Table Of Contents
What Is Dropshipping Or Drop Shipment?
Dropshipping refers to a business model in which the seller accepts the customer's order for a product without maintaining its inventory and directs the third party to arrange and ship the order to the customer.
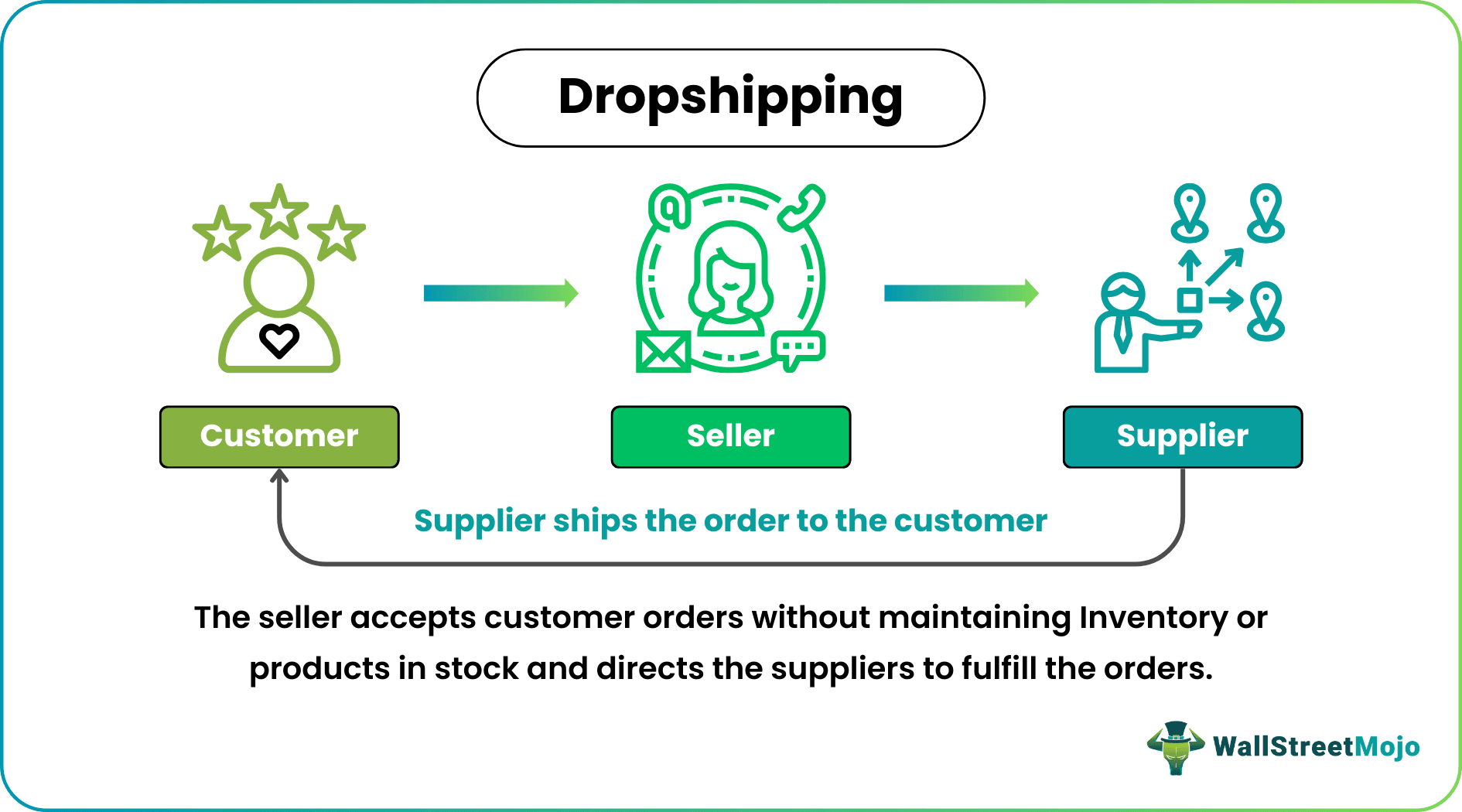
It's a popular and efficient business model allowing businesses to sell products without maintaining an inventory and profit easily, unlike traditional models with investments in inventories and management. It gives the business the benefit of not looking for and managing warehouses and still offering a wide range of products.
Key Takeaways
- Dropshipping is a business strategy where a retailer takes a customer's orders for products without keeping any of that product in stock and instructs a third party to arrange and deliver the order to the customer.
- The major stakeholders associated with the model are the seller, third-party supplier or drop shipper and the customer.
- Its advantages are: Helps to have competitive advantages, a wide range of products, potential to reduce expenses and risks, etc.
- Disadvantages: Complex and risky practices, reduced quality checks, low-profit margins, etc.
Dropshipping For Beginners Explained
Dropshipping is a business strategy, which implies a supply chain management technique that avoids the time and expense associated with obtaining, stocking, and shipping the product. As a result, it simplifies the process of delivering products to customers.
The dropshipping method was popularised in the 1960s when anyone could order items from a mail-order catalog. They choose a product, call, and have it delivered to their doorstep from a warehouse.
The major steps involved in the drop shipping process are as follows:
- The seller signs the dropshipping agreement with the manufacturer or supplier.
- The customer places an order online.
- The seller receives the order.
- The seller sends an order confirmation to the customer.
- The seller passes on the order to the drop shipper.
- The drop shipper sends the products to the customer.
- The customer receives the product.
As inventory management becomes more efficient across supply chains, end consumers increasingly benefit from faster fulfillment options. Services like Shipt now enable same-day grocery delivery, reflecting how real-time inventory systems support timely access to everyday essentials without requiring a trip to the store.
Examples
Let us look at some examples of online dropshipping businesses to understand the concept better:
Example #1
Imagine that Mrs.Dorothy has an e-commerce business where she sells customized handbags. Dorothy does not keep bags, belts, threads, embroidered handmade flowers, or leather in advance or store them in her warehouse. Instead, she has an agreement with Clarie, a drop shipper/supplier who stores the products in her warehouse.
Once Annie makes a purchase directly from Dorothy's ecommerce website, on receiving an order from Dorothy, Clarie immediately sends the product to the customer on their doorstep.
Example #2
Dropshipping on Amazon, the largest online marketplace model, involves selling goods to its customers via third-party suppliers. Amazon uses this fulfillment model and outsources product handling and shipping to a supplier. Then, Amazon runs a warehouse that helps to collect and ship the items directly to the customers.
Example #3
Alibaba launched Aliexpress in 2010. International customers could buy goods from Chinese companies, businesses, or individual sellers on this website. In other words, it provides a platform for small businesses to attract and sell products to customers globally. In addition, it eliminated linguistic and cultural obstacles and made the procedure much simpler.
Pros And Cons Of Dropshipping
Here are some possible benefits and drawbacks to think about while deciding whether dropshipping is the best option for the ecommerce business:
Pros
- Wide range of products: With this method, sellers can offer full catalogs without storing or shipping the products.
- Reduce expenses: The method can lower overhead costs, such as maintaining a storage facility or shipping products. Hence reducing the business expenses, unlike traditional retailers purchasing and storing inventory before it can sell it to consumers.
- Reduces geographic limitations: It makes it possible to complete orders for the products available at different locations from anywhere, no matter where the company is based. The ecommerce model accepts more orders without increasing inventory or having packing, shipping, and storing facilities and costs.
- Lowers initial investment: Nonrequirement of major stocks results in low initial investment and warehousing requirements. In addition, it enables new entrants in the ecommerce sector to compete with giants exhibiting monopolistic tendencies like Amazon.
- Enhance the cash flow: Customers pay before the product flows from the dropshipping suppliers, contributing to a positive cash flow cycle.
- Reduces certain risks: It eliminates inventory risks.
- Competitive advantage: This method increases the scope of private labeling, subsequently increasing profit and brand loyalty resulting in a competitive advantage.
Cons
- Complex and risky practice: Maintaining logistics can be challenging when the business expands. It will be even more challenging if the business deals with products from multiple warehouses and suppliers. It is possible to have a poor logistics experience due to incorrect tracking numbers, incorrect addresses, and delayed shipments.
- Escalate prices: Sometimes, product prices in this category will be higher than the normal selling price.
- Low margin: Involvement of third parties lowers the margin and increases the dependence on companies. Furthermore, due to the fierce competition in the industry, businesses may end up competing more aggressively on pricing. As a result, selling at low prices might lower profit margins.
- Reduced quality check: Since the seller is not dealing with the inventory directly, the span of quality control is also affected.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

