The DMCA is a recent act that protects digital work in the same way the Copyright Act shields traditional creations. However, the following are their significant differences:
Table Of Contents
Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) Definition
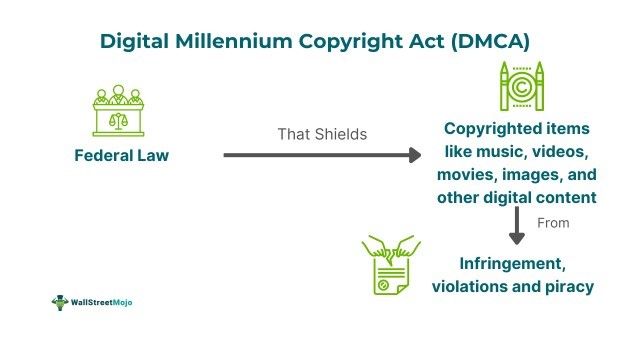
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) refers to a Federal copyright law passed with the aim to safeguard the interest of copyright holders from online infringement and unauthorized use of intellectual property. It was passed on October 28, 1998, to make amendments to the United States Code Title 17.
It was an initiative of the Congress government under Bill Clinton's presidency. The imposition of this law became significant due to the rapidly growing digital environment, where the downloading and use of copyrighted items like music, images, games, movies, etc., was not bounded by strict regulations. Hence, the primary motive of the DMCA was to address copyright violations.
Key Takeaways
- The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) refers to a legal mechanism that shields copyright owners from online infringement, piracy, and other unauthorized use of their copyrighted items, such as videos, music, vlogs, images, movies, and other content.
- It was implemented as part of Title 17 of the U.S. Code on October 28, 1998, by the Congress government when Bill Clinton was President.
- The copyright owner or claimant can issue a Digital Millennium Copyright Act takedown notice to the alleged infringer if they believe that the latter has misused their work without their permission.
Digital Millennium Copyright Act Explained
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is a Federal government law that governs the rights of copyright owners in the present era of digital or intellectual property published on the Internet. This amendment was passed on October 28, 1998, under Title 17 of the U.S. Code. The primary objective of this regulation was to shield intellectual property, I.e., digital work like music, movies, images, games, and other such copyrighted items from infringement, unauthorized use, or violation. President Bill Clinton passed the law at the time of Congress's government.
For instance, the Digital Millennium Copyright Act YouTube protects the original content, including vlogs, music, promos, movies, and other entertainment of informative content creators, from unauthorized usage of their work or from online piracy.
Therefore, any copyright holder who finds that any Online Service Provider (OSP) or other account holder is making personal copies of their work, posting it on other websites in an unauthorized manner, or using it beyond the permissible terms and conditions can file a complaint under the DMCA. For this purpose, the complaint filer can fill out the DMCA takedown form online. Thereby, a Digital Millennium Copyright Act takedown notice is sent to the respective OSP, who further informs the alleged infringer, I.e., the subscriber or user engaged in such copyright infringement. The infringer would send a counter notice addressing the OSP, who would then forward it to the copyright owner. The OSP can wait for 10-14 days after receiving a legal DMCA counter notice, within which timeframe the copyright holder can file a suit against the alleged infringer.
Purpose
The DMCA mainly aims to govern the intellectual property rights of copyright holders and ensure that consumers don't engage in copyright violations by unethically using copyrighted items. It further checks for online infringements and imposes penalties upon such misdeeds. Given below are the various other objectives of this Federal law:
- Prohibits Circumvention: It prohibits the circumvention of technological protection like Digital Rights Management (DRM), which the copyright owners use to protect the authenticity of their work, by considering such actions as criminal offenses.
- Safe Harbors: Safe harbor security further protects online service providers (OSPs) from the liabilities of their users' copyright infringements.
- Notice and Takedown System: It implemented the Digital Millennium Copyright Act notice and takedown mechanism to frame policies that emphasize terminating the online accounts of those who often engage in copyright infringements. Also, it enables the copyright holders to inform the OSPs of the alleged copyright infringement and let them delete such content.
- Digital Content Exposure Support: It also provides legal safety to copyright holders from unauthorized uses, such as encryption circumvention and password hacking, of their intellectual property and allows a wider exposure to their digital work.
- Copyright Details Disclosure: The law considers it unlawful to state, amend, or delete the false copyright management information.
Provisions
The DMCA is a legal framework that governs the interaction between the Internet and copyrights. The following are the primary provisions under this law:
- Safe Harbors and Notice and Takedown System: Congress enacted section 512 of the Copyright Act to address the legal uncertainties of the internet industry regarding potential liability for copyright infringement on their platforms. It allows copyright holders to request the deletion of infringing content without any legal consequences and provides legal protection, I.e., safe harbors for OSPs regarding their legal compliance.
- Section 1201 and Anticircumvention: Section 1201 of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) restricts the circumvention of the technological protection measures (TPMs) governing the use of copyrighted items, like password protection for streaming; and also producing, importing, offering, or distributing tools, products, services, devices, or components intended to bypass TPMs. Additionally, it includes a triennial rulemaking process that grants temporary exemptions for specific non-infringing access to copyrighted items.
- Copyright Management Information Protection: Section 1202 restricts the circulation of false copyright management information (CMI) with the intention of copyright infringement. These details include author, title, copyright holder, and usage terms associated with copies, performances, phonorecords, or displays of copyrighted items. The section exempts certain authorized activities of law enforcement, intelligence, or government agencies and specific transmissions performed through broadcast stations or cable systems.
Examples
Let us consider the following scenarios to understand the relevance of DMCA in the digital space:
Example #1
Suppose ABC Fintech Ltd. is known for providing a seamless user experience due to its unique software code. However, its software engineer, who shifted to a competitor firm, disclosed these coding secrets, and the company used the same software codes in its new project. On learning about it, ABC Fintech Ltd. filed a DMCA takedown notice against its competitor firm and thereby sued their previous software engineer for using these copyrighted items in an unauthorized way.
Example #2
The Dolphin emulator's projected release on Steam has been indefinitely deferred after a DMCA notice from Nintendo. Notably, this notice cites violations related to the inclusion of the Wii Common Key in Dolphin's source code, which indicates circumvention of anti-piracy measures. Moreover, the emulation experts, including Modern Vintage Gamer and Twitter user @LuigiBlood, have brought this issue to the limelight, emphasizing that the keys are part of Nintendo's copyrighted BIOS files. Hence, it raised concerns about the legality and vulnerability of other Dolphin versions. Further, Nintendo has recently issued DMCA notices against other homebrew tools, such as Lockpick, which extracts encryption keys from Nintendo Switch consoles, challenging their legality even for personal use.
Digital Millennium Copyright Act Vs Copyright Act
| Basis | Digital Millennium Copyright Act | Copyright Act |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | It is an enactment that shields the copyright owners from the unauthorized use or infringement of their work. | It is the law that protects exclusive creative work from copying. |
| 2. Introduced In | 1998 | 1976 |
| 3. Purpose | Check online piracy and copyright infringement or unauthorized use of copyrighted items. | Provide exclusive rights to creators for the development of useful arts and science. |
| 4. Items Covered | Copyrighted intellectual items like music, movies, videos, games, images, etc. | Physically created artworks, scientific formula, literature, music, drama, choreography, motion pictures, sound recordings, architecture or other such exclusive items |
| 5. Provisions | Anti-circumvention, safe harbours, notice and takedown, | Relief from statutory damages, actual damages, and injunctive relief for copyright infringement |
| 6. Penalties | Fine upto $250,000 and imprisonment of around 5 years | Additional legal advantages, like claiming relief for statutory damages and attorney's fees in court |
