Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
- The debt to GDP ratio determines an economy's financial leverage, or its capacity to repay its debt, by comparing a nation's debt to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- A nation with a high ratio would struggle to pay back its debt and wouldn't need debt from its lenders because the likelihood of default is higher.
- The government utilizes this ratio for economic and financial planning. In addition, it allows investors in government bonds to compare debt levels between countries.
- While an economy is steady and growing, each nation establishes its place in trade and investments. They are in a terrible position on the global market with a bigger percentage. They also begin to lose their marketability on the international stage.
What is the Debt to GDP Ratio?
The debt to GDP ratio is a metric used to compare a country's debt to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and measures the economy's financial leverage, i.e., its capability to repay its debt. A country with a high ratio would have difficulty repaying its debt and would not seek debt from its lenders, as there are higher chances of it defaulting.

The debt to GDP ratio is an important parameter for the government to assess the country’s stand in international trade. Every country marks its place in trade and investments when it has a stable and developing economy.
Debt To GDP Ratio Explained
The debt to GDP ratio is the ratio that compares the debt an economy records against its GDP. Having a higher percentage places them poorly in the international market, and they start losing their scope in the global market. Such economies start providing goods and services at a lower cost, making it even more difficult to cope with their debt (for example, Greece).
However, such is not always true for countries like the USA, Japan, Germany, etc. They are strong economies and show growth year on year. Therefore, we must look at such a financial matrix and do trend analysis to understand it.
A country with a high debt to GDP ratio will boost its economy and growth and need heavy finances. But, due to a high percentage, it is often unable to raise money from domestic and international markets. Therefore, the countries try to lower their ratio, but it is not an overnight change, and a few years pass by to reduce the rate.
The unrest in this ratio is often seen during an economic recession, wartime, or other lending practices of the nation. It is expressed as a percentage. But can do further dimensional analysis to calculate how one can repay the number of years' debt.
According to the IMF, in 2019, Japan's debt to GDP ratio was 234.18%, the highest, followed by Greece at 181.78% and Sudan at 176.02%. The United States was at 109.45%, France at 96.2%, the United Kingdom at 85.92%, India at 67.29%, and China at 54.44%.
As per the records from IMF, below is the graph that shows the debt to GDP Ratio for a few countries for 2018 and 2019.

Video Explanation of GDP vs GNP
Formula
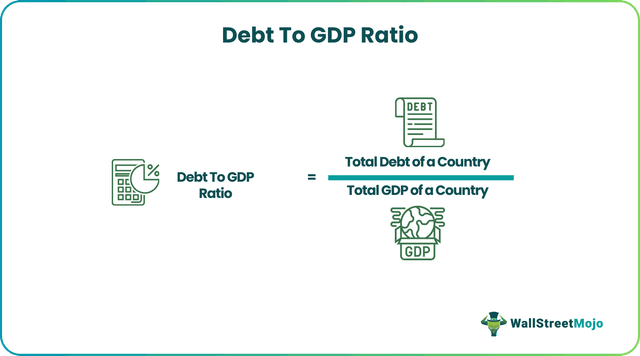
Given below is the formula to calculate the debt to GDP ratio: -
Debt to GDP Ratio = Total Debt of a Country/Total GDP of a Country
Calculation Example
Below are some simple examples to understand this concept in a better manner.
We want to calculate the debt to GDP ratio for five countries (hypothetically). For this, we would need their total debt and total GDP.
Calculation of Debt to GDP Ratio of Country A

- =50/75
- =66.67%
Similarly, we can calculate for the remaining countries.

As we can see, country B has the highest GDP, which means it may have difficulty repaying its debts. It is often assumed that countries with a ratio above 100% have a chance of default, which is not true. In the above example, we can understand that country Z can repay 78.26% of the total debt
How to Use?
To understand the debt to GDP ratio meaning more clearly, it is important to know how it is used.
The government uses this ratio for economic and financial planning. For example, with a high debt-to-GDP percentage, the government may often push more money into the economy by printing new currency notes, issuing foreign currency instruments, providing low-interest rates to banks and insurance sectors, and bringing new opportunities for its public. In addition, it allows investors in government bonds to compare debt levels between countries.
A study conducted by the World Bank found that if the debt-to-GDP ratio exceeds 77% for a long period, it slows economic growth by 1.7% for every percentage point of debt above this level. Moreover, the growth rate will decline by 2% for each additional percentage of debt above 64% for growing economies.
How To Reduce?
There are two ways in which the debt to GDP ratio can be reduced:
- Minimizing budget deficit figures
- Increasing the size of the economy
The government tries to take control of the budget deficit by converting it into a budget surplus by keeping the expenditure less than the revenue generated through taxes. However, it does so, while ensuring the growth of the economy is not negatively affected. This is because if reducing the budget deficit triggers a recession, it would become counterproductive.
Thus, the government must be careful while determining how much to do to reduce the ratio should be made.
Advantages
- It allows investors to compare debt levels between countries before they invest in bonds issued by governments.
- It helps governments and economists to understand the trend and pattern of fall in the economy. This helps them find a solution to get out of it.
Disadvantages
- The ratio, to an extent, gives a brief idea about the performance of an economy. However, due to the vast data, it is not possible to get accurate details regarding debt and GDP.
- One cannot solely compare countries based on the debt to equity ratio. Every country is different in terms of its size and population. Government policies, inflation rate, etc. They should also consider other factors to have an equal base for comparison before investing in the stock market..