Table Of Contents
What is Current Yield of Bond?
The current yield of a bond calculates the rate of return on a bond by using the market price of the bond instead of its face value. It is calculated as the annual coupon payment divided by the current market price. The current yield is an accurate measure of bond yield as it reflects the market sentiment and investor expectations from the bond in terms of return.

It is essential to keep in mind that the current yield is a primary metric and doesn't consider factors like changes in interest rates or the bond's maturity. Investors should also assess other metrics to make informed investment decisions. For instance, the yield to maturity provides a more comprehensive picture, considering all relevant factors for a bond held until maturity.
Key Takeaways
- The current yield of a bond is a measure of its return based on the annual interest payments relative to its current market price. It is calculated by dividing the bond's annual coupon payment by its current market price.
- Current yield gives investors an estimate of the income a bond generates about its price. It helps assess the bond's cash flow potential and can be compared to the yields of other investment options.
- Current yield is influenced by both the bond's coupon rate and its market price.
- Current yield is a simple measure that does not consider the time value of money or the bond's future cash flows, such as the return of principal at maturity.
Current Yield of Bond Explained
The Current yield of a bond's relevance can be seen in the evaluation of multiple bonds of the same risk & maturity. The coupon rate of a bond usually remains the same; however, the changes in interest rate markets encourage investors to constantly change their required rate of return (Current yield). As a result, bond prices fluctuate, and prices increase/decrease as per the required rate of return of the investors.
The current yield of a discount bond is greater than the annual coupon rate because of the inverse relationship that exists between the yield of a bond and its market price. Similarly, the yield on a premium bond is lower than its annual coupon rate and equal for a par bond. The reason why current yield fluctuates and deviates from the annual coupon rate is because of the changes in interest rate market dynamics based on Inflation expectations of the investors.
Current yield, when used with other measures such as YTM, Yield to the first call, etc. helps the investor in making a well-informed investment decision.
Video Explanation of Current Yield of a Bond
Formula
Let us understand the formula that shall act as a basis for our understanding of the current yield of a bond calculator through the discussion below.
Current Yield of Bond Formula = Annual Coupon Payment / Current Market Price
How To Calculate?
Calculating the current yield of a bond is an essential skill for investors looking to assess the potential returns on their fixed-income investments. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the current yield:
- Current yield is a simple measure of a bond's return, comparing the annual interest payment to the bond's market price.
- Find the bond's current market price, which you can obtain from financial news sources or your broker.
- Determine the bond's annual interest payment, also known as the coupon payment.
- Divide the annual interest payment by the bond's current market price.
- Current Yield = (Annual Interest Payment / Bond's Market Price) x 100
- The current yield is expressed as a percentage, representing the bond's yield based on its current market value.
Examples
Now that we understand the basics, formula, and how to calculate using the current yield of a bond calculator, let us apply the theoretical knowledge to practical application through the examples below.
Example #1
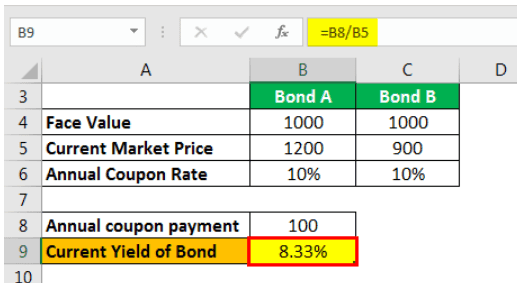
Suppose there are two Bonds. Bond A & B. The details are as follows:
| Particulars | Bond A | Bond B |
|---|---|---|
| Face Value | 1000 | 1000 |
| Current Market Price | 1200 | 900 |
| Annual Coupon Rate | 10% | 10% |
The current yield of A & B Bond will be calculated as follows:
For Bond A
Step 1: Calculate Annual coupon payment

- Face value * Annual coupon rate
- 1000 * 10%
- = 100
Step 2: Calculate Current Yield

- = Annual coupon payment / Current market price
- = 100 / 1200

- = 8.33%
For Bond B
Step 1: Calculate Annual coupon payment

- = Face value * Annual coupon rate
- = 1000 * 10%
- = 100
Step 2: Calculate Current Yield

- = Annual coupon payment / Current market price
- = 100 / 900
- = 11.11%
Example #2
Let us now analyze how current yield differs under various scenarios for a bond.
| Particulars | Discount Bond | Premium bond | Par bond |
|---|---|---|---|
| Face Value | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Current market price | 950 | 1050 | 1000 |
| Annual coupon rate | 10% | 10% | 10% |
| Annual coupon payment | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Scenario #1: Discount Bond
Suppose the Bond is trading at a discount, meaning the current market price is lesser than the face value.

In this case, the current yield will be;

- = Annual coupon payment / Current market price
- = 100/ 950
- = 10.53%
Scenario #2: Premium bond
Suppose B is trading at a premium, meaning the current market price is greater than the face value.

In this case, the current yield on a Premium bond will be;

- = Annual coupon payment / Current market price
- = 100/ 1200
- = 9.52%
Scenario #3: Par bond
Here the current market price is equal to the face value.

In this case, the current yield on a par bond will be;

- = Annual coupon payment / Current market price
- = 100/ 1000
- = 10%
The above relationship can be understood in the below table:

A well-informed investor relies on various types of calculations to better analyze the multiple investment opportunities and decide which opportunity to pursue. Some of the calculations that are relevant for the bond market are Yield to maturity, Current Yield, Yield to the first call, etc.
Example #3
Suppose an investor wants to invest in the Bond market and shortlists two bonds according to his risk tolerance. Both bonds have the same level of risk & maturity. Based on the details provided below, which bond should the investor consider investing in?
| Bond | Annual coupon payment | Face value | Current market price |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC | 100 | 1000 | 1500 |
| XYZ | 100 | 1000 | 1200 |
Let us calculate the current yield of both bonds to determine which one is a good investment
For ABC

- = Annual coupon payment / Current market price
- = 100/ 1500
- =6.66%
For XYZ

- = Annual coupon payment / Current market price
- = 100/ 1200
- = 8.33%
Well, clearly, it is the Bond with a higher yield that attracts the investor, as it gives a higher return on Investment. Therefore, Investors will select bond XYZ for investment, as it offers a higher current yield of 8.33% as compared to 6.66% offered by ABC.
Relevance and Use
- One of the essential uses of the Current Yield is to identify the yield of a bond that reflects the market sentiment. As the current yield is calculated based on current market prices, it is said to be the accurate measure of yield and reflects the true market sentiment.
- The Investor who wants to make an effective investment decision would rely on the current yield to make a well-informed decision. Suppose an investor is considering investing and finds Bond A & B. The bond with higher is more attractive to the investor.
- It is considered to be a dynamic and fundamentally accurate measure as it keeps on changing as per the inflation expectations of the investors, as opposed to the coupon rate that stays constant over the period of the bond.
- It is always higher for a discount bond, as investors demand a higher yield for the amount of risk they are taking by investing in it.
Current Yield of a Bond Vs Yield to Maturity
Distinguishing between the current yield of a bond and the yield to maturity is crucial for investors seeking a comprehensive understanding of their bond investments. Below is a detailed comparison of both these metrics.
Current Yield of a Bond
- Current yield is a straightforward measure of a bond's return and is calculated by dividing the annual interest payment by the bond's current market price.
- It provides a snapshot of the bond's yield based on its current market value.
- It's expressed as a percentage and offers a quick assessment of the income generated by the bond.
- Current yield does not consider the bond's price fluctuations, time to maturity, or reinvestment of coupon payments.
- It is handy for investors looking to gauge the short-term income potential of a bond.
Yield to Maturity
- Yield to maturity is a more comprehensive measure that considers the bond's total return if held until maturity.
- It factors in the bond's current market price, coupon payments, and the difference between the purchase price and the face value of the bond.
- YTM accounts for the effects of price changes, the reinvestment of coupon payments, and the time value of money.
- It provides a more accurate reflection of the bond's overall profitability, taking into account both income and capital gains or losses.
- YTM is essential for investors with a long-term investment horizon, as it reflects the bond's potential return over the entire holding period.