Table Of Contents
Debt To Income Ratio Definition
The Debt to Income (DTI) ratio measures the ability of an individual or entity to pay back their debt or installments easily without any financial struggle. It is expressed as the ratio of the monthly debts people need to pay to the gross income they make every month.
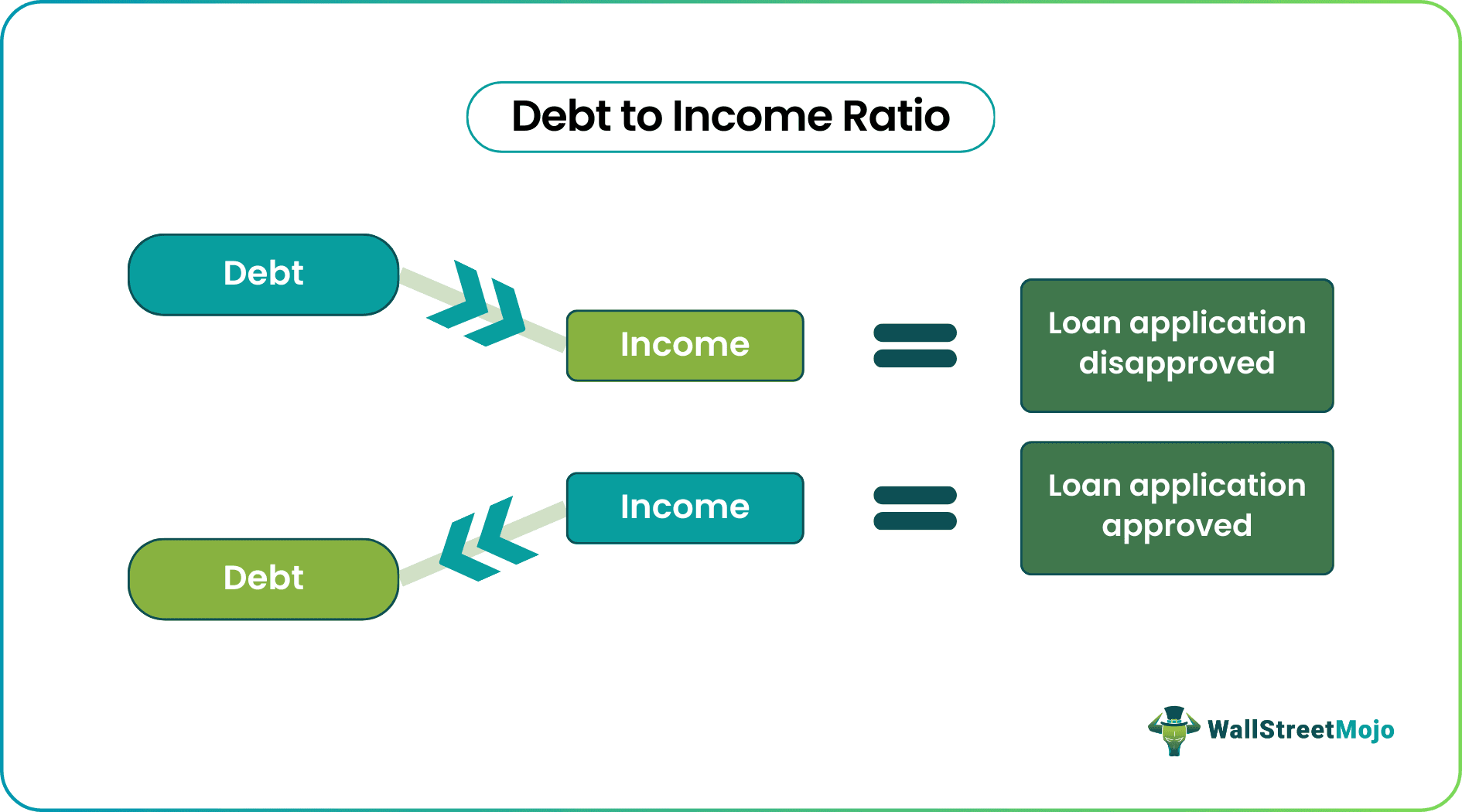
A good balance between the debts to handle and the gross income assesses a borrower's ability to make loan repayments. The DTI ratio is a key factor for lenders to consider before approving a mortgage loan application. If the debt to income ratio calculation results in a lower figure, it assures lenders of receiving timely installments from the borrowers.
Key Takeaways
- The debt to income (DTI) ratio specifies the portion of the gross monthly income dedicated to borrowers' financial obligations.
- DTI ratio is a key factor that lenders calculate to assess how capable a borrower is of repaying the loan easily.
- The front-end ratio (monthly financial liabilities) and back-end ratio (recurring payments including front-end liabilities) are the two types of DTI ratios.
- Maintaining a good DTI ratio balance is a must for borrowers to get their further loan applications approved without much struggle.
Debt To Income Ratio Explained
A debt to income (DTI) ratio is obtained when the monthly dues, debts, and liabilities are divided by the gross monthly income of an individual or organization. The market lenders use the resulting figure as a parameter to judge if they should approve or disapprove a loan application.
If the ratio obtained is higher than expected, the banks and financial institutions do not agree to offer finances in such a scenario. A higher DTI ratio indicates the debts and liabilities are considerably higher, and another loan would be difficult to manage for a borrower. On the other hand, when the debt to income ratio for mortgage is low, lenders know they will receive payments on time.
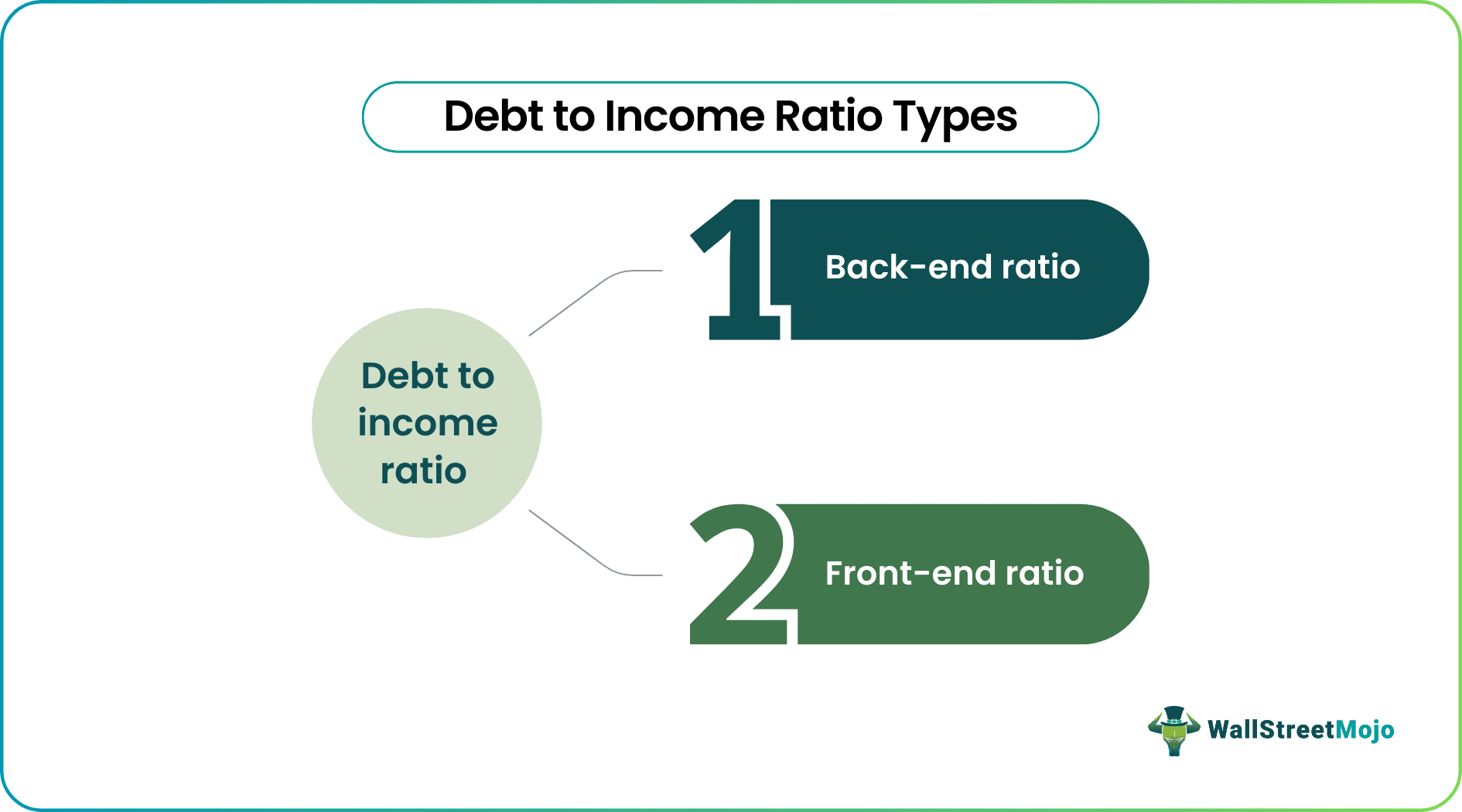
The DTI ratios are of two kinds - front-end ratios and back-end ratios. The front-end ratios include the portion of the gross monthly income used for repaying mortgage installments, rent, property taxes, insurance, etc. On the contrary, the back-end ratios mark all recurring payments that borrowers are liable to pay, including those under the front-end ratios category.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Revenue vs Income Explained in Video
Uses
When borrowers apply for a loan of any kind, the first thing that lenders check is the DTI ratio. Maintaining a good debt to income ratio balance is a must as it builds their trustworthiness. As a result, the lenders approve their loan applications as and when they apply. For example, if the DTI ratio is 10%, it implies that the borrower pays that percentage of the gross monthly income for debts and other liabilities.
Normally, lenders approve loan applications with a DTI ratio of 43% to the maximum. However, borrowers must keep this percentage as low as possible for lenders to trust their ability to repay on time.
DTI Ratio Formula
The debt to income ratio formula is as follows:
DTI = (Total monthly debt payments)/(Gross Monthly Income)
Where,
- The total monthly debt payments include the sum of all the financial obligations borrowers have for a month.
- The gross monthly income is the total earnings of the borrowers for a month.
Debt to Income Ratio Calculation
Let us explore the following DTI ratio example below to understand the concept and calculation:
David applies for a credit card for smaller purchases. The credit card company asks him to provide his proof of income. It finds that David earns around $10,000 per month. Thus, the company calculates the ratio to check if it fulfills the company's repayment terms.
The company also asks for details about the other debts that David has to pay. It comes to know that the credit card seeker has a mortgage loan of $2,000 and a car loan of $1,000 to pay every month. Based on the information, it calculates the DTI ratio:
DTI = (Total monthly debt payments)/(Gross Monthly Income)
= (2000 + 1000) / (1000) = 3000/1000 = 30%
David's credit card application gets approved as he fulfills the company's repayment terms.
How To Improve DTI Ratio?
The DTI ratio calculation considers all financial obligations equally, irrespective of the factors influencing repayment behaviors. For example, the repayment terms for student loans and credit card payments are different. The former is available at lower interest rates, while the latter is at a higher interest rate. However, they are all considered equal while making DTI ratio calculations.
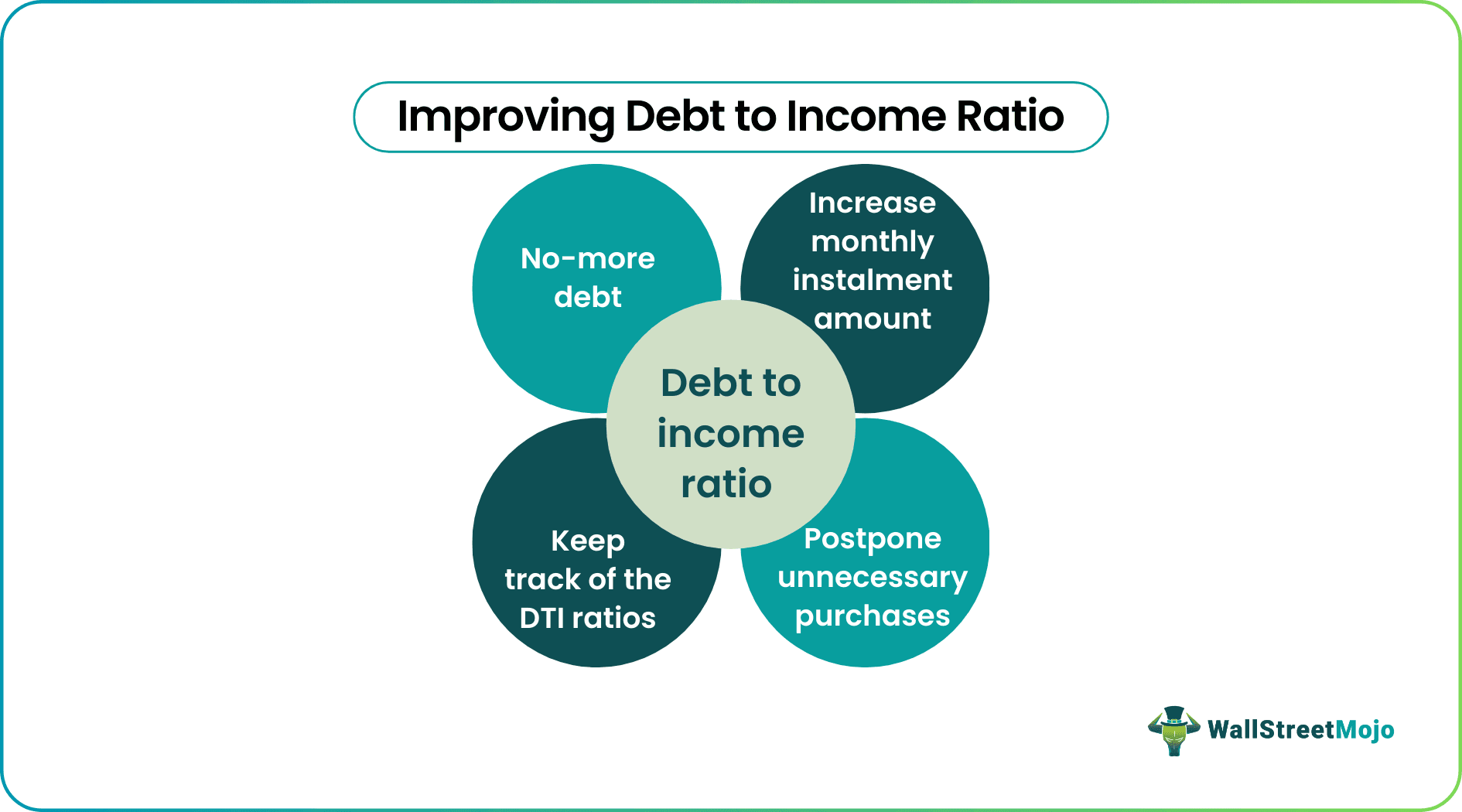
Thus, borrowers should maintain proper repayment behavior. In addition, it lets lenders trust them for approval of their future loan applications. It, in turn, will keep their DTI ratio balanced. Let us look at some of the ways of improving the DTI ratio:
- The borrowers should avoid purchasing unnecessary products. Spending unnecessarily increases their financial obligation, restricting them from delaying buying the required things.
- Borrowers can increase their monthly installment amount for their loans. It might seem to raise the DTI ratio for that period but will greatly help in the long run as the DTI ratio gets reduced to a significant extent.
- Try not to involve in too many loans or financial obligations.
- Keep monitoring the DTI ratios every month and track if the finances are handled well. If the output is unsatisfactory, implement relevant measures to take control of the situation.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

