There can be two different types of title documents based on their transferability, i.e., negotiable and non-negotiable. Its evidence can be differentiated as follows:
Table of Contents
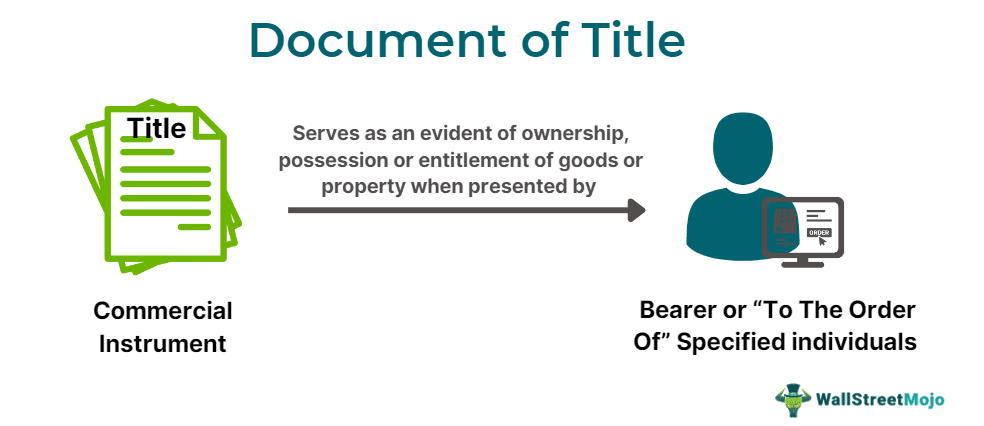
A document of title refers to a written commercial instrument that serves as evidence of the rightful ownership or control of goods or property, transferable through delivery. Thus, the person carrying such a formal commercial document can legitimately claim possession of the respective goods or property.
Such electronic or paper form of documents include bills of lading, delivery orders, dock receipts, dock warrants, warehouse receipts, etc. They serve as a crucial part of any overseas trade and even internal transfer of goods since they ensure greater security and convenience in handing over the consignment to its entitled owner when they present or surrender the original document.
Key Takeaways
A document of title is a written paper or electronic instrument that can serve as proof of ownership of the mentioned goods, assets, or property. It is presented while the person who holds and surrenders such document is taking the consignment delivery. These can be warehouse receipts, dock receipts, dock warrants, bills of lading, railway receipts, and quedan.
Such a commercial instrument facilitates a secured transfer of goods or assets in transit to its rightful owner (i.e., the person who holds and presents the document). It ensures seamless overseas trade and effortless transportation of consignments by a third party who is unaware of the goods' ownership. Even a share certificate serves as a document of title for ownership of shares in a company.
Some of the potential steps in the issuance of a document of title to goods are as follows:
However, such an arrangement is prone to forgery and duplicity. Also, in the case of a negotiable commercial instrument, there is a high chance that goods will be claimed by someone who finds a lost document or steals it from its owner. Moreover, a paper form of a document title can get easily damaged, misused, or stolen if not kept carefully.
Since most of these documents don't name the respective owner, there is a chance of disputes or errors at the time of delivery. Indeed, different jurisdictions have different laws governing such instruments. This may complicate the cross-border transfer of goods using the documents of title.
A document of title decides who can receive, possess, or own the goods, assets, or property upon delivery. It is a widely used commercial instrument worldwide, especially in international trade. Let us find out its uses through the following examples:
Suppose ABC Ltd., an imported cosmetics seller in New York City, placed an order for imported French perfumes with RS Fragrance Ltd. in Paris, France. RS Fragrance Ltd. ships the consignment through the carrier XYZ Carrier Co.
XYZ issues a bill of lading specifying all the relevant details about the goods in the consignment, including the quantity, value, condition, destination, etc., to RS Fragrance Ltd. RS Fragrance Ltd. then sends a copy of the document to ABC Ltd. A worker of ABC Ltd. presents this bill of lading as a document of title to the carrier authority at the destination and receives the consignment delivery.
Suppose Mrs. Anne, living in Baytown, sends her ancestral billiards table to her daughter in Houston through railways. The carrier issues a railway receipt, which Mrs. Anne sends to her daughter online. However, Anne's daughter lost her mobile, and the finder misused this document of title by reaching the railway station at the time of delivery. They presented the receipt to the railway authority and claimed possession of the billiards table.
There can be two different types of title documents based on their transferability, i.e., negotiable and non-negotiable. Its evidence can be differentiated as follows:
| Basis | Negotiable | Non-Negotiable Document Of Title |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | It is a written instrument that allows the delivery of goods or assets to the order of the mentioned person or the bearer of the paper on surrendering the same upon delivery. | It is a commercial instrument that specifies the name of the owner of the goods, assets, or property, making the ownership or control non-transferable to another party. |
| 2. Transferability | Handing over the document to someone can transfer the entitlement to receive the delivery of goods or assets. | Ownership of goods, assets, or property cannot be transferred through such a document. |
| 3. Risk Level | Involves risk of loss, theft, or disputes since anyone who finds the document can take the delivery of goods or assets | Limited risk since the bearer cannot claim goods in case of loss or theft |
| 4. Legal Framework | The endorsement and delivery of such instruments are governed by the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) | Not being governed by the same legal body, however, has specific lawful implications. |
| 5. Uses | Commonly used in overseas transfer of goods or assets | Used for direct delivery of goods to the owner |
Although both documents are presented to prove the ownership of the assets, they are dissimilar in the following ways:
| Basis | Document Of Title | Document Showing Title |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | It is paper proof that the person having the document is entitled to receive the delivery of goods, assets, or property. | It is a written instrument declaring the ownership of the goods, assets, or property that is non-transferable to another person through delivery. |
| 2. Transferability of Ownership | It can serve as a negotiable document, and ownership can be transferred through the mere delivery of goods or assets. | Ownership of the goods or assets cannot be transferred to anyone by just handing over the goods to them. |
| 3. Details Included | Includes all the information about the goods or assets, such as quantity, value, condition, issuer name, issuing date, and other terms and conditions. | States the ownership details, I.e., owner's name, address, etc. |
| 4. Regulatory Framework | Governed by commercial laws | Governed by separate legal regulations |
| 5. Example | Clear warrant, railway receipt, bill of lading | Share certificate, vehicle registration certificate, property deed |