Table Of Contents
What Is Earnings Yield?
Earnings Yield helps the investor understand how much they will be earning for each dollar invested in the company and is therefore calculated as Earnings per share divided by the stock price per share. This ratio helps an investor to make the comparison between two or more companies or between investments in shares versus the investment in risk-free securities.
In some scenarios, an earnings yield calculation is used as a dividend pay-out ratio. It is important to understand that the dividend that is distributed among shareholders is the earnings of the company. Any yield above 10 basis points over the government bond yield for 10 years is considered a significantly good deal for the investor.
Earnings Yield Explained
Earnings yield is the earnings of an investor per share for the last one year divided by the current market price. It gives the investors an idea of the gains they have made for every dollar invested.
It helps the stakeholders to understand about the return for each dollar invested and also to make sure that the additional risk of investing in stock over risk-free security (like treasury bill, gold, fixed deposit) is worth taking or not.
The earnings yield method is the exact opposite of P/E ratio. While the former provides insights into the earning per share, the latter determines how long it would take for the company’s share to reach the current market value per share.
Nevertheless, a higher earning yield would indicate that the stock is undervalued and might be a good opportunity to buy the stock as it is expected to give a significant run-up in the market.
Formulas
Let us understand the formulas to aid earnings yield calculation:
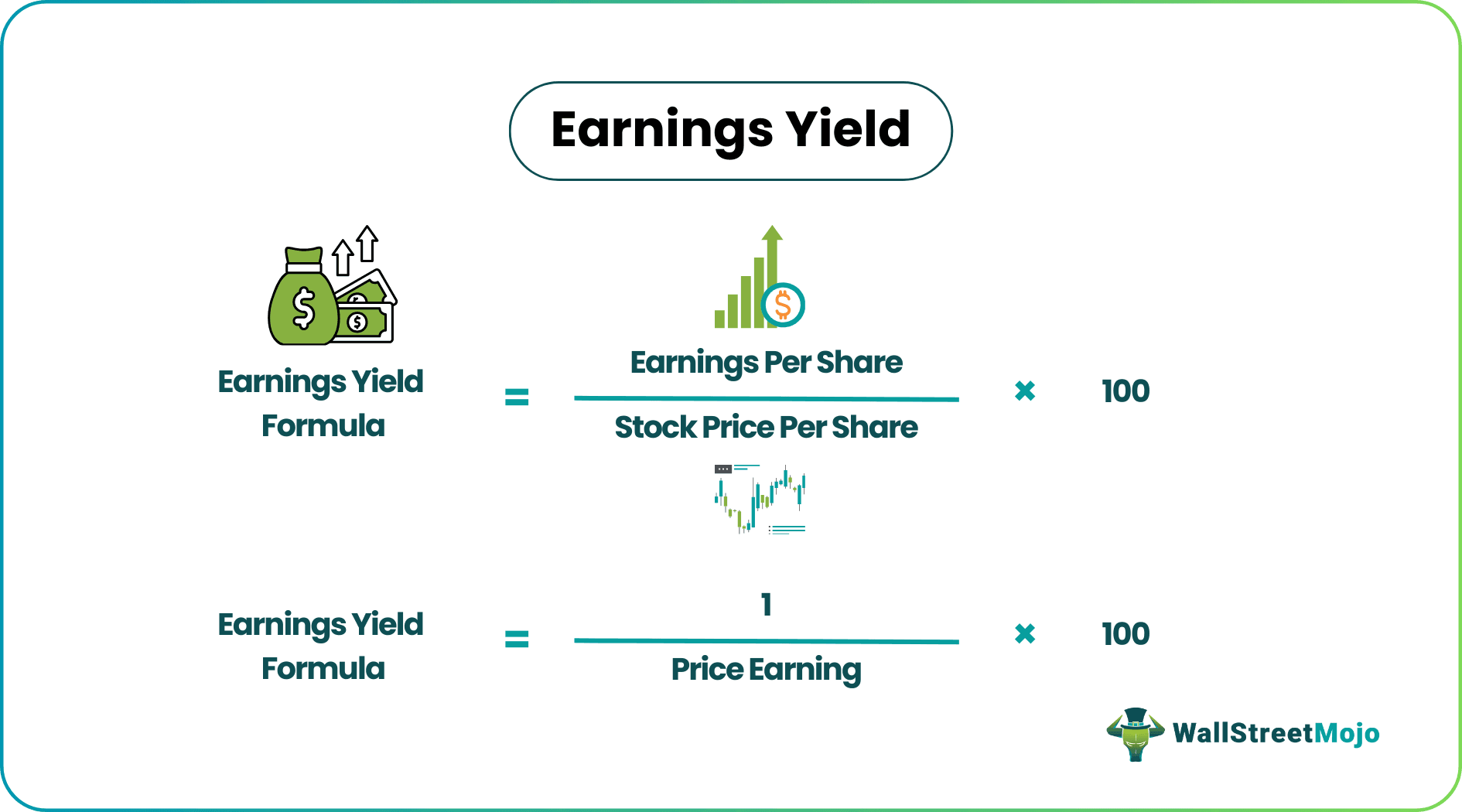
Earnings Yield Formula = Earnings Per Share / Stock Price Per Share*100
Here we take the 12 months earnings per share of the company is divided by the market price per share of the stock and represent in a percent manner to make the comparison.
Earnings Yield Formula=1/Price Earning * 100
As we know that it is the inverse of P/E, we can calculate it by using the above formula and represent it in a percent manner to make the comparison.
Revenue vs. Earnings Video Explanation
How is Earnings Yield used by Investors?
Consider an investment in stock as against an investment in a Treasury bill or a fixed deposit, which are virtually risk-free investments. So, if the earnings yield of an investment in the stock is higher than the treasury bill / Fixed deposit, only then will it make sense to invest in stock as we take risks while investing in stocks.
The Earnings yield calculation of 10 years treasury bill is 4.5%, i.e., we earn 4.5% for each dollar invested, and the yield for the stock of Company A INC is 8.28 %, i.e., we earn 8.28% for each dollar invested. This clearly shows that the additional risk which we are taking by investing in stock instead of the treasury bill is providing additional returns. If the yield of the risk-free security is equal to or more than the stock, we can say that the stock is overvalued stocks. As we can clearly see in such a case, there are no additional benefits received by making a riskier investment.
Examples
Let us understand the earning yield method in depth with the help of a couple of examples.
Example #1
Following is the information provided to us for company A INC and Company B INC.
| Particulars | Company A | Company B |
|---|---|---|
| Earnings Per Share | 15 | 25 |
| Market Price Per Share | 120 | 140 |
Solution
The calculation for Company A

- =15/120*100%
- =12.50%
The calculation for Company B

- =25/140*100%
- =17.86%
Here as we can see that the earnings yield of company B is higher than company A, i.e., for each dollar invested in company B, we will earn 17.86% as compared to only 12.50% in company A. So, we conclude that investment in Company B is better.
Example #2
We are given that the stock Mr. A has an investment to be made, and he is having 2 options of the same he is providing us with the following details.
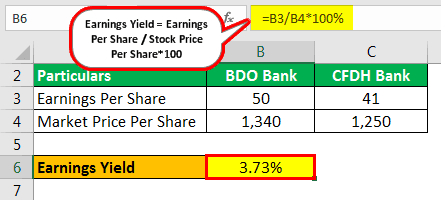
- BDO Bank is currently trading at $ 1340 per share, and it’s earning per share is $ 50.
- CFDH Bank is currently trading at $ 1250 per share, and its earnings per share is $ 41, which of these banks he should select to maximize his earnings.
| Particulars | BDO Bank | CFDH Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Earning Per Share | 50 | 41 |
| Market Price Per Share | 1,340 | 1,250 |
Solution
The calculation for BDO Bank

- =50/1340*100%
- = 3.73%
The calculation for CFDH Bank

- =41/1250*100%
- = 3.28%
After calculating it, we can understand that BDO bank is earning 3.73% for each dollar invested and CFDH Bank is earning 3.28% for each dollar invested. Therefore, it is clear that to maximize the returns, Mr. A should invest in BDO Bank.
Importance
Let us understand the importance of the earnings yield method through the discussion below.
- It is used for both to know the rate of return as well as for the purpose of valuation. We can consider it as a valuation because here we divide the earnings with the market value of the share.
- It acts as a tool to compare equity stock and the T-Bills, Fixed Deposits, and other risk-free security to understand whether the stock is undervalued or overvalued.
- It provides information about the per dollar earning from the investment, which makes comparison and decision making simple.
Earnings Yield Vs Dividend Yield
Below are certain differences between Earning and Dividend Yield. This comparison will help us understand the earnings yield calculation in detail.
- As we know that earnings yield provides the percentage of returns for each dollar invested in the company, dividend yield, in the same way, provide the amount of dividend that a company pays for every invested.
- The dividend yield is used to make investment decisions for companies paying dividends.
- Dividend yield can be used only in the case of companies who payout dividends, whereas it has no such restrictions as all companies are required to report their earnings per share.
- It can be used as a method of comparison for the stock, bond, fixed deposits, T-bills, etc. whereas, dividend yield cannot compare instruments other than stocks.