Table Of Contents
Direct Tax Definition
Direct tax is a type of tax in which the payment burden falls directly on the payer, and the liability cannot be shifted to others. Direct taxation is imposed on a person's income or wealth, such as the federal income tax, as opposed to indirect tax, which is levied on goods and services.
All entities must pay taxes on their personal properties and assets, including individuals and organizations. Hence the liability, incidence, and impact fall on that entity only. Nevertheless, it is a source of income for the government, which in turn uses it to redistribute societal resources.
Key Takeaways
- Direct taxes are based on the income of a person or an organization where the entity is taxed for its assets.
- In direct taxes, the incidence and impact fall on the assessee. However, the same entity has to bear the tax, and as a result, it hurts the taxpayer.
- In a progressive taxation system, a taxpayer's tax is proportionately increased as their tax base increases.
- These taxes benefit the government in numerous ways, such as providing income for supporting welfare programs like the social security system, health care, and education. They can also be used to control inflation.
Direct Tax Explained
Direct taxes are taxes that fall under the likes of income tax. Taxes are levied on earned and unearned income (such as salaries, wages, tips, and commissions). Both businesses and individuals may be subject to income taxes by way of personal income taxes and business and corporate income taxes. In the United States, income taxes are collected by the federal agency known as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), and the collecting agency differs with the country.
The tax policies significantly impact the national economy for the overall economy and specific economic groupings. Although economists have wildly divergent opinions regarding the tax policies which are the most effective at supporting growth, tax policies often materialize the purpose of stimulating the economy. The money helps to sustain the economy and boost growth whenever and wherever it is needed.
Taxation is allocating financial resources to people with low incomes or special needs. It is also known as "income redistribution." Taxation is an essential function of the government as tax policies influence the national economy, help the redistribution of resources, and support growth. In addition, they frequently help with the purpose of stimulating the economy.
Critical public services like social security, health care, national defense, and education require ongoing funding, and the amount collected from taxes is the funding source.
Different countries follow different taxation systems. The U.S. tax system followed is a "progressive taxation system, "where the tax rate paid by an individual (or household) as a proportion of their income increases with increasing income. People who earn more not only pay more in taxes overall, but they also pay taxes at a higher rate in a progressive tax system. As income rises, the potential costs lean more toward pleasures than necessities. The ability-to-pay principle acknowledges that low-income households would bear a heavier penalty for sacrificed essentials under a flat (or regressive) tax rate than high-income households.
Types
There are many types of direct taxes, and some of them are as follows:
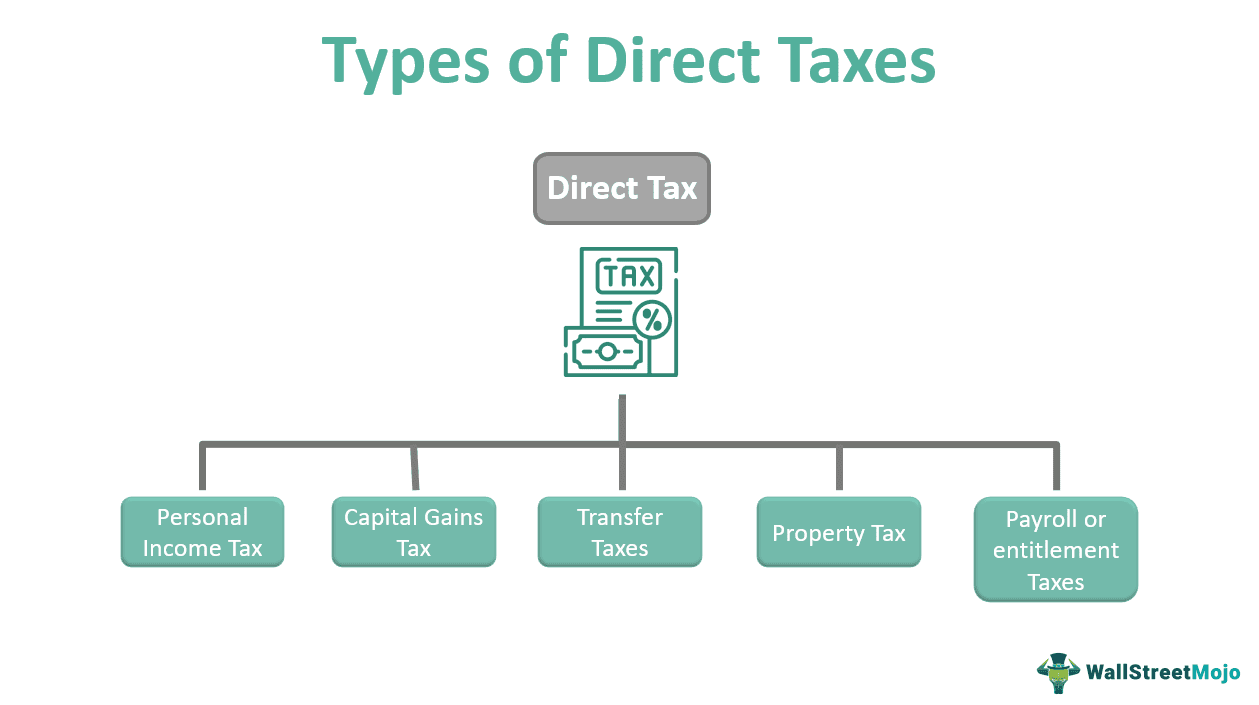
#1 - Personal Income Tax
The income earned by a person, irrespective of salaries or dividends, is considered for taxation. It is deducted based on predetermined rates that are revised periodically.
#2 - Wealth tax or property tax
The government charges a wealth or property tax on people on the proceeds from owning property (land and buildings) based on its market value.
#3 - Capital gains tax
This tax levies when a person sells assets like stocks or a company. The tax estimation involves calculating the gap between the purchasing and selling amounts of the respective asset.
#4 - Transfer taxes
The estate tax is a type of transfer tax. The taxable portion of a deceased person's property is an example. Another type of transfer tax is a gift tax, levied when someone transfers property to another person and a specific sum is required.
#5 - Payroll or entitlement taxes
These direct taxes are used to pay for social security and health care. Authorities use payroll deductions to collect the entitlement tax.
Features
The following are the key features of direct taxes:
#1 - Calculated on income
The money a person receives as income is used to calculate direct taxes. For example, income tax is a direct tax.
#2 - Incidence and impact
The calculation of direct tax payment involves a person's income—the money earned by salary, dividends, and other profits. Since earnings form the basis of it, the obligation to pay it off also falls on the same individual. Therefore, incidence and impact fall on the same person.
#3 - Transferability
One of the significant differences between direct and indirect taxes is that direct taxes are not transferable. In indirect tax, the end customer pays the tax, which is therefore transferable to another person. Direct taxation does not allow the transfer of liability for payment.
Examples
Check out these examples to get a better idea of direct taxation:
Example #1
Susan has worked for over a decade, and her career has grown so tremendously that she has to pay taxes under all slabs. For example, in 2009, her income was initially $10000, and people belonging to that tax slab had to pay 10% tax; therefore, she had to pay $1000 in tax.
Example #2
The US states offer rebates and expanded tax credits to taxpayers to combat the effect of high inflation. The state payments act as inflation relief as the hard-hitting economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic is easing across the country.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Here are the main advantages and disadvantages of direct taxes:
Advantages
#1 - Source of government income
The government runs the country, and for that, it needs funds. Therefore, direct taxes on people's income form a significant part of the government's income. This helps to fund social security schemes, education, health care, and other social infrastructures.
#2 - Certainty
An individual can be sure about the tax, as they can know the amount and due date in advance. The taxpaying party is aware of their tax obligations' amount and due date and embraces certainty. In addition, there are certain benefits to regular payment of taxes, such as getting loans and good credit scores.
#3 - Economic control
Increasing direct tax payments can be a valuable tool to control inflation. Similarly, the reduction of taxes can be a tool to induce spending and increase money circulation in the economy.
#4 - Redistribution of wealth
When the rich are taxed, higher rates are used to deduct tax, and that money is used to service welfare schemes such as social security schemes, education, and public health policies. This helps reduce the burden on the poor and needy, and they also get to access necessary resources.
Disadvantages
#1 - Taxation system
The system opted by a country plays a significant role in whether it will be a disadvantage for the poor, such as the regressive tax system. For example, under a regressive tax system, people with low incomes pay more taxes than people with high incomes.
#2 - Liability and transferability
Taxe calculation involves individual income and is hence not transferrable to other people. Therefore, the liability to pay also falls on the same person.
