Table Of Contents
What Is The EBITDA Formula?
The EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization) formula, as the name indicates, is the calculation of the company's profitability which can be derived by adding back interest expense, taxes, depreciation & amortization expense to net income. The operating EBITDA formula helps understand the overall financial performance of the company.

EBITDA is not represented in the income statement as a line item; rather, an EBITDA calculation must be done using the other already available items reported in every income statement. An EBITDA of over 10 is generally considered good. Investors and shareholders keep a close eye on this metric as it reflects the growth opportunities in the company.
EBITDA Formula Explained
EBITDA is the earning recorded before deducting the interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization expenses. It can be calculated using two methods. These calculations help companies calculate using an adjusted EBITDA formula for their valuation and other financial purposes.
Method 1 - Starts with Net Income
- EBITDA = Net Income + Interest Expense + Taxes + Depreciation & Amortization Expense
Method 2 - Starts with EBIT
- EBITDA + EBIT + Depreciation & Amortization Expense
- or EBITDA = EBT + Interest Expense + Depreciation & Amortization Expense
Although the above formula is predominantly used in the calculation of earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization and will be discussed in detail in this article, there is another way for EBITDA calculation. In the second method, EBITDA can be calculated by deducting all expenses from net sales other than interest, taxes, and depreciation expenses. But this method is not popular and is not elaborated on in this article.
How To Calculate?
Let us understand the steps involved in the calculation of an operating EBITDA formula of an organization through the steps explained in detail below.
It is very simple since the entire information required for its calculation is already contained in the income statement. The first step in calculating EBITDA from the income statement is to arrive at the operating profit or Earnings before Interest and Tax (EBIT). The data can be found in the income statement after the depreciation & amortization expenses and selling, general & administrative (SG&A) expenses.
- Now that EBIT has taken out the depreciation and amortization expense in the income statement, it is required to add back the expense to assess the company's cash flow. When these non-cash expenses are added to EBIT, it is then recognized as the earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization, which is the real amount of cash generated by the company's operation. Various investors and users of financial statements use the EBITDA equation because they believe that non-cash expenses are not actual cash outflow and, as such, should be considered during the assessment of the company's real cash flow. Consequently, it is considered that the EBITDA formula is the financial metric that reveals the true cash flow position of the company.
Examples
Let us understand EBITDA and adjusted EBITDA formula and its workings with the help of a few examples. These examples would help us understand the intricate details of the concept.
Example #1
J.C. Penny is an American furniture, bedding, and department store company. Below is the screenshot of the Income Statement of J.C. Penny:

Source: jcpenney.com
In 2017 the company's total revenue was $12.5 Bn, with a net loss of around $116 million.
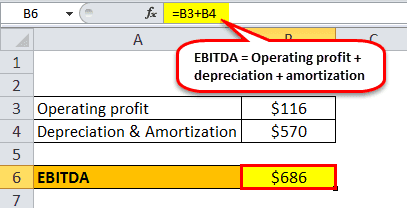
- Calculation using Formula 1

Operating Profit given as $116 million and Depreciation and Amortization is $570 million.
EBITDA = 116 + 570 = $686 million
- Calculation using Formula 2

So, EBITDA = -116 +325 -126 +570 = $653 million.
Now you will notice some differences between the values of formula#1 and #2. The reason is that there is an exceptional item called "Loss on extinguishment of debt," which is around $30 million that comes between Operating Income and Net Income. Still, we have not added that amount in Formula#2.
Example #2
Starbucks Corporation is a U. S. company founded in Seattle, which is in the coffee and coffeehouse chain business. Below is the screenshot of the 2018 Income Statement of the corporation:

Source: Starbucks.com
We can see that in 2018 the company's total revenue was $24.7 Bn, with a net income of around $4.5 billion. Using the above-given values, we will calculate EBITDA with both the formulas:
- Calculation using Formula 1

Operating Profit given as $3,883 million and Depreciation and Amortization is $1,247 million.
EBITDA = 3383 + 1247 = $4,630 million
- Calculation using Formula 2

Interest Expense = -$170.3 + 191.4 million = $21.1 million
So, EBITDA = 4518 +21.1 +1262 +1247 = $7,048 million.
The difference using formula#1 and formula #2 is because of some one-time expenses, such as the acquisition of joint venture and divestiture of some operations, which are not added back while calculating in formula #2.
Example #3
Google is a U.S. company in the internet service and products business, such as a search engine. Below is the snapshot of the 2018 Annual report:

Source: Google
In 2016 the company's total revenue was $90.3 Bn, with a net income of around $19.5 billion. Therefore, using the above-given values, we will calculate EBITDA with both the formulas:
Operating profit is given as $23,716 million. Depreciation can be seen from the Cash flow statement as is $5,267 million, while amortization is $877 million.
- Calculation of Formula 1

EBITDA = 23716 + 5267 + 877 = $29,860 million
- Calculation of Formula 2

So, EBITDA = 19478-434+4672+6144 = $29,860 million.
Example #4
Apple is an American multinational company developing consumer electronics products such as the iPhone, iPad, Mac, etc. Below is a snippet from the annual report of 2018:

Source: Apple Inc
We can see that in 2018 the company's total revenue was $266 Bn, with a net income of around $59.5 billion. Therefore, using the above-given values, we will calculate EBITDA with both the formulas:
Operating profit is $70,898 million, and Depreciation and Amortization are $10,903 million.
- Calculation of Formula 1

EBITDA = 70898 + 10903 = $81,801 million
- Calculation of Formula 2

So, EBITDA = 59,531-2005+13372+10903 = $81,801 million.
Example #5
Berkshire Hathaway is an American multinational company headquartered in Omaha. Renowned investor Warren Buffet funds it. Below is a snippet of the annual report for 2018:

Source: Berkshire Hathaway
We can see that in 2018, the company's total revenue was $23.855 Bn, with a net income of around $5,219 million. Therefore, using the above-given values, we will calculate EBITDA with both the formulas:
Formula #1: EBITDA = Operating profit + depreciation + amortization
In the above report, operating profit is not given directly, so we will calculate that by the given information.
Revenue = $23,855 million and operating expenses = $15,951 million
Operating Profit = Revenue – operating expenses
- Operating Profit = 23855- 15951 = $7,904 million
And Depreciation and Amortization is $2,317 million.
- Calculation of Formula 1

EBITDA = 7904 + 2317 = $10,221 million
- Calculation of Formula 2

So, EBITDA = 5,219+1041+1644+2317 = $10,221 million.
Relevance
The relevance of operating EBITDA formula for an organization irrespective of their intentions to attract new funding or otherwise. This metric defines the financial health and future prospects of a company better than most metrics. Let us deep dive into the concept through the discussion below.
- It is a profitability metric that helps assess how a company is performing, which is calculated by measuring profit before payment of interest to lenders or creditors, taxes to the government, and other non-cash expenses like depreciation and amortization. This is not a financial ratio but a profitability calculation measured in dollars and not in percentages like most other financial terms.
- However, the EBITDA's limitation is that it is particularly useful when comparing similar companies in the same industry. Since the EBITDA equation only measures profit in terms of dollar amount, investors and other financial users usually find it difficult to use this metric to compare differently sized (small & medium enterprise, mid-corporate, and large corporate) companies across the industry.
Calculation In Excel
The EBITDA and adjusted EBITDA formula can be calculated using MS Excel as well. Let us understand how through the explanation below.
Now let us take the real-life earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization example of Apple Inc.'s published financial statement for the last three accounting periods.

Based on publicly available financial information, the EBITDA (in dollar terms) of Apple Inc. can be calculated for the accounting years 2016 to 2018.
Here we have used the EBITDA equation i.e EBITDA = Net income + Interest expense + Taxes + Depreciation & Amortization expense.

From the table below, we can see that the earnings before the interest, tax, depreciation and amortization level of Apple Inc. in dollar terms have been growing, which is a positive sign for any company.