Table Of Contents
What Is Direct Market Access (DMA)?
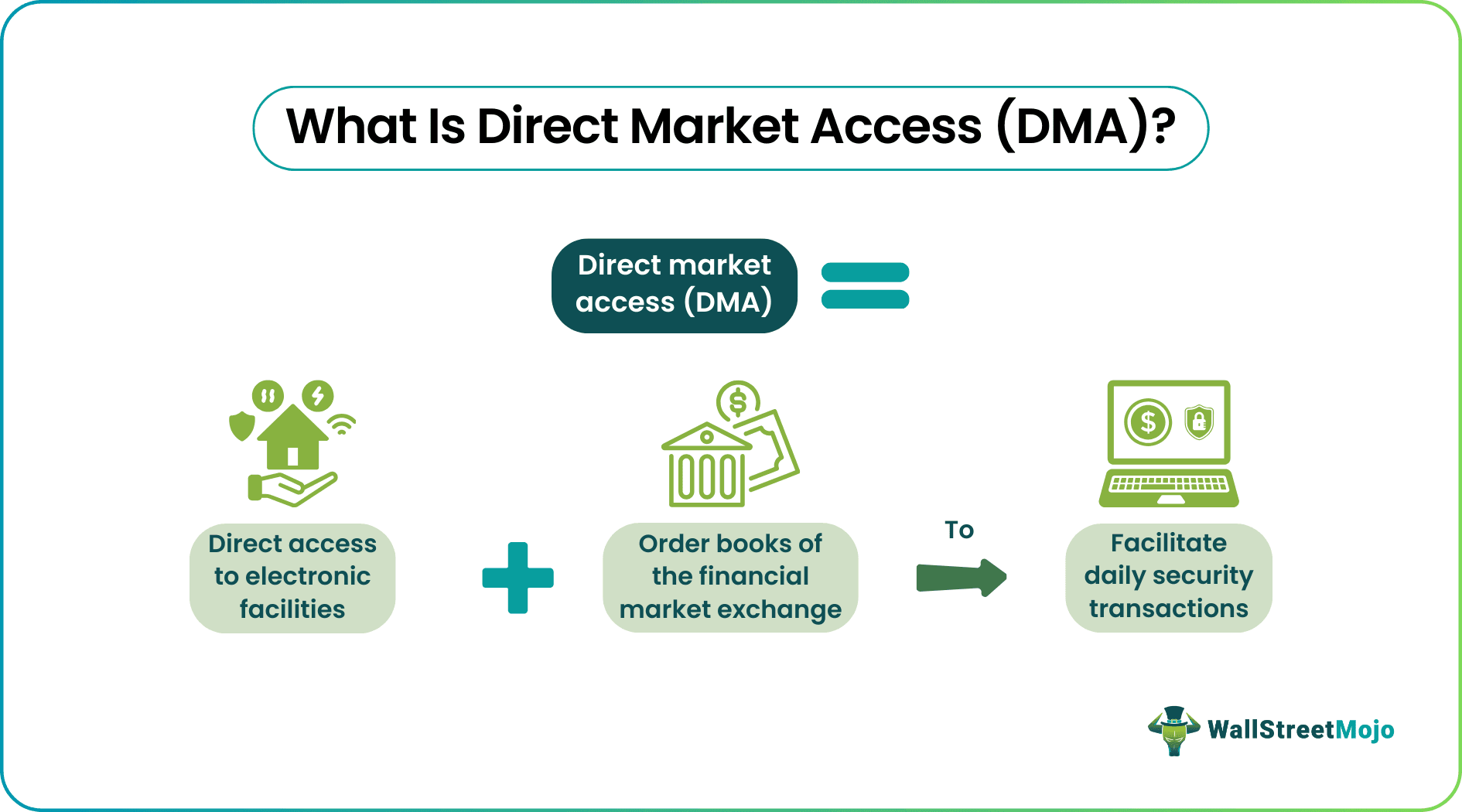
Direct market access (DMA) in trading refers to the process where investors directly access and execute trades via exchanges such as NYSE, NASDAQ, etc., rather than operating through a brokerage firm. Therefore, traders can directly quote their prices, buy, or sell without intermediaries.
DMA requires a sophisticated electronic infrastructure to allow investors to operate independently. Investors who wish to have DMA should earn their membership with stock exchanges and complete the necessary legal requirements. Depending on the country, they must also register with the financial regulatory authority.
Key Takeaways
- Direct market access for retail investors and institutional traders allows these parties to directly interact with the exchange, place buying, and selling orders, and execute them without involving intermediaries like broker-dealers.
- Brokers usually have direct access to the market and exchanges. Sometimes, they sponsor this market access to their clients, trading frequently.
- The clients can directly place and execute orders for which they will pay a fee to the broker.
- DMA has many benefits for investors. However, there are concerns about security and fraud by specific traders.
Direct Market Access Explained
Direct market access allows retail investors to buy and sell financial instruments directly over the stock exchange by eliminating intermediaries such as brokerage firms. Here, they have direct access to the electronic order book, which contains the details of all the orders traders place. The order is fulfilled when the bid and ask prices match on the exchange. They can also re-quote until they accomplish the desired task.
In the past, investors relied on brokerage firms to communicate their trading requirements, including price and specifications. The broker would then place the order on the exchange. However, with DMA, investors are actively involved in the trading process, including subsequent steps such as payment and transfer of ownership.
Direct market access agreements offer numerous benefits to investors, while broker-dealers may face potential customer loss. Experienced traders often combine DMA with algorithmic trading, leveraging automation and computer technologies to execute trades and secure more favorable deals on the exchange.
In the realm of forex trading, DMA caters explicitly to foreign exchange trades and transactions involving investors, buy-side firms, and sell-side firms. Sell-side firms, including brokerage firms and investment bankers, create and promote products for the buy-side of the financial industry. The buy-side, comprising mutual funds, asset managers, and individual investors, conducts market research and invests in these products.
Independent forex agencies that provide the necessary electronic infrastructure and interface facilitate forex direct market access. Forex DMA exhibits specific unique characteristics compared to other DMA platforms. For example, while re-quoting is allowed in traditional DMA, it is impossible in forex markets. Forex platforms display variable spreads due to the higher volatility and sensitivity observed in global markets, shaping the distinct operational dynamics of forex direct market access.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Examples
Let us explore real-world and hypothetical examples showcasing the application and potential of direct market access (DMA) in the financial markets.
Example #1
Stacy has been an investor for more than 30 years. Recently, after her retirement, she found excess time, as a result of which she decided to get direct access to the exchange. After completing the legal procedures, Stacy contacted the exchange and became a direct access member. Now, she doesn’t have a broker and doesn’t have to pay any commissions. She can also execute trades faster, thus, making more profits.
Example #2
Options Technology, the leading Capital Markets services provider, announced its expansion to global market data services. The company acquired ACTIV Financial and integrated its normalized data services and application programming interface (API). Currently, the firm offers high-performance trading infrastructure and cloud-enabled services to over 550 businesses across nine cities globally. With its expansion, it will be able to provide direct access to the financial markets and reduce the total cost of ownership for its clients.
Benefits
Let us understand DMA's advantages to traders in the financial markets.
- Since DMA eliminates the need for broker-dealers, the traders can reduce the costs associated with brokerage, such as commissions, fees, etc. It also reduces the time involved as the traders need not wait for brokers to execute the order.
- Data privacy and security are another critical advantage. Investors do not have to transfer their personal information to brokerage firms.
- The traders will have a higher degree of control in investing. It will also increase their responsiveness to market changes and fluctuations.
- Finally, DMA allows traders to participate in pre-market and post-market auctions.
Direct Market Access vs Sponsored Access
Sponsored and direct market access (DMA) are distinct approaches in trading, each offering unique advantages and considerations. Let us understand the differences between them.
- Sponsored access is provided by broker-dealers, allowing their clients to trade directly on an exchange, while DMA involves traders using their MPID for direct market access.
- Sponsored access is often offered to high-frequency traders operating in low-latency markets, enabling them to respond to market movements and potentially generate profits quickly.
- Traders using sponsored access typically pay additional fees to their brokers, making it a form of DMA through brokers.
- Sponsored access has faced regulatory constraints, especially after its involvement in the flash crash of 2010, making it more challenging to obtain.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A direct market access (DMA) broker is a financial intermediary that provides retail investors with the technology and infrastructure to trade directly on the stock exchange. They enable investors to access the electronic order book, execute trades, and have greater control over their trading activities. By eliminating the need for traditional brokerage firms, DMA brokers offer faster trade execution, increased transparency, and potentially lower costs.
In retail trading, investors place and execute buy and sell orders through intermediaries like brokerage firms, who then access the exchange on their behalf. Individual investors commonly use this approach. On the other hand, DMA allows investors to access the exchange directly, quote their prices, and buy or sell securities without intermediaries.
Market makers are institutional investors directly accessing the market to trade securities for their accounts. In DMA, trades are executed now on the exchange, while contracts for differences (CFDs) may be offered afterward. In contrast, market makers create a market for CFDs and use them as a hedging method.

