Table Of Contents
Electronic Commerce (e-commerce) Meaning
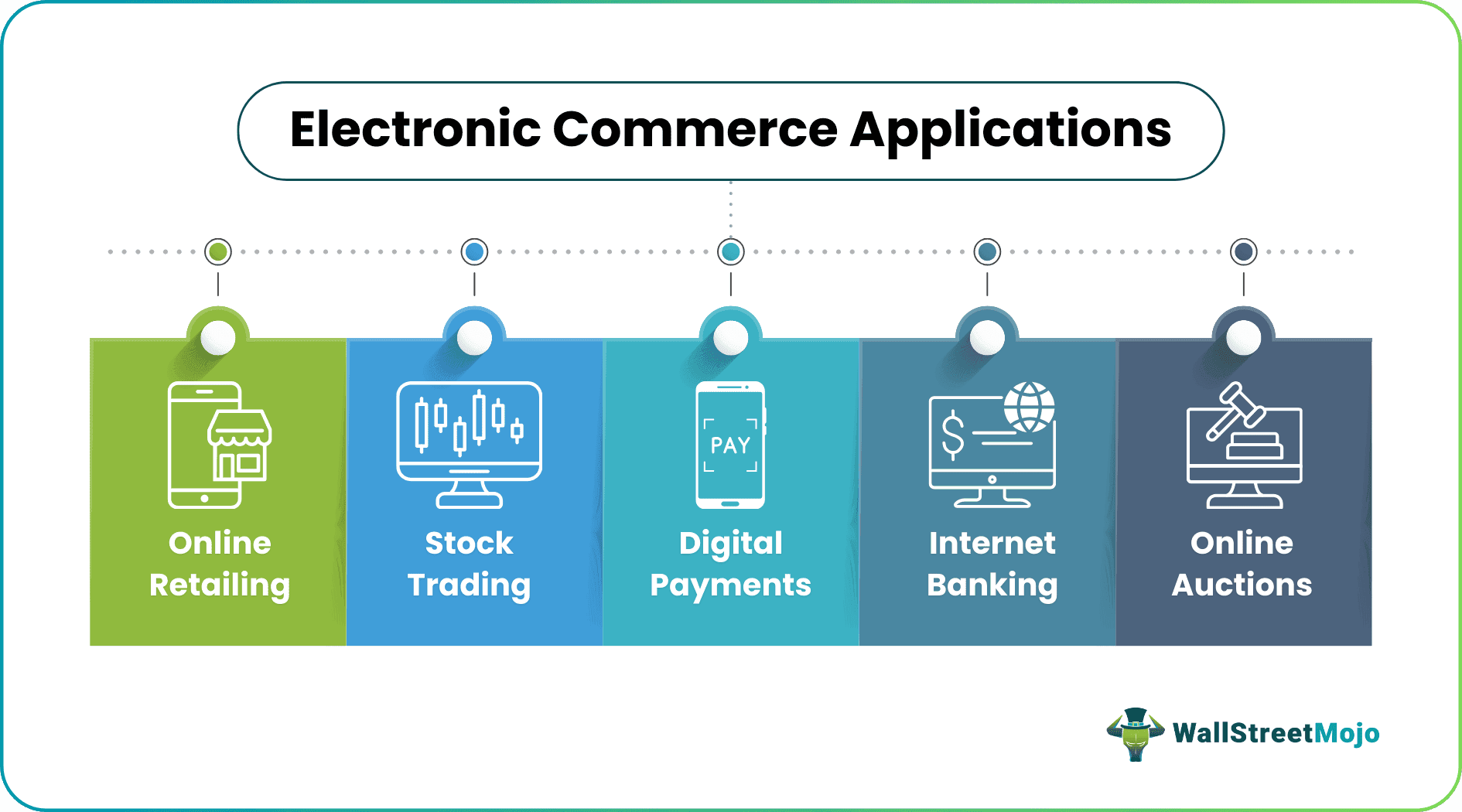
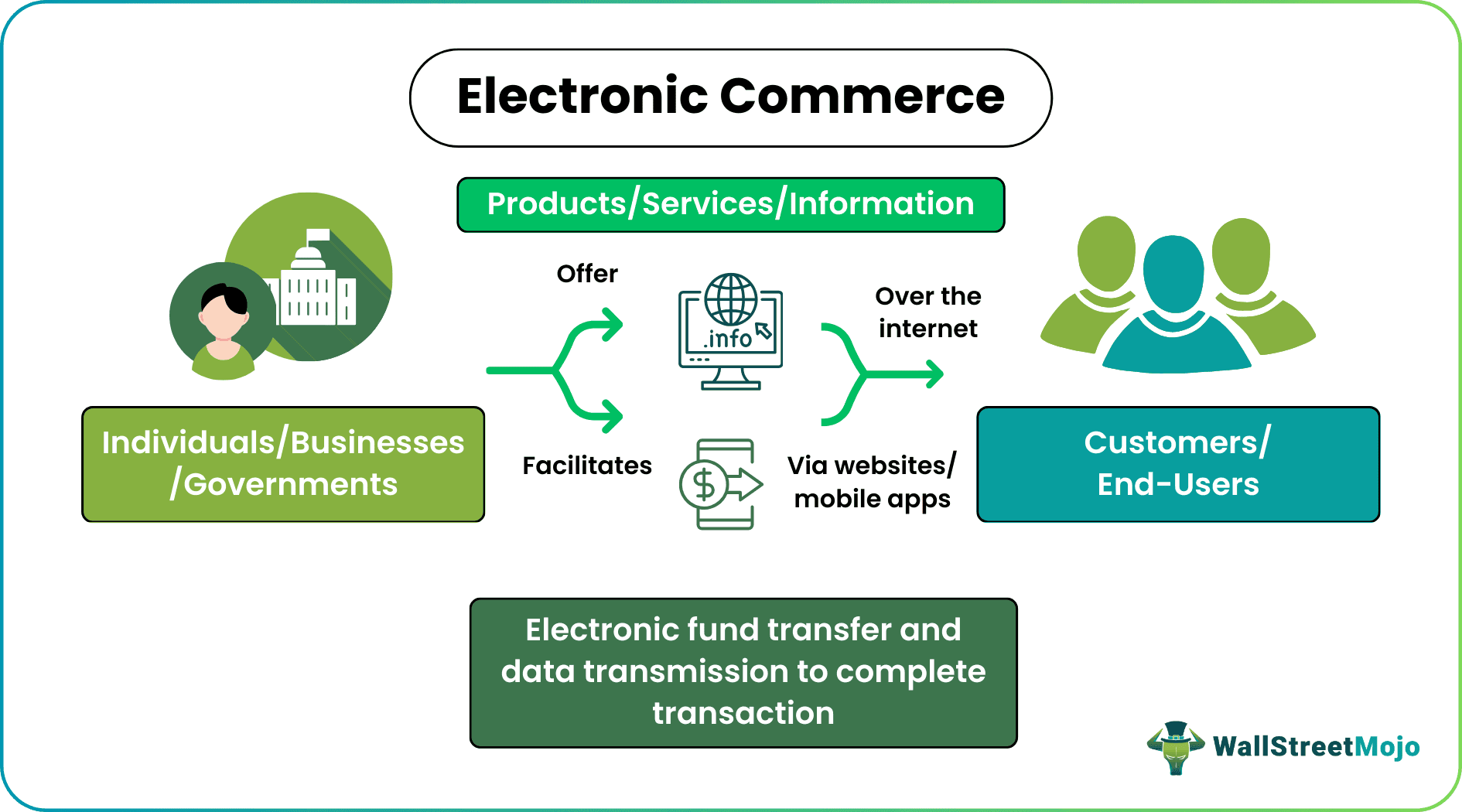
Electronic commerce (e-commerce) refers to the online presence of individuals, businesses, and governments, which they use to provide products, information, and services. In addition, this business model enables electronic fund transfer and data transmission to execute purchases and sales over the Internet. Besides online retailing, it finds its application in internet banking, stock trading, online auctions, and digital payments.
Anything offered, sold, or bought via e-commerce primarily occurs through computers, smartphones, and tablets. Online commerce handles anything from enrolling in government programs to purchasing basic and luxury items to ordering on-demand movies. While e-commerce is a cost-effective approach for businesses to establish a global market presence, it helps consumers get what they need.
Key Takeaways
- Electronic commerce is a marketplace where individuals, businesses, and governments sell products, information, and services to customers. Furthermore, this business model allows for the electronic transfer of funds and data during online transactions.
- Enrolling in government-sponsored schemes, purchasing essential and luxury goods and services, or obtaining on-demand movies are all possible through online commerce.
- E-commerce business encompasses four key market segments - business to business (B2B), business to customer (B2C), customer to customer (C2C), and customer to business (C2B).
- While e-commerce allows businesses to grow and earn profits, it makes it easier for customers to discover and purchase what they want at their convenience.
How Does Electronic Commerce Work?
Electronic commerce functions via a website or mobile application that serves as a catalog of goods and services. These online marketplaces provide several products with varied models, colors, patterns, pricing, and other characteristics. While most companies conduct business through websites, others use e-commerce apps. However, their purpose remains the same that is to improve the customer experience. Online marketplaces serve as a means for buying and selling information, services, and digital products in addition to physical commodities.
Once a business goes online, it has a better chance of expanding its market on a local, regional, and global scale. Also, it keeps both potential and loyal customers informed about the latest products on the market. It, in turn, allows them to find and purchase what they require at their leisure. The entire procedure runs without a hitch. Consumers who have access to the Internet can-
- Visit an online store
- Search for the desired item(s) or service(s)
- Compare them to others of a similar nature and choose the best
- Create an account
- Place the order
- Provide personal and financial details like their email address, phone number, credit/debit card information
- Schedule the delivery
Electronic commerce services utilize market data and efficient distribution channels to provide the best products and services at reduced marketing and operating costs. Online commerce giants offer the best products while maintaining high levels of consumer satisfaction. In contrast, some online stores offer discounts, first-order benefits, free shipping, and promotional codes to entice customers to purchase the same goods from them. The most prevalent best practices that e-commerce companies use include customer segmentation, marketing automation, ecommerce email marketing, etc.
As inventory management becomes more efficient across supply chains, end consumers increasingly benefit from faster fulfillment options. Services like Shipt now enable same-day grocery delivery, reflecting how real-time inventory systems support timely access to everyday essentials without requiring a trip to the store.
Types Of Electronic Commerce
E-commerce plays a vital role in four market categories when purchasing and selling products or providing services. These four main types of electronic commerce business models involving businesses as well as consumers are:
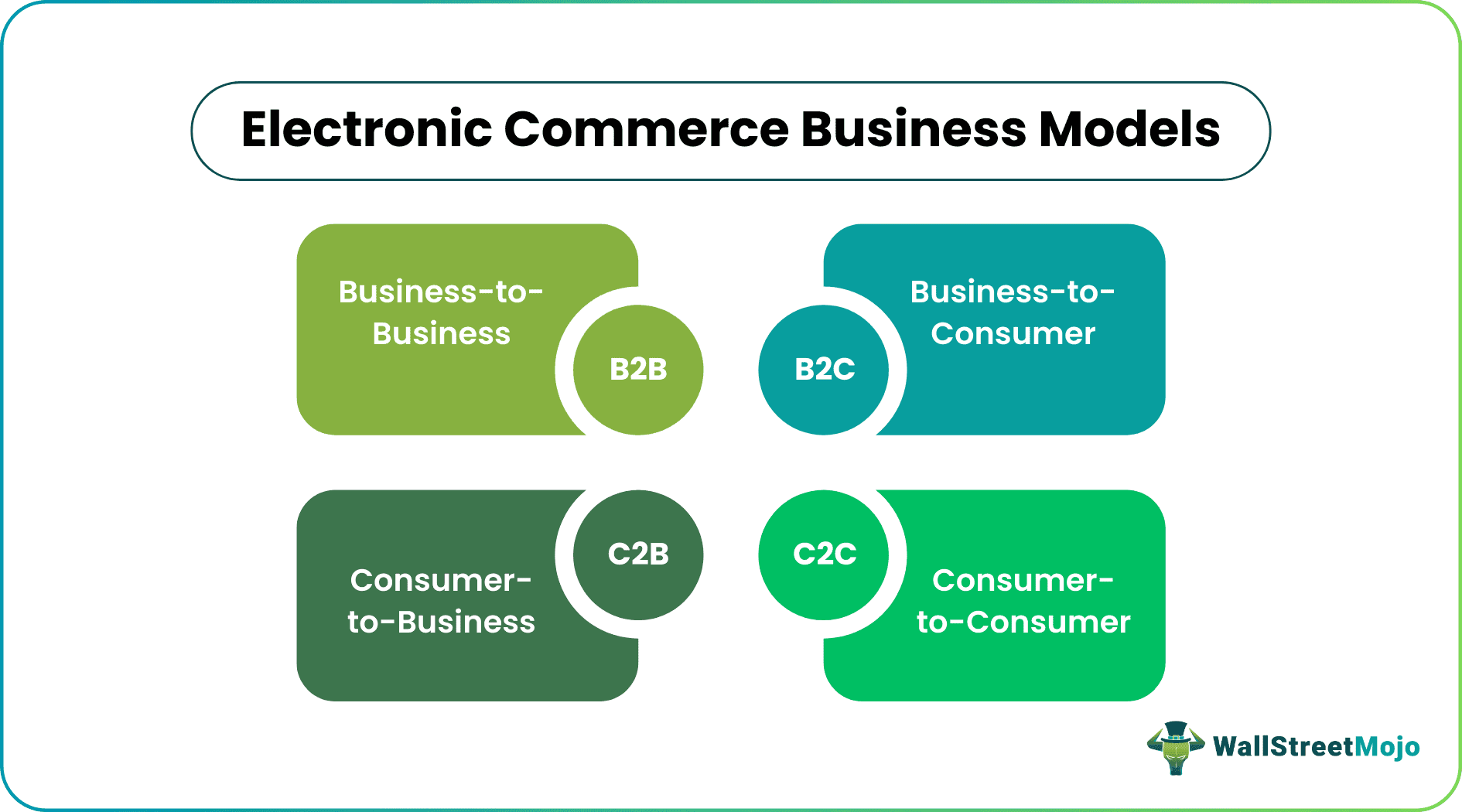
1. Business To Business (B2B)
This category involves two or more companies in a business transaction, such as manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, and retailers. Examples include raw material suppliers, software solution providers, website hosting services, and financial services providers.
2. Business To Customer (B2C)
It is the most popular segment in which businesses sell, rent, or offer services to individual customers. The electronic commerce company Amazon.com is a significant example of the B2C market.
3. Customer To Customer (C2C)
This model supports commercial transactions between individual and private consumers through third-party e-commerce platforms, such as eBay. Examples include online auctions, information exchange, sale of used items, service delivery, classified advertisements, etc.
4. Customer To Business (C2B)
In this type of e-commerce, the customer provides the product or service to a business online, thereby adding value to the market segment. Examples include photographers, freelancers, consultants, influencers, etc.
E-Commerce Examples
Let us consider the following electronic commerce examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
Laurel wants to buy a new pair of jeans, but she cannot go out due to health issues. So, she picks up her smartphone and accesses the website of an online clothing retailer. Laurel types “jeans for women” in the search bar and sets her preferences like size, price, color, pattern, discount, and so on. Finally, she finds a model of jeans fitting her requirements.
Laurel decides to buy instantly. She fills in standard details, such as her mobile number or email address, postal address for delivery, and payment mode. Laurel receives the digital invoice containing the order number, order tracking link, the amount payable, delivery date, and discounts or taxes (if any). Upon placing the order, she receives a confirmation email and SMS on her registered number or email. The e-retailer delivers the product on time, and Laurel pays with her debit card.
Example #2
The electronic commerce industry witnessed unprecedented growth during the COVID-19 pandemic crisis of 2020. According to the data released by the United States Department of Commerce in February 2021, e-commerce sales increased by over 30% in 2020 compared to 2019.
Nationwide lockdowns and closure of physical stores due to the coronavirus spread forced Americans to turn to e-retailers for their daily needs. As per the U.S. Census Bureau, items with record growth in year-over-year sales included groceries, personal care products, furniture, sporting goods, gardening supplies, etc.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Since the advent of e-retailers, such as Amazon and eBay, online commerce has evolved into one of the fastest-growing industries worldwide. Market research by Meticulous Research has forecast the sector to be worth $16,215.6 billion by 2027. As a result, the majority of brick-and-mortar retailers are increasingly incorporating e-commerce. But online business, like everything else, has its benefits and drawbacks, which are as follows:
Advantages
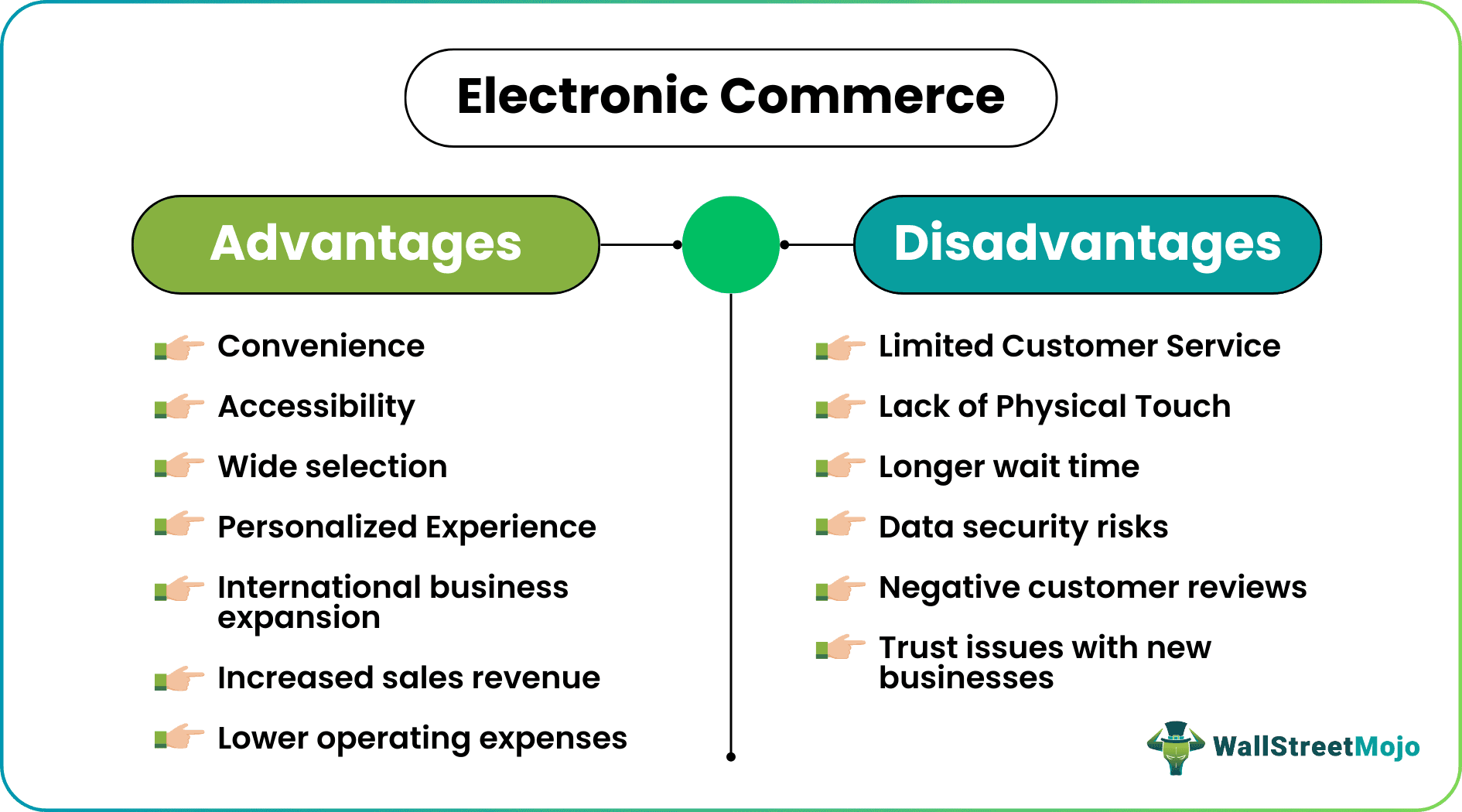
- Convenience and Accessibility: Anyone can order and receive what they need from online businesses at any time, with the quickest possible delivery and easy returns. Also, consumers can access e-commerce websites or apps from their computers or smartphones.
- Wide Variety: E-retailers offer an increased selection of products and services, making it easier for customers to pick the best deal. Sometimes what cannot be found in the local market can be found on the internet store.
- Personalized Experience: Potential buyers can specify their preferences for a particular product. Likewise, loyal customers will see personalized offerings in their feeds.
- Reduced Operating Cost: Businesses operating over the Internet do not need to spend on physical stores or marketing efforts.
- International Presence: Most e-commerce enterprises have branches outside their jurisdiction, allowing customers worldwide to shop from them. It helps expands their business and increase sales revenue.
Disadvantages
- Limited Customer Support: While shopping online, consumers do not have the opportunity to speak with a sales professional regarding product or service features, as they do in brick-and-mortar establishments.
- No Physical Touch: Another disadvantage of purchasing online is that one cannot touch the desired goods, try it in real-time, or check if it meets their needs. Getting products not matching expectations leads to unsatisfactory customer experiences, product returns, and loss of funds in some cases.
- Waiting Time: The time taken from placing an order online to getting it delivered is relatively greater than if the consumer bought it from a retail store.
- Security: Electronic commerce services require customers to provide personal and financial information to proceed with a purchase. Hackers and cybercriminals can attack websites or apps and steal these sensitive details.
- Customer Reviews: Almost every e-commerce platform has a dedicated section where buyers share their personal experiences with the product or service. Unfortunately, there are sometimes thousands of mixed reviews that may positively or negatively impact sales.
- Trust Issues: Customers who are satisfied with their purchases from reputable brands are more likely to use them again in the future. Conversely, the arrival of a new electronic commerce company causes consumers to hesitate before placing their first order with them.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Electronic commerce services enable individuals, businesses, and governments to sell items, information, and services to customers online. Anything offered, sold, or purchased through e-commerce is primarily done through computers, smartphones, or tablets. It is applicable in internet banking, stock trading, online auctions, and digital payments.
The four electronic commerce business models are Business-to-Business (B2B), Business-to-Consumer (B2C), Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C), and Consumer-to-Business (C2B). All these segments deal with the purchase and sale of goods or the provision of services.
E-commerce offers many advantages for businesses and consumers, such as convenience and accessibility, a wide selection of products and services, lower operating expenses, and international reach. Disadvantages of online business include longer wait time, data security risks, negative customer reviews, and trust issues with new market entrants.

