Table Of Contents
Economic Reform Definition
Economic reform refers to the deliberate modification of a country's economic structures and policies to increase efficiency, support growth, and increase overall economic well-being. It promotes efficiency and competition, better fiscal stability, improved private sector participation, and integration of the nation's economy with the global market.
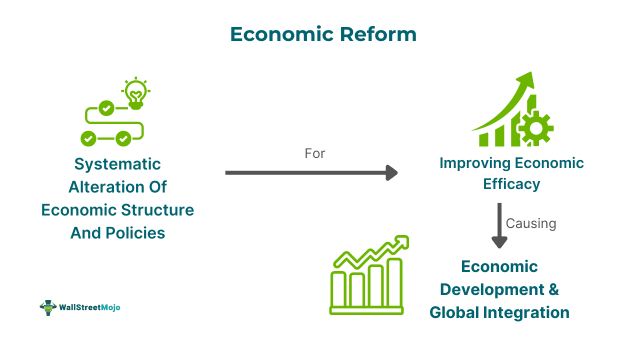
It conventionally comprises adjustments to government regulations, financial systems, trade policies, and fiscal policies to address existing economic problems. It consists of measures like deregulation, liberalization, tax reform, deficit reduction, privatization, and investment, plus trade reforms. Developing nations use it to grow their economies and increase their standards of living.
Key Takeaways
- Economic reform represents the purposeful change of an economy's structures and regulations so as to improve the nation's general state of affairs, boost productivity, and encourage growth.
- It elevates the role of the private sector, increases fiscal stability, and encourages efficiency and competitiveness while connecting the domestic economy with the international market.
- Its types include liberalization, which involves sectoral measures to promote free market efficiency; privatization, which enhances productivity in specific industries; and stabilization, which addresses economic imbalances.
- Its importance lies in stabilizing systems, supporting individuals during crises, stimulating growth, and reducing poverty through proper tax, structural, and public policies.
Economic Reform Explained
Economic reform represents a systematic alteration in regulations and policies with the objective of improving economic efficacy and resolving the economy's structural issues. It commonly consists of fiscal reforms, deregulation, and privatization in an effort to increase the market's operations and promote growth.
It has a special way of working that involves eliminating barriers to investment and trade, restructuring public sector and government-owned enterprises, and establishing regulatory frameworks to encourage market competition. All these processes mostly need meticulous strategizing and stakeholder engagement to be implemented successfully.
It can have profound implications resulting in higher economic growth, better resource allocation, a profound level of productivity, and a high degree of competitiveness. Nevertheless, the reforms may also have downsides, like job losses in some specialized sectors, increased economic inequality, and short-term disruptions.
Many countries facing economic crises or lacking development, industrial growth, and poor investment from foreign investors often take this route toward economic empowerment.
As a result of reforms in the economy, countries can achieve the following:
- Attract large amounts of foreign direct investment.
- Formulate a more attractive business environment.
- Stimulate their economic activity.
- Open up their economy for global trade
- Decrease government interference in market functioning.
- Correct the existing inefficiencies.
- Produce an ever-changing economic environment.
Nevertheless, there must be an effective social protection net and resolve any possible negative impacts on weaker sections. Furthermore, economic reforms can create a more transparent and predictable economic environment, enhancing complete economic stability and financial market and investment. As a result, it instills confidence in the market, better access to funds, and increased financial stability. Consequently, more foreign direct investment comes to the country and improves economic growth holistically.
Types
It can be divided into the following categories:
- Liberalization involves dismantling government regulations and restrictions, promoting free market efficacy through deregulating industries, decreasing import tariffs, and permitting additional foreign direct investments, as in Argentina's economic reforms.
- Privatization consists of government-owned companies being transferred to private business people, maximizing competition through sales, and reducing the government's stake in companies, as in economic reforms in Vietnam.
- Stabilization reforms of short-duration measures focus on addressing economic imbalances, such as inflation control, by tightening finances and decreasing government deficits.
- Structural reforms are centered on long-duration improvements in the economy's efficiency, such as an overhaul of social security, labor market deregulation, and tax system reforms.
- Sectoral reforms aimed at specific industries enhancing their productivity using privatization, deregulation, and attracting foreign investment in strategic sectors.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
An online article published on 16 August 2024 discusses bold and new economic reforms focused on growing and stabilizing its economy with support from the World Bank and IMF. It has initiated reforms consisting of active interest and floating exchange rate policies that coincide with almost USD 20 billion of financial aid. In this manner, Ethiopia anticipates saving almost USD 5 billion using credit restructuring.
However, despite the growth of 10% on average in the last twenty years, it has been facing challenges such as more than 30% inflation and persistent shortages of foreign exchange. More importantly, the reforms' success is based on the independence of central banks, managing the rate of floating exchange, and efficient interest rate policies. In fact, the significant implications of reforms of the Ethiopian economy lie in its horn of Africa's stability.
Example #2
Let us assume that Old York City's mayor, Janey, spearheads a new economic reform in 2024. Under the reform, the floating exchange rate related to the York dollar stabilizes the city's financial markets. Meanwhile, the Old York Exchange supervises the transition during the reforms. The reform consists of tax benefits for small companies in Old York City to encourage local people to do business.
As a result of the reform, the city experiences a 20% hike in fresh business registrations, adding 5% to the overall growth of GDP. Nevertheless, as soon as the floating exchange rate's introduction is implemented, it leads to a 25% fall in the valuation of the York dollar, raising fears of inflation. Furthermore, many local retailers experience mixed results, gaining from enhanced tourists but needing help with increasing import costs.
Importance
For countries suffering from weak economies, reforms in the economy have special importance, as listed below:
- It stabilizes and improves systems such as unemployment insurance supporting individuals during crises.
- This can lead to economic recovery because insurance reforms lead to stability, equity, and efficiency, making it key to economic recovery and the lifeline of families.
- Tax reforms like income and corporate taxes stimulate economic growth as it enhances employment and GDP.
- Structural reforms also stimulate economic growth.
- Public policies to reduce economic inequality include a progressive tax code and increasing the minimum wage while reducing poverty and enhancing economic growth.
- It also leads to faster growth, greater economic equality, and a major reduction in poverty in developing countries.
