Table Of Contents
Dividends in Arrears Meaning
A dividend in arrears is nothing but the cumulative amount of dividend, unpaid on an expected date to a cumulative preferred stockholder. It can happen because the company may not have sufficient cash balance to pay dividends.
Key Takeaways
- A dividend in arrears means the cumulative dividend amount unpaid to a cumulative preferred stockholder on an expected date. It occurs due to the company's need for more cash to pay dividends.
- Ordinary shares/equity shares, cumulative preference shares, and non-cumulative preference shares are the essential terms of the dividend in arrears.
- It benefits the investors since they may obtain a fixed dividend and preference over ordinary shareholders. Sometimes it may get delayed by the company due to insufficient cash.
Important Terms
To understand the dividend in arrears, we need to know about the below terms first:
- Ordinary Shares/Equity Shares: Ordinary shareholders are the company’s owners. They have voting rights. They get the dividend only after paying dividends to preferred shareholders.
- Cumulative Preference Shares: Cumulative preference shareholders receive the fixed dividend rate, and they have a preference over ordinary shares. But they do not have voting rights. If the company does not have sufficient cash to pay the dividend, the dividend of cumulative preference shareholders will accumulate. It will be delivered in the future when the company declares the dividend.
- Non-Cumulative Preference Share: Non-cumulative preference shares have the same features as cumulative preference shares, except for an accumulation of dividends. Suppose the company cannot make payment of dividends in any year, then they cannot claim unpaid dividends in the future.
Features of Dividend in Arrears
Some of the features are as below:
- It applies to cumulative preference shares.
- Paid before making payment to common shareholders or non-cumulative preference shareholders.
- There is no maximum time limit for accumulation. It can accumulate for any number of years.
- The company does not require paying these dividends unless the dividend declared in the future.
- Dividends in arrears are not the actual liabilities. Therefore, it does not need to be considered in accounts.
- It needs to disclose under notes to accounts on the balance sheet.
- It does not carry any interest in the arrear period. Thus, the company is not required to pay any claim for the unpaid period.
Example of Dividends in Arrears
Let us understand this with the below example of dividends in arrears on cumulative preferred stock :
ABC Inc issued 10000 ordinary shares and 1000 cumulative preference shares. A cumulative preferred shareholder will receive a guaranteed $5 per share each year as a dividend. These shares were issued on January 1, 2015. As of December 31, 2015, the company does not have a sufficient cash balance to make the payment to its preferred shareholder. Therefore the total dividend amount on cumulative preference shares remains unpaid and will be treated as a dividend in arrears. How? Let us find out:
Solution:
Calculation of dividend in arrears on December 31, 2018, will be –

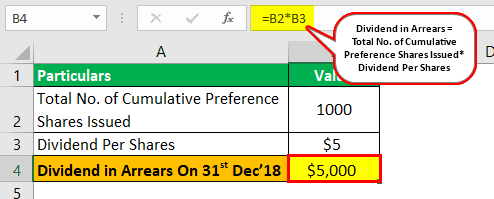
- Dividend in Arrears as of December 31, 2018, = Total No. of Cumulative Preference Shares Issued * Dividend.
- Dividend in Arrears as on December 31, 2018 = 1000 * $5 = $5,000
- Second and third-year also, ABC Inc cannot pay dividends because of the unavailability of cash balance. Therefore, the total unpaid dividend on December 31, 2017, will be $15,000.
- Now, the company does good business in the fourth year and has sufficient cash balance to make the dividend as follows:
Case #1
ABC Inc will pay a total dividend of $40,000 to its shareholders in the below manner:
- The dividend will be first payable to cumulative preference shareholders with the arrears of dividends.
Calculation of total dividend in arrear will be –

- Total dividend in arrear = No. of shares * Dividend per share * No. of Years
- Total dividend in arrear = 1000 * $5 * 4 = $20,000
- After paying a cumulative preference shareholder balance of $20,000, the company will pay to a common shareholder $2 per share.
Case #2
- ABC Inc will pay a total dividend of $20,000 to its shareholders in the below manner:
- The dividend will be first payable to cumulative preference shareholders with the arrears of dividends.
- Total dividend in arrear = 1000 * $5 * 4 = $20,000
- There is nothing in balance, so common shareholders will not get dividends.
Case #3
ABC Inc will pay a total dividend of $10,000 to its shareholders in the below manner:
- The dividend will be first payable to cumulative preference shareholders with the arrears of dividends.
- Total dividend in arrear = 1000 * $5 *4 = $20,000
| Arrear Years | Amount |
|---|---|
| 2015 | $5,000 |
| 2016 | $5,000 |
| 2017 | $5,000 |
| 2018 | $5,000 |
- ABC Inc will pay only $10,000. Therefore, it delivers the first arrears of 2015 and 2016, and 2017 and 2018 will remain as it is.
- Since no balance is left, ordinary shareholders will not receive any dividends.
Conclusion
Dividends in arrears are a cumulative amount of unpaid dividends of past years payable on cumulative preference shares only. Cumulative preference share helps the company raise funds, and it is a financial instrument because it carries the nature of equity and debt.
It benefits the investors because they will get a fixed dividend and preference over ordinary shareholders. Sometimes it will be delayed if the company does not have sufficient cash, and they will also not get any interest in the delayed payment of dividends.
At the same time, it is beneficial for the company that does not require to pay every year compulsorily. It can be paid in the latter year with the arrear of the past year without any interest.