Table of Contents
What Is A Debtor Ledger?
A debtor ledger is a financial record that has information on individual trade debtors of the business. They are debtors or customers who have recovered goods kept for sale on credit. Individual trade debtors can be individuals, firms or even institutions.
It reflects the actual current liabilities for transactions by defaulting on the date of the present date. The ledger account records the sales made under the debit column, credits the payments received and returns inward. The internal control of organizations uses the total individual debtor's ledger and compares it with a total debtor ledger control account for verification of balances.
Key Takeaways
- A debtor ledger is an account or financial report that carries descriptions of the amount owed by trade debtors.
- They are a record of credit payments, sales transactions and credit returns. It is also known as the debtor's balance.
- It is used for understanding the accounts receivable of the company and for the internal control team to verify accuracy.
- The process typically involves small steps, and it includes recording of invoices, recording in debtor and general ledgers, sending invoices to customers and updating of receipts paid in the debtor and general ledgers.
Debtor Ledger Explained
A debtor ledger is a ledger that contains all transactions of individual trade debtors engaged in the business. Trade debtors can be firms, institutions or individuals who acquire goods and services kept for sale on credit. The ledger shows a detailed summary of all debtors' transactions in the business. It is a record of all sales transactions, credit payments and returns that are received from the debtor or made to them in the past. All these details are gathered to understand the balance a debtor owes. In other words, it is also known as the debtor's balance.
The ledger can be termed as a financial report that gives the interested parties a summary of all accounts with outstanding balances in a comprehensive manner. It is prepared by collecting all receipts from the business's debtors and is accounted for in a cash book. These receipts are later posted to the ledger of debtors. The cash book typically contains accounts of cash received from cash sales and debtors that will be deposited in the banks. Similarly, the statement of account debtor's ledger contains all transactions pertaining to the debtor's adjustments, invoices, receipts and reversals.
In essence, the debtor ledger account typically involves few processes.
- Recording the invoices of sales made.
- Recording invoices the keep track of balances in both the debtors and general ledger.
- Sending the customers the invoices either physically or through mail.
- Update the receipts when outstanding debtors make payments. This will revise the balances in the debtor and general ledgers.
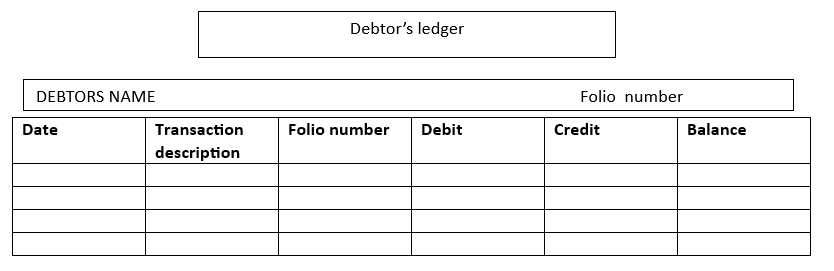
Format
Given below is a general format of a debtor ledger account.
Examples
Let us look into examples that help us understand the concept better:
Example 1# - A Hypothetical Example of an Accountant
Suppose Dan works as an accountant for ABC Ltd, a cloth manufacturing firm. Let us look at the process he goes through while recording in the ledger of debtors. His recording sessions typically involve 5 steps:
- Recording sales invoices: Dan receives invoices from the sales department and records them. This may include details such as the customer's name, date, invoice number, quantity, amount and discounts, if any.
- Updating the balances in general and debtor ledgers: The accounts receivable balances are recorded in the ledger of debtors. It is basically a record of how much a customer owes to the business and is estimated through the sales invoices. Similarly, the received amount is recorded in the general ledger to update the balances as a reflection of the amounts received.
- Sending invoices to customers: After posting the invoices, Dan physically prints them and sends them to the customers or mails electronic copies of the same. Through this step, he makes sure the customers are aware of the amount owed.
- Update payments made: Once the customers make payments to eliminate the debt owed, he processes the debtor receipts. He records the payment details, which may include the customer's name, amount, and quantity paid for, payment made, invoice number etc. He also simultaneously records updates in the general ledger. He may, as a final step, print the updated receipts for the customers.
Example #2
Given below is the debit ledger of Sunlight industries. Let us calculate the amount they owe at the end of the month.
| Date | Transaction description | Folio number | Debit | Credit | Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| March 1 | Opening balance | B/D | - | - | $1100 |
| March 5 | Invoice 1 | A1 | $500 | - | $1600 |
| March 9 | Invoice 5 | B3 | $2000 | - | $3600 |
| March 15 | Invoice 7 | C3 | - | $1500 | |
| March 20 | Invoice 9 | A1 | $1200 | - | |
| March 30 | Invoice 50 | C3 | - | $500 |
Solution:
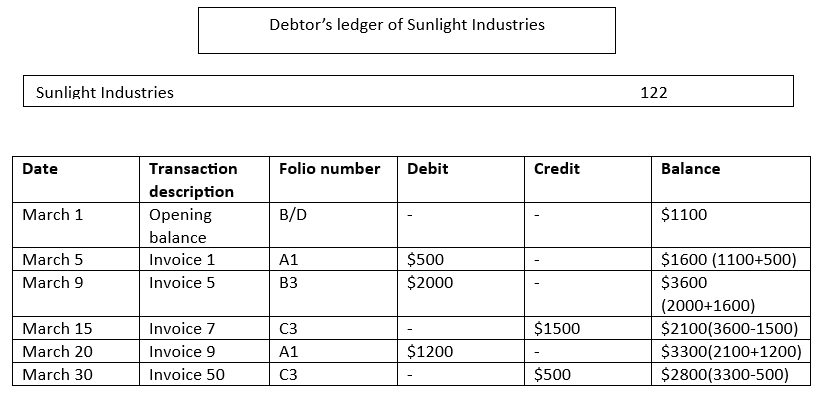
Here, the amounts in the debit columns are added, and credit amounts are subtracted. This is because debit amounts are owed to the business, and credit is subtracted as they decrease the amount owed. Accordingly, the amount owed by Sunlight Industries at the end of the month is $2800.

