Table Of Contents
What is Doubling Time?
Doubling time refers to the time period required to double the value or size of investment, population, inflation etc and is calculated by dividing the log of 2 by the product of number of compounding per year and the natural log of one plus the rate of periodic return.
Key Takeaways
- The doubling time formula is a mathematical calculation that estimates the time required for investment, population, or another variable to double in value or size.
- The doubling time formula is based on the concept of exponential growth. Therefore, it assumes a constant growth rate over time.
- The doubling time formula is typically used in finance and economics to assess the growth rate or compounding of investments or to analyze population growth or other similar phenomena.
- The doubling time formula is derived from the compound interest formula and can be applied to various situations where exponential growth is observed.
Doubling Time Calculation (Step by Step)
Follow the below steps:
- Firstly, determine the rate of annual return for the given investment. The annual rate of interest is denoted by ‘r.’
- Next, try to figure out the frequency of compounding per year, which can be 1, 2, 4, etc., corresponding to annual compounding, half-yearly, and quarterly, respectively. The number of compounding periods per year is denoted by ‘n.’ (The step is not required for continuous compounding)
- Next, the rate of periodic return is calculated by dividing the rate of annual return by the number of compounding periods per year. Rate of periodic return = r / n
- Finally, in case of discrete compounding, the formula in terms of years is calculated by dividing the natural log of 2 by the product of no. of compounding period per year and the natural log of one plus the rate of periodic return as Doubling time = ln 2 /
- On the other hand, in the case of continuous compounding, the formula in terms of years is derived by dividing the natural log of 2 by the rate of annual return as,
Doubling time = ln 2 / r
Example
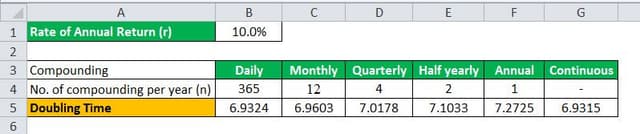
Let us take an example where the rate of annual return is 10%. Calculate the doubling time for the following compounding period:
- Daily
- Monthly
- Quarterly
- Half Yearly
- Annual
- Continuous
Given, Rate of annual return, r = 10%
#1 – Daily Compounding
Since daily compounding, therefore n = 365
Doubling time = ln 2 /
- = ln 2 /
- = ln 2 /
- = ln 2 /
- = ln 2 /
- = ln 2 / [1 * ln (1 + 10%/1)
- = 7.2725 years
#6 – Continuous Compounding
Since continuous compounding,
Doubling time = ln 2 / r
- = ln 2 / 10%
- = 6.9315 years
Therefore, the calculation for various compounding periods will be –

The above example shows that the doubling time depends not only on the rate of annual return of the investment but also on no. of compounding periods per year and it increases with the increase in the frequency of compounding per year.
- = ln 2 /
- = ln 2 /
- = ln 2 /
Relevance and Use
It is important that an investment analyst understands the concept of doubling time because it helps them to roughly estimate how many years it will take for the investment to double in value. Investors, on the other hand, use this metric to evaluate various investments or the growth rate for a retirement portfolio. In fact, it finds application in the estimation of how long a country would take to double its real gross domestic product (GDP).