Table Of Contents
What Is A Cyclical Industry?
Cyclical industries are those industries whose performance cycle is highly correlated and sensitive to the economic cycles; these companies grow when the economy is in the growth or expansion stage and decline when there is a recession or depression in the economy, for instance, automobiles, aviation, construction are few examples of cyclical industries.
Processing and identifying different business cycles and anticipating the upcoming help an investor make an appropriate decision. A thorough understanding of cyclical industries enables us to optimize different economic phases for monetary yield. On the contrary, non-cyclical industries also play a crucial role in a portfolio; a smart investor should keep the optimum balance to get the best of both worlds.
Cyclical Industry Explained
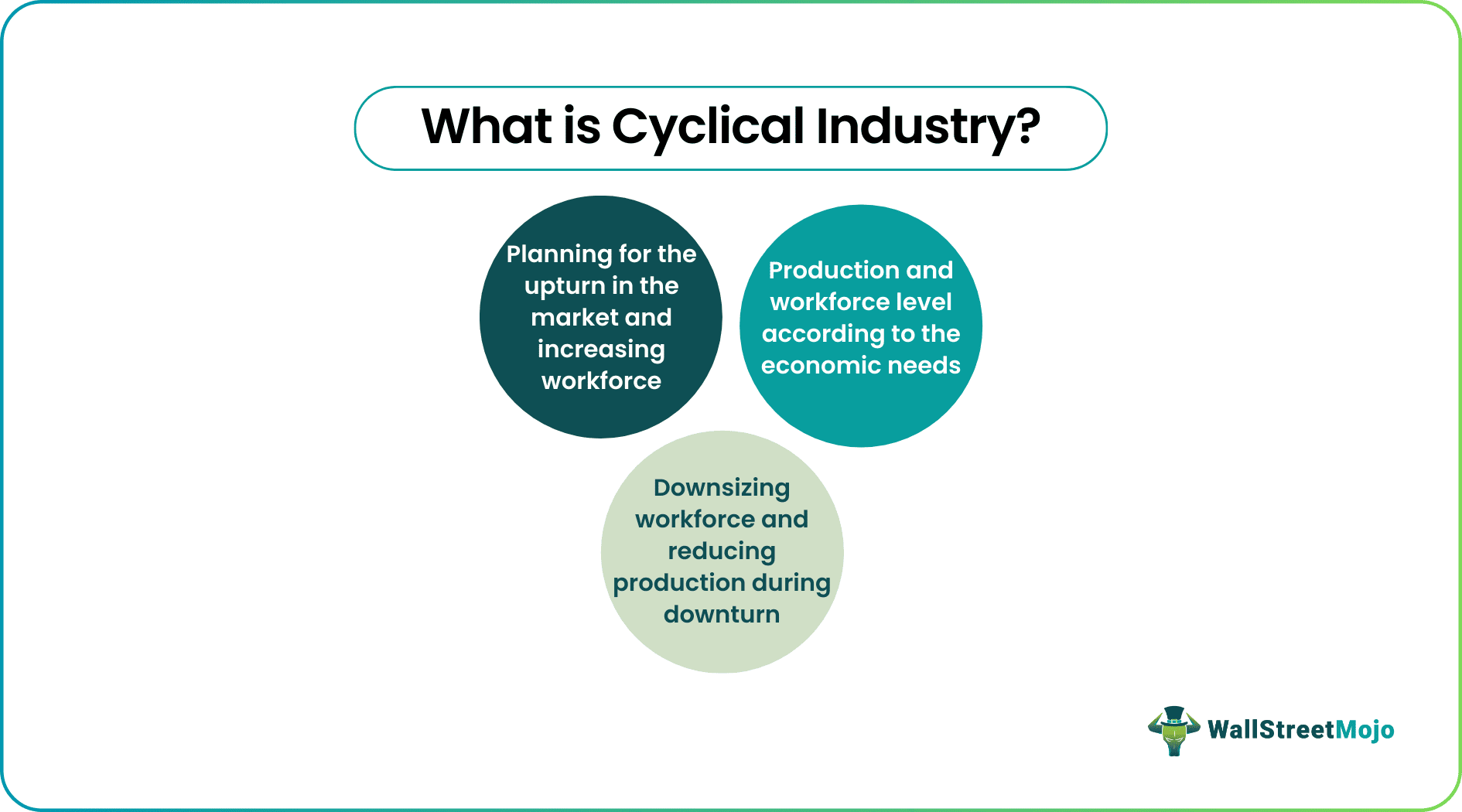
A cyclical industry is a company whose operations and profitability directly relate to the market's push and pull. It is a common feature that these industries produce non-essential products or services that consumers purchase less during an economic decline period. An organization that produces essentials or are unaffected by economic state of their markets is referred to as non cyclical industry.
Cyclical industries however, plan extensively to ensure they survive economic downturns. Since the volatility in the market is beyond the control of the management of the organization, they tackle such situations by reducing production, workforce, and raw materials.
Nevertheless, in the situation of economic growth, these industries increase their workforce, purchase excess raw materials to meet the requirements, and increase their production. Moreover, the salaries and wages of their employees are often increased to motivate them to produce more.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Classification
Standard and Poors (S&P) is a renowned USA stock market index that measures the performance of 500 large companies, basically classifying these stocks into ten sectors as listed below. But, first, let's discuss the classification of the cyclical industry for a better understanding; we will classify these sectors into cyclical and non-cyclical sectors.
Cyclical Sectors
- Energy
- Financials
- Health Care
- Industrials
- Information Technology
- Materials
- Telecommunication Services
Non-Cyclical Sectors
- Consumer Discretionary
- Consumer Staples
Factors Affecting Cyclical Industry
The following are the factors affecting the cyclical industry.

#1 - Total National Output (GDP)
- Cyclical businesses are legitimately affected by the economy’s general execution, estimated by the GDP, an estimation of monetary yield.
- The ascent in GDP shows that the economy is developing, prompting a higher work rate and, along these lines, higher extra cash, driving individuals to expand their spending for different purposes. It likewise demonstrates an ascent in government spending on the foundation and unified exercises.
#2 - Shopper Spending Levels
- It affects the repeating business and its stocks. It can be checked by following COI (Consumer Confidence Index), which gives knowledge on how much individuals are sparing when contrasted with the amount they are spending and the general feeling administering the market. It quantifies how idealistic or cynical buyers are about the economy's present and future exhibition. A consumer cyclical industry closely looks at these factors.
- When the file is high, purchasers are relied upon to expand their spending on products and services. When the record is low, a decline in spending is normal. Along these lines, the loads of repeating enterprises head southwards. That is why loads of organizations like Tata Motors, Omega, LG, and Indian Hotels normally observe a flood when the economy performs well.
#3 - Interest Rates
- Interest rates are the global indicator to see the economic stability of any country; while it is the lending and borrowing rate benchmark, cyclical stocks are highly affected due to the fluctuation in these rates.
- If the interest rates are higher, it means that the economy is expanding and consumers have a high purchasing power, so to control the spending central bank keeps the rate high; accordingly, if the interest rates are low, the government tries to inject liquidity in the market to regain the economy.
#4 - Inflation
- Inflation is one of the crucial indicators of the economy; it is the increase in the prices of overall goods and services over a certain period.
- For instance, a normal pizza in 2009 would cost you $8, but the same pizza in 2019 would cost around $12, the rise in the currency's value is because of inflation.
- Higher inflation is bad for the economy, and cyclical stocks may dip at this stage, whereas low inflation signals a healthy sign helping cyclical stocks surge.
Cyclical Industry Video Explanation
Indicators
The cyclical industry has three major indicators through which one can measure if the stocks are performing well or not; let us discuss these indicators of a cyclical industry.

#1 - Purchasing Managers Index
- It is a month-to-month study directed by privately owned businesses or exchange affiliations (ex. Markit) among the obtaining supervisors of privately-owned companies in a specific nation.
- This review intends to decide rapidly whether there has been an improvement in the business movement or not. These pointers permit us to distinguish the monetary cycle and, in this manner, help the investor in his choice.
#2 - Index of Industrial Production
- This index depicts the growth rates in various industries in the economy within a certain period.
- It will guide the investor to assess the performance of stocks industry-wise to make an informed decision.
#3 - Consumer Price Index
- This indicator shows the prices of goods and services, allowing the investor to know the current economic phase like inflation, deflation, or stagflation.
Examples
Let us understand the concept better with the help of a couple of examples.
Example #1
ABC Motors is a car manufacturer based out of Detroit. They get contracts from the largest automobile companies to manufacture their cars for them. Since the automobile industry is a largely cyclical industry, ABC motors have most of its employees on the factory floor on a daily wage basis.
This way, it is easier to downsize their workforce during an economic downturn. Moreover, It is also easier to increase their workforce and achieve high production levels through bonuses and incentives during an economic growth phase.
Example #2
The airline industry is one of the most cyclical industries in the market. Barring frequent flyers, families, and tourists do not prefer purchasing pricy tickets to travel when the economy is not doing particularly well.
However, in 2023, the demand for the airline industry reached its pre-pandemic highs. This theory can be confirmed by the development and growth of the economy in the three years post-pandemic.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Performance Drivers
Aspects that drive cyclical stocks performance and price are listed below:
#1 - Beta of Stock
- The first is the Beta coefficient or systematic risk. The beta coefficient is the statistical measure of the stock sensitivity vs. the market. Cyclicals will, in general, have a high beta, which is typically higher than 1.
- A beta of 1.5 implies that if the market falls 10 %, the stock will probably fall 15 percent. On the contrary, non-cyclical stocks have a comparatively low beta, which indicates that these stocks are less affected by the rise or fall of the market.
#2 - Earnings Per Share (EPS)
- The EPS refers to the income an organization makes from its actions post every one of its costs. The EPS are firmly connected to the incomes of an organization. To be sure, the higher your income, the higher are your EPS expected to be.
- Cyclical stocks tend to have very volatile earnings per share or EPS compared to non-cyclical stocks, as their earnings keep on fluctuating about the sentiment in the economy.
#3 - Price-Earnings Ratio (PE Ratio)
- The PE proportion is one of the most regularly utilized by speculators in the market. It thinks about the cost of the stock to its EPS (Price/EPS).
- If a stock is 12, it implies that the financial investor is paying multiple times of EPS to purchase the stock (expecting that the EPS stays equivalent). This proportion is generally used to decide the expensiveness of the stock.
- Generally, as per historical trends, cyclical stocks tend to have a lower PE than non-cyclical stocks. Since non-cyclical stocks guard against the downturn in the economy, they tend to charge a premium.

