Table Of Contents
Formula to Calculate Effective Annual Rate (EAR)
The formula of Effective Annual Rate(EAR) can be calculated based on the nominal rate of interest and number of compounding periods per year.
The effective annual rate is also known as an effective rate, or an annual equivalent rate, is the rate of interest that is actually earned or pay after compounding, and it is calculated by one plus annual interest rate, which is divided by a number of compounding periods to the power number of periods whole minus one.
Effective Annual Rate = (1 + r/n)n – 1
where r = Nominal interest rate of interest and n = number of compounding periods per year.

However, in the case of continuous compounding formula, the equation of effective annual rate is modified as below,
Effective Annual Rate = er – 1
The effective annual rate is also known as an effective interest rate, annual equivalent rate, or effective rate.
Steps to Calculate Effective Annual Rate (EAR)
Firstly, figure out the nominal rate of interest for the given investment, and it is easily available at the stated rate of interest. The nominal rate of interest is denoted by u2018r.u2019
Next, try to determine the number of compounding periods per year, and the compounding can be quarterly, half-yearly, annually, etc. The number of compounding periods of nominal interest rate per year is denoted by u2018n.u2019 (The step is not required for continuous compounding)
Finally, in the case of discrete compounding, the calculation of Effective Annual Rate can be done using the following equation as,
Effective Annual Rate = (1 + r/n)n u2013 1
On the other hand, in case of continuous compounding, the calculation of Effective Annual Rate can be done using the following equation as,
Effective Annual Rate = er - 1
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Examples
Let us take an example where the effective annual rate is to be calculated for one year with the nominal or stated rate of interest of 10%. Calculate the effective annual rate for the following compounding period:
- Continuous
- Daily
- Monthly
- Quarterly
- Half Yearly
- Annual
Given, Nominal rate of interest, r = 10%
#1 - Continuous Compounding
The calculation of EAR is done using the above formula as,

Effective annual rate = er – 1
Effective annual rate = e12% - 1 = 10.5171%
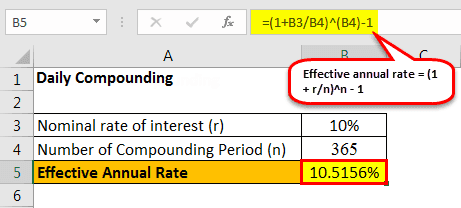
#2 - Daily Compounding
Since daily compounding, therefore n = 365
The calculation of Effective Annual Rate is done using the above formula as,

Effective annual rate = (1 + r/n)n – 1
Effective annual rate = (1 + 10%/365) 365 – 1 = 10.5156%
#3 - Monthly Compounding
Since monthly compounding, therefore n = 12
The calculation of Effective Annual Rate is done using the above formula as,

Effective annual rate = (1 + 10%/12)12 – 1 = 10.4713%
#4 - Quarterly Compounding
Since quarterly compounding, therefore n = 4
The calculation of EAR is done using the above formula as,

Effective annual rate = (1 + 10%/4)4 – 1 = 10.3813%
#5 - Half-yearly Compounding
Since half yearly compounding, therefore n = 2
The calculation of Effective Annual Rate is done using the above formula as,

Effective annual rate = (1 + 10%/2)2 – 1 = 10.2500%
#6 - Annual Compounding
Since annual compounding, therefore n = 1
The calculation of Effective Annual Rate is done using the above formula as,

Effective annual rate = (1 + 10%/1)1 – 1 = 10.0000%
The above example shows that the formula for EAR depends not only on the nominal or stated rate of interest of the investment but also on how many times the rate compounding happens during a year, and it increases with the increase in the number of compounding per year.

The below-given graph shows the rate of compounding happens during a year

Relevance and Use
The concept of an effective annual rate is an indispensable part of investing for a financial user since it is the interest rate effectively received from an investment. Further, an investor will be benefited in case the effective interest rate is higher than the nominal rate of interest offered by the issuer.
From a borrower’s point of view, also it is vital to understand the concept of an effective annual rate because it will impact their solvency and profitability. A higher expense towards interest payment eventually lowers the interest coverage ratio for a borrower that could negatively impact the borrower’s ability to service the debt in the future. Further, a higher interest expense also reduces the net income and profitability of a company (all other factors being equal).
The effective interest rate is one of the simplest forms of interest rate, and in the actual monetary terms, it is basically the rate at which a borrower pays to a lender to use its money. Further, the concept of effective annual rate also encapsulates the impact of no. of compounding per year, which eventually helps in the calculation of redemption value at maturity. Normally, the effective annual rate is greater than the nominal rate of interest because the nominal rate is expressed in terms of yearly percentage irrespective of the number of compounding per year.
If we increase the number of compounding periods, then the effective annual rate also increases in line with the nominal rate. Additionally, if an investment is compounded annually, then it will have an effective annual rate, which is exactly equal to the nominal rate of interest. On the other hand, if the investor had invested on a quarterly compounding basis, then the effective annual rate would be greater than the nominal rate of interest.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.