Table Of Contents
What is Dividend Growth Rate?
The dividend growth rate is the rate of dividend growth over the previous year; if 2018's dividend is $2 per share and 2019's dividend is $3 per share, then there is a growth rate of 50% in the dividend.
Although it is usually calculated on an annual basis, it can also be calculated quarterly or monthly if required. In addition, it can be calculated (using the arithmetic mean) by adding the available historical growth rates and dividing the result by the number of corresponding periods.
Dividend Growth Rate Formula
Formula (using Arithmetic Mean) = (G1 + G2 + …….. + Gn) / n
where
- Gi = Dividend growth in the year,
- n = No. of periods
It can be calculated using the compounded growth rate method by using the initial dividend and final dividend and the number of periods in between the dividends.
Formula using Compounded Growth) = (Dn / D0)1/n – 1
where
- Dn = Final dividend
- D0 = Initial dividend
- n = No. of periods

Explanation
Finally, the formula for dividend growth rate can be derived by dividing the sum of historical dividend growths by the no. of periods, as shown below.
The formula using the arithmetic mean can be calculated by using the following steps:
- Firstly, gather all the company's historical dividend growth and add up all of them. It will be easily available from the annual report of the company. The periodic dividend growth can be calculated by dividing the current dividend Di by the last dividend Di-1 and subtracting one from the result, then expressed in percentage. Gi denotes it.
Gi = (Di / Di-1) - 1 - Next, determine the number of periods for which the historical growth rates have been collected, denoted by n.
- Finally, the formula for dividend growth rate can be derived by dividing the sum of historical dividend growths by the no. of periods, as shown below.
Dividend Growth Rate = (G1 + G2 + ......... + Gn) / n
The formula using compounded method calculation can be done by using the following steps:
Step 1: Firstly, determine the initial dividend from the annual report of the past and the final dividend from the recent annual report. The initial and final dividends are denoted by D0 and Dn, respectively.
Step 2: Next, determine the number of periods between the initial and the recent dividend periods, denoted by n.
Step 3: Finally, dividend growth calculation can be derived by dividing the final dividend by the initial dividend and then raising the result to the power of reciprocal of the no. of periods and subtracting one from it, as shown below.
Dividend Growth Rate Formula = (Dn / D0)1/n – 1
Calculate Dividend Growth Rate
Let us take the example of Apple Inc.'s dividend history during the last five financial years starting from 2014.
Given,
- Final dividend, D2018 = $2.72
- Initial dividend, D2014 = $1.82
- No. of periods, n = 2018 – 2014 = 4 years
Determine the dividend growth based on the given information using the following methods.
- Arithmetic mean formula
- Compounded growth method
Below is data for the calculation of Dividend Growth (using the arithmetic mean & compounded growth method) of Apple Inc.’s
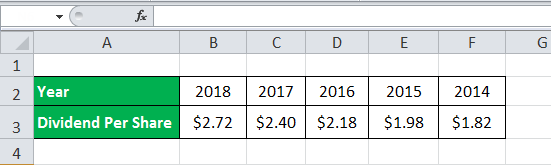
As per the question,
- Dividend growth in 2015, G2015 = * 100% = 8.79%
- Dividend growth in 2016, G2016 = * 100% = 10.10%
- Dividend growth in 2017, G2017 = * 100% = 10.09%
- Dividend growth in 2018, G2018 = * 100% = 13.33%
Now, no. of periods, n = 2018 – 2014
= 4 years

Therefore, the annualized dividend growth using arithmetic mean method can be calculated as,
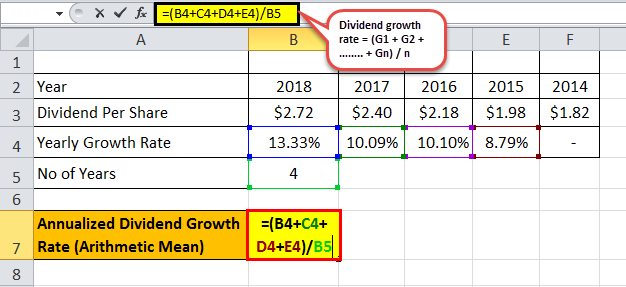
Dividend Growth Rate = (G2015 + G2016 + G2017 + G2018) / n
= (8.79% + 10.10% + 10.09% + 13.33%) / 4
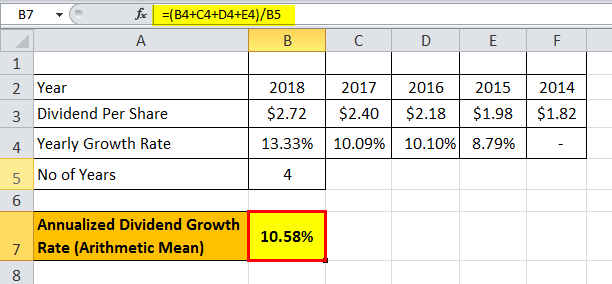
Dividend Growth = 10.58%
Therefore, the annualized dividend growth rate calculation using the compounded growth method will be
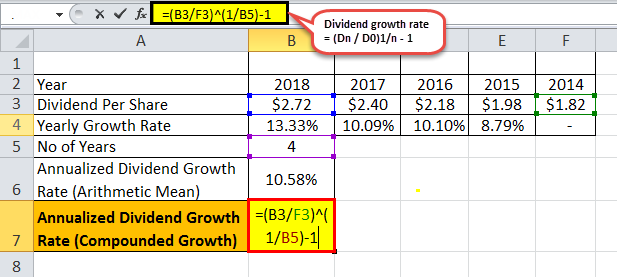
Dividend Growth Rate Formula = * 100%
= * 100%

Dividend Growth (Compounded Growth)= 10.57%
From the case of Apple Inc.'s dividend history, it can be seen that the dividend growth rate calculated by either of the two methods gives approximately the same results.
Relevance and Uses
From an investor's perspective, it is important to understand this concept to assess earnings from a stock investment. For instance, a strong dividend growth history could indicate future dividend growth, which is a sign of long-term profitability for the stock. Further, a financial user can use any interval for the dividend growth calculation. Finally, this concept is essential because it is primarily used in the dividend discount model, which finds extensive application in determining security pricing.
You can download this Excel Template here – Dividend Growth Rate Formula Excel Template
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the dividend growth rate. Here we discuss the formula for calculating dividend growth rate using the arithmetic mean and compounded growth rate method, examples, and a downloadable excel sheet. You can learn more about accounting from the following articles –
