + Preferred stock + Outstanding debt + Minority interest - Cash and cash equivalents
- Enterprise value Apple Inc. (millions) = $1,073,391 + $0 + $114,483 + $0 - $25,913
- Enterprise value Apple Inc. (millions) = $1,161,961
- Therefore, Apple Inc.'s enterprise value as on September 29, 2018, stood at around $1,161.96 billion or 1.16 trillion.
Relevance and Use
The importance of enterprise value revolves around the fact that it helps assess the worth of a company. Further, the enterprise value can also be seen as the theoretical takeover price of a company to be acquired. It accounts for the impact of the outstanding debt and the cash balance that the acquirer also takes over during the transaction. However, the acquisition of the outstanding debt increases the cost of acquisition, the acquisition of the available cash balance moderates the acquisition cost to some extent.
Given that the debt portion is included in enterprise value, it enables the comparison of companies with different capital structures, which eventually helps in acquisition. In addition, the acquirer can use enterprise value to compare returns from different businesses in which they intend to buy controlling stakes.
Calculate Enterprise Value in Excel
Let us take the case of Apple Inc. mentioned in EV Formula Example #2 to demonstrate in an excel template the working towards the calculation of the Enterprise Value:
In the below template is the data of Apple Inc for September 2018 to calculate its Enterprise Value.
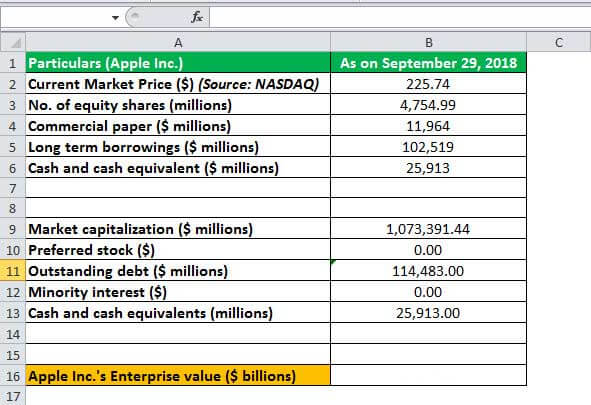
In the below given excel template, we have used the calculation of Enterprise Value to find Apple Inc.'s Enterprise Value.
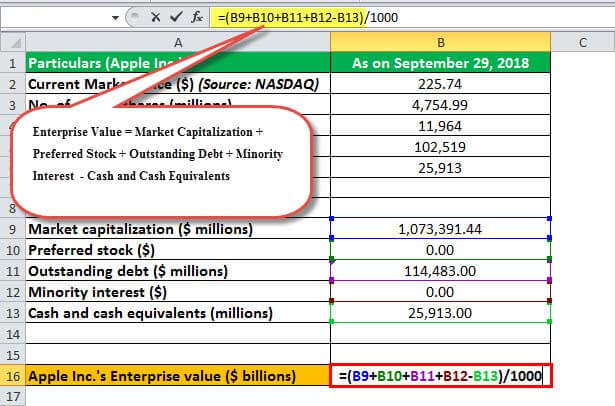
So the Calculation of Enterprise Value will be:-