Table Of Contents
What Is E-Discovery?
E-discovery or electronic discovery is a type of digital investigation employed in legal proceedings. It includes information collected in electronic or digital format that is utilized in litigation and criminal cases. It is a valuable tool that helps legal professionals collect and analyze information related to a specific legal case.
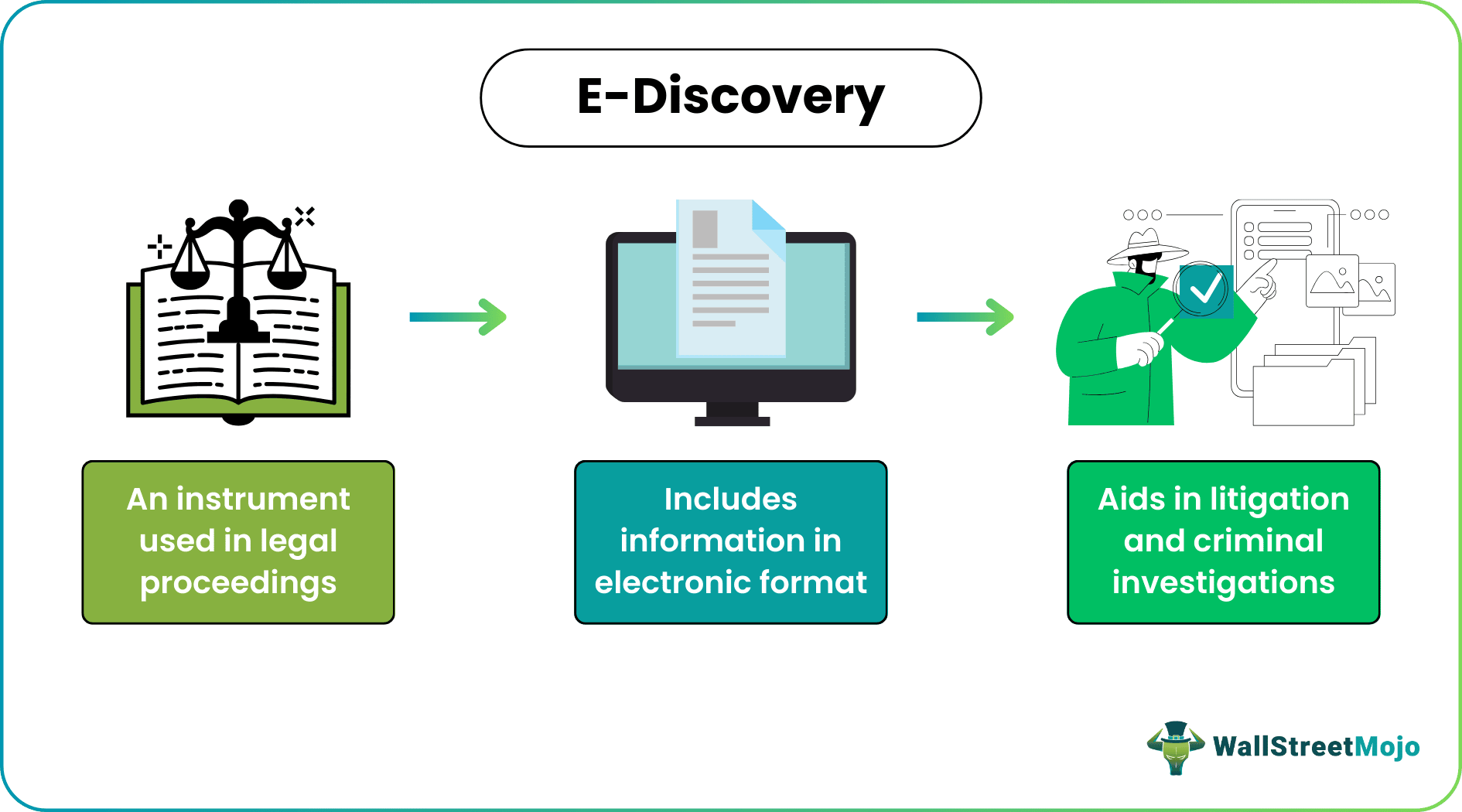
This instrument is generally used in the initial stages of litigation, where the concerned parties are required to submit the necessary evidence related to the case. The process involves gathering and transmission of digital data that is searched, stored, located, and secured as a form of evidence.
Key Takeaways
- E-discovery is the method of gathering, storing, protecting, and using digital or electronic data as a form of evidence in legal proceedings.
- This process allows legal professionals to collect, assess, and analyze the relevant data in a specific civil or criminal litigation case.
- The steps involved in this process are identification, preservation, collection, processing, reviewing, and production of the information.
- However, managing an extensive volume of digital data may be challenging for users. Furthermore, the data may contain errors and inconsistencies, which can pose a significant problem in the process.
E-Discovery In Banking And Finance Litigation Explained
E-discovery is the process of collecting, storing, safeguarding, and utilizing digital or electronic information as evidence in legal proceedings. It enables legal professionals to gather and examine the data that is relevant to a particular case. The data includes essential elements or metadata like information about the sender and recipient, timestamps, and file properties.
In the electronic discovery process, several types of data can act as evidence. It may include electronic documents, like text messages, audio clips, images, video clips, emails, and other instant messages. It may also include mobile phone data, calendars, spreadsheets, databases, websites, and other computer programs or documents that can be used in civil or criminal litigation.
Process Steps
The E-Discovery process steps are as follows:
- Identification: In this stage, a team identifies what data will be preserved. They interview the crucial stakeholders, examine the case facts, and assess the digital environment.
- Preservation: This phase involves formal instructions provided to data owners for preserving the necessary information.
- Collection: In the next step, the team selects a technological instrument to collect data that follows a pre-established legal process. They also ensure that the digital information is preserved without modifying any essential metadata like file creation dates, file size, and the audit logs attached to each file.
- Processing: This phase includes organizing the raw data and using suitable assets for further processing and analysis.
- Review: In this stage, the organized data is examined, and the relevant information is extracted for further use. This phase also recognizes the documents that are subject to privilege.
- Production: The final phase in the e-discovery process steps involves converting the final digital assets into physical documentation. The attorneys transform the data into presentable evidence.
Examples
Let us study the following examples to understand the e-discovery process:
Example #1
Suppose Sam is a bank employee who has allegedly been providing loans to customers without them meeting the eligibility requirements in exchange for monetary benefits. An investigation was conducted against him, and the legal professionals interviewed the relevant parties to obtain further information. Additionally, Sam's call records, text messages, emails, and other conversations were tracked to gain relevant data for the case. The attorney sorted and organized all the information he received, extracted the necessary information that was related to the case, and presented it in the legal proceedings.
Example #2
There has been a significant rise in digital information generated by businesses, such as social media content, documents, emails, and other various electronic records. It has triggered the need for electronic discovery solutions to manage and examine this extensive volume of information effectively. Market.us suggested that the market size for this discovery would reach up to $14.8 billion by the end of 2024. Furthermore, the size is expected to be of $32.5 billion by 2033.
Benefits
Finding relevant data has become increasingly difficult for compliance managers, regulatory professionals, and data administrators. It often involves searching for confidential data across user devices, different systems, and various environments. This tedious approach delays the progress and elevates the threat of overlooking crucial and valuable data.
One of the significant benefits of e-discovery services is that they offer the required tools to swiftly handle and react to litigation, legal compliance, and regulatory requirements. Relevant information can be easily identified across a wide range of digital scenarios, and it can be quickly saved in transferable formats for assessment. Organizations that implement sufficient electronic techniques save budget and effort while limiting risks associated with the e-discovery process.
Challenges
Some challenges associated with the e-discovery process include the following:
- The information sources are diversified and complicated. They are available on the scene, in the cloud, and on social media. They also include different file formats. Identification, gathering, and processing of data from such diversified sources need advanced tools and techniques.
- High volumes of electronic data are generated and stored in the systems. Managing such large volumes of information requires a robust infrastructure and efficient algorithms.
- The information is susceptible to inconsistencies, errors, and incompleteness. It is challenging to categorize and extract the data, especially when handling various data formats and languages.
- The e-discovery process must comply with the legal and regulatory requirements that govern data privacy, confidentiality, and preservation. Managing efficiency with legal frameworks necessitates appropriate protection measures.
- Adapting to the fast-paced technological advancements is a significant challenge. Maintaining compatibility and introducing integration with existing systems can be a complex process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
These tools enable legal professionals to manage digital documents in investigations. The instruments aid in automating the general E-Discovery processes like virus scanning, data ingestion, and file indexing.
The FRCP 26 is a significant rule that is associated with this discovery process. It states that any nonprivileged information related to any party's claims or response that is suitable for the case does not have to be admitted at trial.
Privilege is a provision in the electronic discovery process where the parties enjoy the lawful right to retain information from being revealed in the legal proceedings. The information may be privileged or confidential. Thus, this provision aids in filtering who can access the information and how they will use it.
Preservation is a process where the physical objects and the electronically stored information (ESI) are kept intact. These items are used in the E-Discovery process during legal proceedings. These elements serve as evidence in the legal process. As a result, the concerned parties must safeguard them from being erased, lost, modified, or damaged.
