Table Of Contents
Electronic Filing Meaning
Electronic filing, commonly known as e-filing, is a method of filing individual and corporate income tax returns using authorized tax preparation software or websites. The tax forms directly reach the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or the relevant tax authorities in each country via approved e-file providers, i.e., tax professionals and accountants.
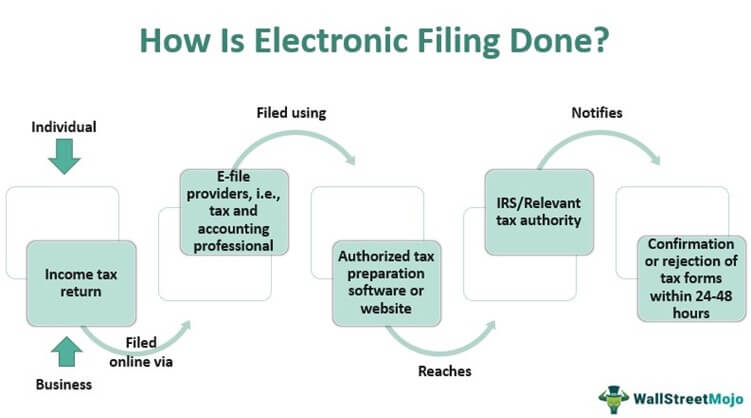
The procedure makes filing returns and reimbursements for overpayments faster and more convenient than paper filings. Individuals and enterprises can easily file their taxes electronically per tax regulations of their country, state, or province. However, government regulations and other factors influence the filing of taxes digitally that taxpayers must consider before e-filing their taxes.
Key Takeaways
- Electronic filing, also known as e-filing, is the process of filing individual or business income tax returns with the relevant tax authority using an authorized tax preparation software or website.
- It cuts down on processing time, operating costs, transmission errors, and paper use.
- If a tax form has any inaccuracy, the tax authority can reject it and notify the taxpayer of it within 24-48 hours of submission. The rejection note contains the portion to be corrected.
- It makes tax filing and reimbursements for overpayments swift, convenient, flexible, safe, and time-efficient. However, the process becomes a bit complex at times due to the software involved.
Understanding Electronic Filing
The electronic filing system enables taxpayers to submit their tax documents to a tax authority or revenue service 24/7. Submission of tax forms occurs through e-file providers approved by relevant tax authorities. Governments started adopting this system to reduce processing time, operating expense, transmission errors, and paper usage.
One can e-file from the comfort of home, office, or other convenient location. Individuals or corporations with annual incomes below a certain threshold must file an income tax return using separate tax forms. As a result, they should select from the tax forms 1040, 1040-SR, 1040X, 7004, and 941 based on what is appropriate for them.
The software, authorized by tax authorities, could be trusted with tax filing as it transmits information through IRS-approved electronic channels. Taxpayers can either install the software or contact an e-file provider to file returns on their behalf. IRS programs like the Tax Counseling for the Elderly and the Volunteer Income Tax Assistance offer free tax assistance and advice to help taxpayers file their tax returns electronically.
With the convenience that e-filing provides, more than 80% of tax filings reach the IRS electronic filing database. The tax authority notifies the taxpayer of the confirmation or rejection of the tax form within 24-48 hours of its submission. The rejection note also specifies the portion to be corrected. Faster e-filing of tax returns results in a quicker tax refund.
Deadline For Electronic Filing
The deadline for filing tax returns is the 15th of the fourth month, i.e., April following the conclusion of each fiscal year. If April 15 is a Saturday, Sunday, or legal holiday, the due date shifts to the next business day. The taxpayers who file electronically are less likely to miss out on the due date as they can do it anytime.
If they wish to extend their electronic filing deadline, they must submit Form 4868 – the Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. It will automatically grant them a 6-month extension to file their tax returns.
Electronic Filing Examples
Let us consider the following e-filing examples to understand the concept even better:
Example #1
Stacy, an IT professional, attempted to file her tax returns electronically multiple times, but the IRS denied her application every time. Despite her best efforts, she could not locate the problem in the submission, as mentioned in the rejection note.
Thus, she gave a call to her friend, Maria, a tax professional. Maria rectified the errors and resubmitted the application. This time, the filing gets eventually confirmed within 48 hours.
Example #2
Taxpayers who take the services of a tax professional or accountant to assist with an IRS notice about refund processing must approve authorization requests. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the IRS has made the process of e-filing tax returns and obtaining approval easier for professionals to represent taxpayers.
The IRS has introduced a practitioner portal cum submission and approval system. Tax professionals can use this system to send authorization requests to their clients for approval. The tax practitioners fill-up the Form 2848 (Power of Attorney) or Form 8821 (Tax Information Authorization) electronically signed by their clients and submit it online to the Centralized Authorization File (CAF) database.
Benefits
Income tax electronic filing has transformed the tax management system and offers significant benefits to taxpayers:
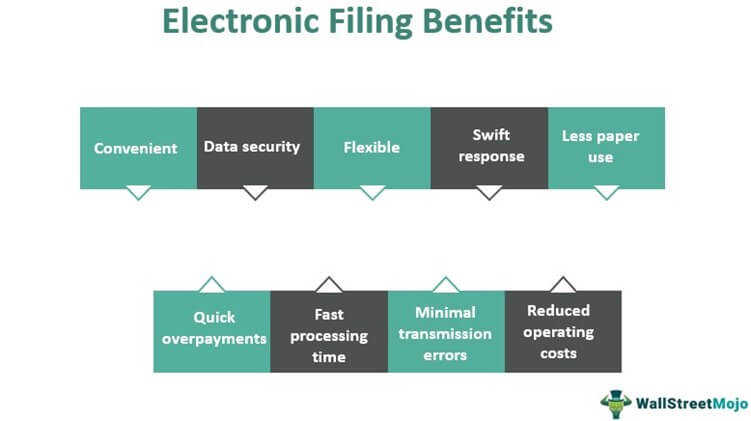
#1 - Swift Response
Taxpayers will receive confirmation or rejection of their tax forms within 24-48 hours of filing. In the event of inaccuracies, the notification explains reasons, thus giving taxpayers a chance to correct any inaccuracies.
#2 - Convenient
Taxpayers or tax practitioners do not need to restrict the electronic filing of tax returns during office hours. They can do it at any hour of any day. In addition, they can do it at their convenience, be it from home, cafe, or office.
#3 - Flexible
Apart from flexible hours, taxpayers get multiple options as well for e-filing their tax returns. They can either do it all by themselves or hire a tax professional or accountant to file the returns on their behalf.
#4 - Time-Efficient
Manual tax filing involved transferring information from paper to online systems, which took a lot of time. But e-filing saves time as it directly transmits data to the IRS or relevant tax authorities, depending on the country.
#5 - Safe
E-filing not only transfers data securely but also prevents it from being manipulated or tampered with. It happens because online inputs reach the tax authority portals directly without being stored anywhere in the middle. Besides, it reduces transmission errors and improves data accuracy during the tax filing process.
Limitations
Along with the benefits, the electronic filing also has some limitations, which taxpayers must know about:
- The software needed to e-file tax returns is complex and might be complicated to use. Therefore, taxpayers should hire tax and accounting professionals for this purpose.
- Though the e-filing procedure involves various technology equipment and software, the process poses no security risk. However, hardware failure or unethical hacking can lead to the loss of sensitive financial information.
