Table Of Contents
What Is A Depositary Receipt?
A depositary receipt is a financial instrument that allows investors to invest in the equity of foreign companies. These depositary receipts can be traded on the stock exchange representing the underlying equity shares of the foreign companies. It helps companies raise capital from the international market; financial intermediaries such as domestic custodian banks and overseas depositary banks help the domestic company raise funds from foreign investors.
Depositary Receipts is the financial instrument that serves the purposes of both investors and issuing firms. This provides a platform where a firm can raise funds from a foreign country. In addition, the investor gets the opportunity to diversify his portfolio by investing in these depositary receipts of foreign companies.
Key Takeaways
- Depositary Receipts are a medium through which investors can invest in the shares of foreign companies. These Depositary Receipts can also be traded in the stock markets of the respective country.
- A depositary bank facilitates the raising of foreign capital. It buys the shares from a foreign country and lists them concerning the underlying shares on the domestic stock market.
- There are three types of Depositary Receipts: American Depositary Receipts, Sponsored or Unsponsored Depositary Receipts, and Global Depositary Receipts.
- Depositary Receipts can help a company raise foreign capital at a low cost, however, features high risk in the process.
How Does A Depositary Receipt Work?
Depositary receipt is issued by a bank as a negotiable instrument to signify shares in an overseas public company. These receipts allow the investor to widen their geographical limit of investing through allowance to invest in global markets.
It is important to note that American Depositary Receipts are issued only to the investor in the United States & Global depositary receipts are given to all investors in the world except to investors in the United States.
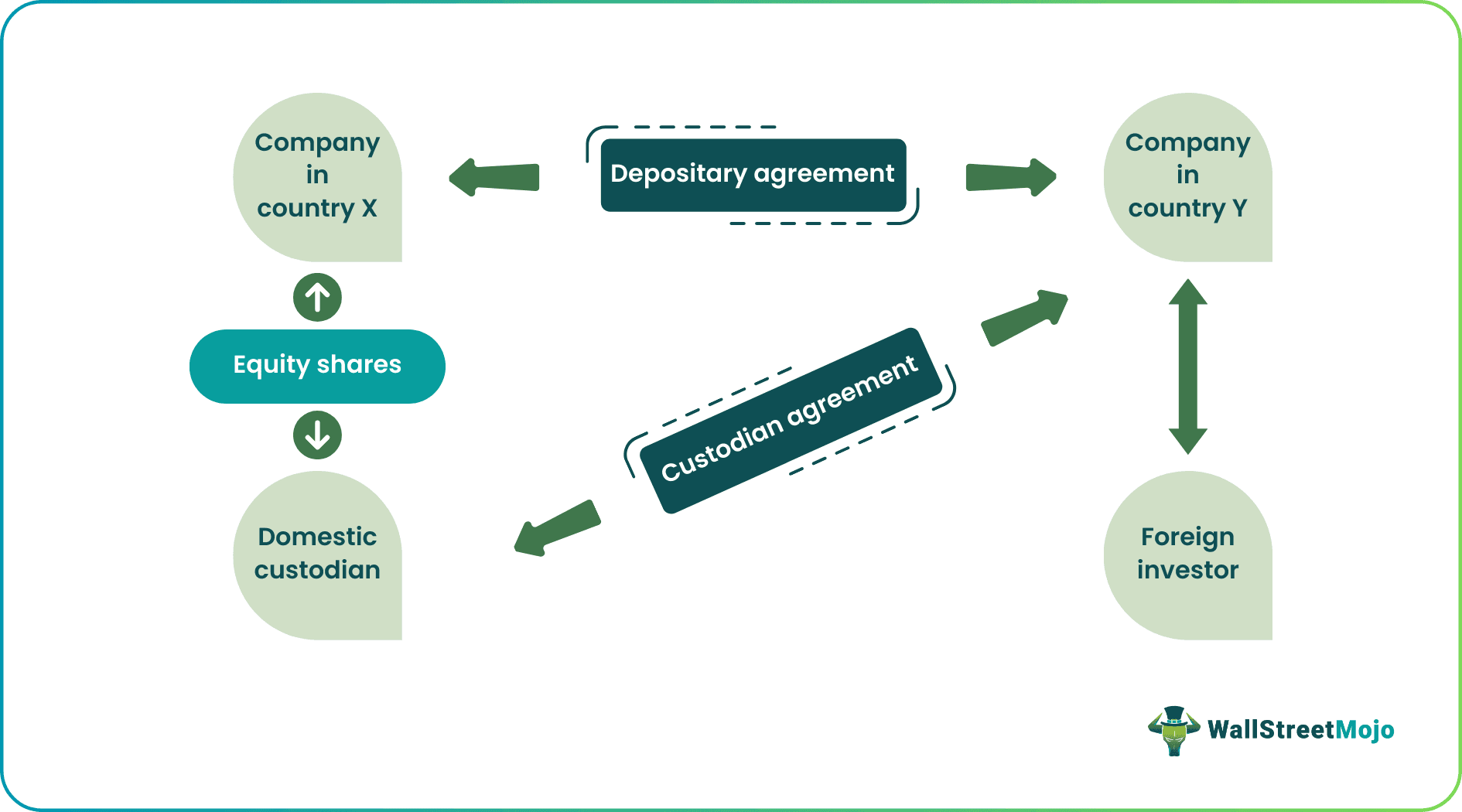
When a public company in a particular country, say The United States of America wants to allow foreign investors to be able to invest in their company, they enter into a depositary agreement with the company in another country who has a custodian agreement with the custodian in the U.S. This allows the investors to invest beyond the geographic limits of their countries which gives them a wider array of companies or even asset classes to invest and let asset appreciation happen over time,
An Indian firm – Infosys, which is listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange, wanted to raise more funds to expand its business from foreign investors in Japan. So, Infosys will first go to the depositary bank in Japan & ask them to help raise funds from the Japanese investors. Infosys has to provide the depositary bank with detailed financial reports, which makes it easier for the depositary bank to assess the financial health of the issuing company.
Depositary Bank will purchase the shares. Then, it can contact its business counterpart in India to buy the specified number of shares and offer Infosys's depositary receipt to the Japanese investors. These depositary receipts can be listed on the Tokyo stock exchange & also it can be traded on the counter market. Usually, one unit of depositary receipts holds around ten shares of underlying companies.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Types
The most common types of depositary receipts are American Depositary receipts & Global Depositary receipts. Let's discuss the types in detail through the discussion below.

#1 - ADR- American Depositary Receipts
An American Depositary Receipts is a financial instrument representing a certain number of shares in the company situated outside the United States. The United States depositary bank issues ADR to the investors. This ADR gets listed on the stock exchange in the United States & trades like the other shares on the exchange. Therefore, ADR benefits the foreign firm to attract & raise the fund from the investor without listing its equity shares in the United States at a lower expense than if the firm chooses to list its shares in the United States.
Depositary Bank holds the underlying security of the foreign firm, which is offered to the investor as 'ADR' which is denominated in U.S. Dollar & get listed on the recognized stock exchanges in the United States, e.g., NYSE, NASDAQ, etc. or also get traded on over the counter market. American investors who hold ADR realize any dividend or capital gain in USD but after net of foreign exchange expense and taxes.
By this time, you understand that an ADR represents the underlying foreign security in some ratios, such as one ADR consisting of 10 shares or maybe one share. The depositary bank ensures the value or price of the ADR is in line with this conversion ratio.
- Unsponsored ADR: Investment Bank or Brokers, with the help of depositary banks, create & issue unsponsored ADR to the investor by holding shares in the foreign company. Unsponsored ADR cannot be listed on the American stock exchange as this ADR has not registered with the regulator and has no foreign company involvement. Unsponsored ADR only trades on Over the counter.
- Sponsored ADR: Under this ADR, Foreign firms, with the help of depositary banks, create & issue ADR to the investor who is registered with the regulators & can be traded on the stock exchange..
Further, ADRs are categorized into three levels when fulfilling the requirement to list their shares on the stock exchange.
- Level 1: This type of ADR is usually traded on Over the counter market as this firm does not meet the criteria to the reporting standard (US GAAP) or register with the regulator (SEC) to get its share listed on the stock exchange. This ADR is considered to be risky among investors.
- Level 2 & 3: The Firm must register its ADR with the regulator (SEC) & also submit the financial reports of the firm, which should be U.S GAAP compliance. Level 2 registered ADR can't raise funds in the market. But Level 3 ADR is considered one of the most efficient ADRs among all levels and can raise funds for the firm. Level 3 ADR can be listed on the American stock exchange, such as NYSE or NASDAQ.
#2 - GDR - Global Depositary Receipts
GDR is another type of depositary receipt that can be issued to investors in most foreign countries in the world. By issuing GDR, the firm can raise funds from the financial market of more than one country and be traded in multiple stock exchanges simultaneously. A GDR also serves the same purpose as ADR, but by issuing GDR, the firm has certain benefits compared to ADR.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Let us understand the advantages and disadvantages of global depositary receipts through the discussion below.
Advantages
- Lower Expenses: Raising funds through depositary receipts in the foreign market can lower expenses for the firm than raising funds by issuing equity shares in the primary market of the foreign country directly.
- Liquidity for Investors: This depositary receipt traded on the stock exchange can provide liquidity to the foreign investor.
Disadvantages
- Risk of Foreign Exchange Rate: As you know, depositary receipts are exposed to currency foreign exchange risk to the investor who wants to invest in foreign companies.
- Regulatory Risk: A firm that raises funds by issuing the depositary receipt in the foreign market has to adhere to the regulation of multiple countries;
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Depositary Receipts are derivatives that derive their value from an underlying share. They generally represent two or more shares of a foreign company. These receipts enable investors to hold and trade shares of foreign companies without directly owning the underlying shares.
Depositary Receipts can be traded in the domestic markets. Hence, this is because they represent the value and ownership of the underlying shares. However, they can be changed within the domestic markets. Hence, when these receipts are listed on domestic exchanges, they are subject to the rules and regulations of those exchanges and can be traded by investors in the market.
American Depositary Receipts (ADR) are the Depositary Receipts that represent the shares of a company foreign to the USA. The original owner is for a Non-US company, whereas the depositary banks list the Depositary Receipts.

