Table Of Contents
Deleveraging Meaning
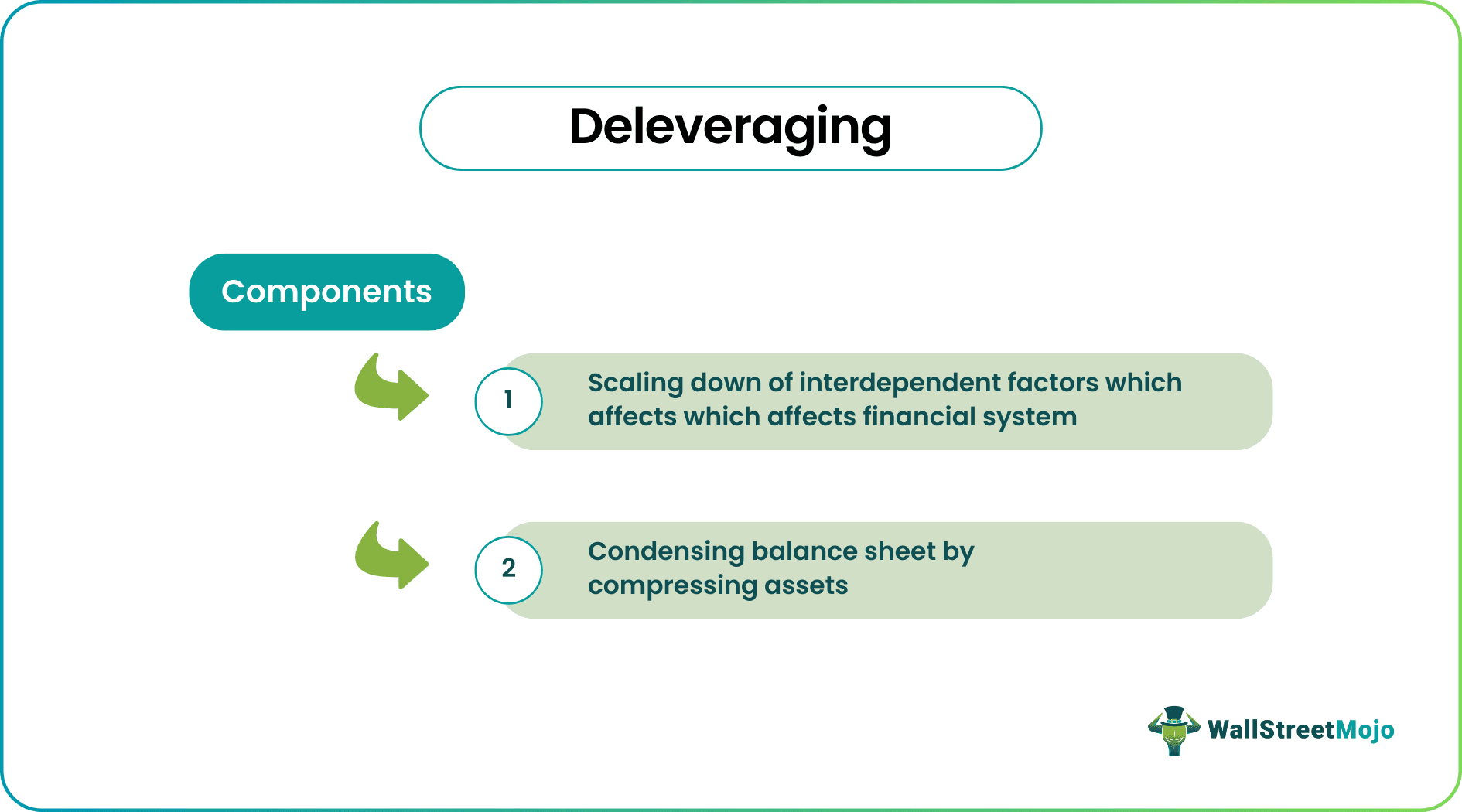
Deleveraging is defined as the process where an organization slashes down its debt or financial leverage by either selling its assets or raising equity capital. The prime goal of deleveraging is to curtail the proportionate percentage of the balance sheet of a business funded by its liabilities.

It is an effective course of action to get a company back to its operation or provide its lifeline. However, deleveraging is not that great to look at from a practical scenario. Job cuts, shutdowns, reducing budgets, and selling off assets are all the results of deleveraging, where the business will seek to store the extra cash to pay off its obligations.
Key Takeaways
- Deleveraging is when a company reduces its financial leverage or debt by selling assets or raising equity capital. Its main objective is to reduce the proportion of a company's balance sheet supported by its liabilities.
- Deleveraging is a cost-effective strategy for monetizing assets, but it carries disorder and limited supply risks, offering potential returns but reducing default risks.
- A corporation can survive in the market by deleveraging to avoid severe fines by reducing holding size, cash reserves, and asset sales.
Deleveraging Explained
Deleverage is to cut down outstanding liabilities without incurring any new ones. Thus, it leads to fall in the debt portion in the capital structure of the company.
An increasing systemic deleveraging can bring about the credit crunch and financial recession and can have a serious negetive macroeconomic effect When the economy faces a downturn, the assets and the income or revenue of the company faces a reduction in value. This leads to losses for companies and create a very delicate financial crunch because the earnings and assets are now not enough to support the debt repayment capacity.
Thus, deleveraging event helps in reducing the debt burden and exposure to market volatility. It keeps the company balance sheet more stable and safe in order to absorb the market downturn during bad times.
The savings rate can sometimes be linked to deleveraging as people/business tend to save more when they are not borrowing from the market.
Failure to deleverage at times of need or financial crisis may increase the risk of default.
Deleveraging is considered an effective strategy if it is implemented by monetizing the assets. The entity needs to either raise the cash balance or pay off the debts which can be done either by selling the assets or through raising of capital
It always carries the risk of becoming disordered and sudden. The solutions are in short supply too. There are very few indicators that the current practice of utilizing leverage will diminish, especially in the scenario of decreasing expectations for economic growth. Thus this calls the very purpose of utilization of deleveraging techniques at all.
Deleveraging in economy shrinks the total intensification of market risk on the entity’s financial statement. Furthermore, that gives up prospective returns in good times, in barter for reduced risk of heavy loss and unpleasant default in harsh times.
Examples
Let us take the examples of deleveraging event to understand the concept.
Example #1
Let’s take the example of deleveraging. Let us assume a business has $ 10 00,000 of assets. The structure of finding the asset is that $5 00,000 is covered by debt, and the rest $5 00,000 is covered by equity. The net income earned during the year was $2 50,000. Considering this, let's calculate a few crucial ratios.
- Debt to Equity = $5, 00,000 /$5, 00,000 = 100%
- ROE (Return on Equity) = $2, 50,000/$5, 00,000 = 50%
- ROA (Return on Assets) = $2, 50,000/$10, 00,000 = 25%
Now let us take a second scenario where deleveraging comes into play where the business has decided to consume $2 00,000 of its assets to pay $2 00,000 of its debt. The business is now left with $8 00,000 out of which equity contribution remains the same as $5, 00,000 but the debt component has been reduced to $3 00,000. On a similar occasion when the company has made a net income of $2 50,000, let us see how the above-calculated ratio changes:
- Debt to Equity = $3, 00,000 /$5, 00,000 = 60%
- ROE (Return on Equity) = $2, 50,000/$5, 00,000 = 50%
- ROA (Return on Assets) = $2, 50,000/$8, 00,000 = 31.2%
We can clearly see the second ratio looks much more financially healthy and profitable and investors would also like to pick up the second option to put their money in.
Example #2
Freeport-McMoRan Inc. is an example of an organization that mainly deals with mining recently implemented deleveraging. It had borrowed too much after the recession period, where its debt increased six times to more than $20 billion due to new business ventures.
However, the decline in prices of oil compelled Freeport to change its plan. It started selling assets and making payments for the bonds, curtailing its overall debt to $11.1 billion. Also, it showed tremendous improvement to its EBITDA, which almost doubled in the second quarter from a year earlier than expected, bringing down the leverage of its cash flow to 1.4 times from 2.9 times.
Advantages
Some of the advantages of deleveraging process are as follows:
- It can be considered as one of the effective methods to cut down debt without raising some additional loan/debt to cover up the present liability, which many companies do and finally lands into a debt trap as what we call.
- The company focuses on its resources in assets to cover up its pending liabilities. Thus there is no scope of any third party or external funding required. The entire debt structuring takes place based on the company's potential.
- The prime advantage of deleveraging in economy is that it helps reduce the risk, i.e., voluntary deleveraging, and helps avoid bankruptcy when financial circumstances are as such.
- When a company is involved in paying a huge penalty, deleveraging it is considered the best option because it sells off its assets, shrinks its holding size, and shores its cash reserve, which allows it to at least at once survive in the market rather than getting shut down.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages of deleveraging process are as follows:
- An increasing systemic corporate deleveraging can bring about the credit crunch and financial recession.
- It means turning down many potential gains that could have been utilized earlier in more profitable ventures.
- The process brings about layoffs, departmental shutdowns, and shrinkage of budgets which is not good from a practical point of view.
- It impacts a company's share prices, even for a short period but greatly.
- Corporate deleveraging always does not go as planned because companies, in selling their assets, give them away at throwaway rates to cover up their debt.
- Creditors get late or fewer payments over an extended period or at a lower interest rate.
Deleveraging Vs Leveraging
- The former is the process of paying off the debt and other liabilities whereas leveraging is the process of acquiring or borrowing money.
- The purpose of the former is to reducing financial risk from owning short and long term liabilities and the purpose of the latter is to raise money for financing the operations.
- The former is done through paying off the debts by accumulating cash or sale of assets, whereas the latter is done through borrowing from banks, financial institutions, or raising capital through issue of bonds or debentures.

