Table of Contents
What Is An Economic Decision?
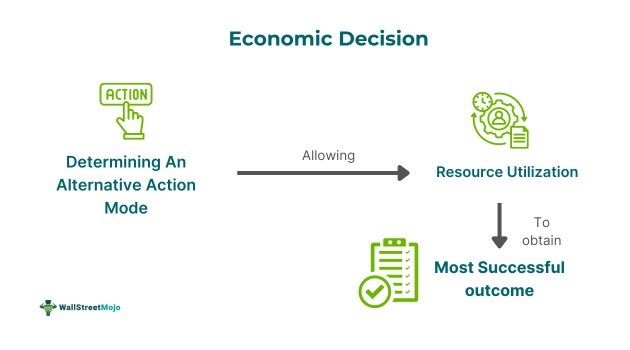
An economic decision refers to the process of selecting the manner in which a resource can be used to accomplish the most successful result. It serves to get any type of incentive, whether personal or economic, that needs sacrifice by identifying a substitute mode of action and choosing the correct alternative in such a situation.
It primarily weighs the benefits and costs of various options and earmarking the one offering the greatest net benefit. It comprises incentives, benefits, and vital skills for businesses and organizations to take informed decisions after consideration of benefits and costs related to every alternative.
Key Takeaways
- Economic decision comprises selecting the most effective way to accomplish a goal, often needing personal or economic sacrifices, through identifying alternative options and choosing the correct one.
- It is influenced by poor decisions, caution and honesty, behavioral biases, emotional and physical factors, knowledge, age, and cooperation.
- Its process comprises defining the problem, collecting information, assessing alternatives, choosing the best option, formulating a plan, and revisiting the decision.
- It is affected by behavioral biases regarding identifying strayed decision-making trends, avoiding costly mistakes, enhancing decision quality, achieving long-term objectives, and making individuals comfortable navigating uncertainty.
Economic Decision Explained
An economic decision can be stated as the methodology of determining an alternative route of action and choosing the most effective substitute in given circumstances to get some personal or economic reward. It consists of an exchange of one thing with another, trade-offs, benefits and marginal costs plus benefits. It depends heavily on accounting data and sets to optimize profits and decrease losses.
The economic decision-making process is affected by behavioral biases, resulting in irrational and inefficient decisions. Many factors are related to behavioral bias, like herd mentality, cognitive biases, bounded rationality, and choice architecture. Governments, families, individuals, and businesses make informed decisions using it. It offers a multitude of techniques and tools for achieving objectives and controlling operations.
It gives valuable insights to companies for price optimization, product design, and marketing. Rational economic decision-making helps in policy choices and designing economic institutions.
Factors
It is affected by several factors, such as:
- Various behavioral biases lead to irrational and ineffective decisions of economic.
- Visceral and emotional factors impact decision-making procedures concerning individuals and businesses.
- It may fail or succeed based on tricks and knowledge of individuals and businesses.
- Aged persons decide on economic activity to build wealth.
- Cooperation and imitation affect the activities for economic gain.
- Poor decisions regarding finances and economics arise due to lack of sleep, hunger and fatigue.
- Precaution and honesty lead to a cautious approach by individuals to achieve excellent decisions in economics.
Process Steps
It has various steps, as detailed below;
- First, define the question or problem that needs to be resolved.
- Then collect related information externally and internally to comprehend the decision context.
- Try to list all possible modes of action to address any decided action.
- Every alternative must be assessed using its outcomes, pros and cons may be by using economic decision trees.
- After that, choose the best available option as per the examination of alternatives.
- Next, one must formulate and implement a suitable plan for executing the selected decision.
- Finally revisit the decision and evaluate the outcomes and results to know of future course of action.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
An online article published on 21 June 2024 discusses a decision of economics concerning revising the Development Control Design Policy (DC15). It said that the planning authority or PA has been conducting public consultation regarding amendments to the controversial policy, possibly permitting the construction of additional floors. However, the chamber of architects and environment NGOs have criticized the move, stressing the importance of a detailed master plan rather than partwise development policies.
Moreover, the Development Planning Act has mandated the enhancement of life quality without neglecting the future needs that PA must uphold. The report also argued that construction costs will not have many economic benefits. Therefore, such an act would decrease the life quality and market losses in the real estate sector. Further, it warns against modifications steered by unsustainable economic models and lobbying.
Example #2
Let us assume that in Old York, the CEO of Greentech Corp has to face a decision-making situation to expand its business operations. As per market research, its green products have shown an increase in demand by up to 30% amongst consumers seeking renewable and green energy products in the coming 5 years. Nevertheless, suddenly market took a dive and caused a decrease in purchasing power by 155 and affected a decline in demand for Greentech products.
However, all these situations had little effect on the return on investment of 20% because of the $20 million investment. All these factors strengthened the resolve of the company to expand its capacity to leverage the projected market development against potential risks.
Impact of Behavioral Biases on Economic Decision-Making
Behavioral biases have several impacts on economic decision-making, as follows:
- It aids in determining strayed decision-making trends.
- It leads to avoiding costly mistakes in investments and finance.
- It assists in enhancing decision quality.
- It facilitates achieving objectives of long-term.
- It makes everyone comfortable in navigating the uncertainty of life and situation.
