Table Of Contents
What Are Crypto Futures?
Crypto futures are derivatives contracts that allow users to trade a crypto token at a predetermined price and date. The primary purpose of this futures contract is to provide exposure to price movements and gain profit from it.
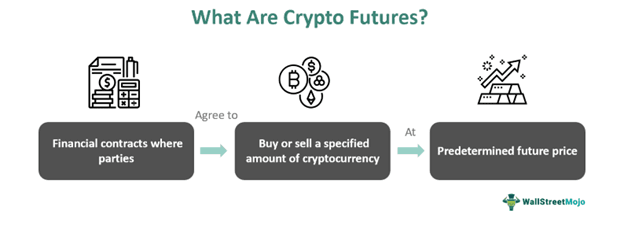
It provides a platform to trade cryptocurrencies without owning them. Users deploy different crypto futures signals to predict (speculate) price movements of the tokens. Thus, they easily hedge the price instability and volatility and earn yield in return. However, an equal risk of liquidation is associated with these futures.
Key Takeaways
- Crypto futures are derivative contracts that allow traders to take positions and profit from the price movements without owning the crypto tokens.
- Bitcoin futures were the first futures launched on the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) but were discontinued later.
- These contracts are executed at a fixed price and date; therefore, they have no expiry. However, settlement is possible as physical delivery (in coins) or cash (usually in dollars).
- Traders must maintain a certain margin amount as collateral in the account. Also, they can leverage their position to gain more exposure by 5x, 25x, 50x, or more.
Crypto Futures Explained
Crypto futures trading is a popular derivatives instrument akin to commodity or asset futures. It provides users with enough exposure to the different cryptocurrencies. As a result, investors speculate on these tokens' prices and make gains. Thus, the volatility of these tokens is not compromised. However, these futures do have an expiration date. For example, Kraken, Bybit, eToro, FTX, and CME are among the best crypto futures trading platforms.
Every crypto futures contract has three significant components: expiry date, units or contract size, and leverage. They operate on a regulated exchange where parties decide on their positions (long and short). If a person feels the token will rise, they prefer an extended position. In short, they buy at a low price and sell at a high price. Likewise, expecting a fall in price will lead to a short position. However, single units are not traded here. Every platform involves a defined contract size that differs across exchanges. For instance, one Bitcoin futures contract in CME consists of five coins. In contrast, the Deribit platform insists on a contract size of 0.004 BTC.
Traders must open an account first to initiate future trading. Later, they deposit a margin amount that makes them own a larger portion of the contract with a small investment. Once a user feels they have the potential to double their gains, they can develop a crypto futures strategy. Plus, they can also leverage their position on their exchange. Users can borrow additional capital from exchanges or other traders to enhance their position. Some leverage rates include 5x, 10x, 25x, 50x, and even more. However, there is an equal chance of loss with this leverage if the price moves in the opposite direction. Therefore, the use of the right crypto futures signals is significantly essential.
For those exploring both crypto and stock investments with a user-friendly interface, eToro provides a unified platform. Some investors prefer platforms it for combining social trading with crypto exposure.
How To Trade?
These futures were first launched by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) in 2017 but were discontinued later. However, many platforms now provide this facility so traders can trade them:
- Set Up An Account With A Broker - The first step to start with Futures is to sign up on the exchange and choose to create an account with them. Usually, the registration process involves email, password, or mobile number. Once registered, users can scroll and select Futures.
- Fund The Wallet - After opening the account, the next step is to deposit tokens in the wallet with respective fiat currency (dollars) or crypto coins. In short, if it is a Bitcoin futures contract, they must deposit BTC, USD, or any other coin, depending on the platform's protocols.
- Choose The Position - Traders can eventually decide on the type of position they wish to take. For example, if people expect Bitcoin to rise, they can long for their position. But before that, they must decide on the contract size and deposit the amount to the wallet. However, they can add more capital if they anticipate the bitcoin prices to rise in this process. It will double the profit chances for the trader.
- Monitor The Account - If a trader entered the position with $10,000 and the price rose to $25,000, it means the trader booked a profit of $15000. However, if the Bitcoin price is $8000, it will result in a considerable loss. As a result, the trader can put a stop-loss that will execute the contract if it touches a specific price.
- Select Settlement Type - On expiry or execution, there are two ways to settle future contracts. Traders can take physical delivery of coins or settle in cash. As a result, in cash settlement, there is no transfer of cryptocurrency, but it happens in USD ($).
Traders looking for lower fees and detailed analytics often explore platforms, such as Coinbase that offer an “advanced” mode with professional-grade features.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to comprehend the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose John is a trader who has operated in the crypto market for three years. However, in a few months, the price of Bitcoin fluctuates, which is a profitable situation for him. As a result, he decides to enter into a futures contract. So, John chose the Binance platform to execute this form of trading. He logs into his Binance account and opens the futures chart. Next, he deposits $1000 as a margin for 1BTC and opts for a long position, as he expects the price to move ahead. Thus, the total sum or worth of futures was $50000 (with the current price as $50,000).
Akin to his expectation, the price touched $60,000 in the later weeks. As a result, he earned a profit of $10,000. But this incentivizes him to leverage more. So, he deposited 5x the amount until the price reached expiration. To maintain this leverage, he added more money to his margin account. But, at expiry, the BTC price fell to $55000. Therefore, he could only make a profit of $5000, which was settled in dollars.
Example #2
As of August 2023, the popular crypto trading platform Coinbase won approval for operating crypto futures on their exchange. The National Futures Association (NFA) approved their request, which was filed two years back. However, this news surged the stock price by 3% ($81.55). Coinbase's approval to offer cryptocurrency futures represents a pivotal moment for the company, marking its expansion into a largely untapped market segment and reaffirming its commitment to regulatory compliance and innovation in the cryptocurrency industry.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Crypto futures allow users to trade hassle-free but have certain downsides. Let us look at them:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| It is easy and convenient to trade as it provides access to the liquid market. | The trader must keep the margin if it falls below the minimum requirement. |
| These trades can occur without holding any coin. | The option of leverage can magnify or multiply the losses. It doubles the risk of liquidation. |
| Traders can leverage the prices of crypto tokens and profit. | The ownership of coins only stays with the trader after expiry. |
| They can speculate the future prices and hedge the price difference. | |
| Traders can deploy their crypto futures strategy without much hassle. They can use stop-and-loss orders to mitigate their risks. |
Crypto Futures vs Crypto Options vs Crypto Spot
Although crypto futures options are a part of the derivative trading, the crypto spot varies. They have different characteristics. So, let us look at them:
| Basis | Crypto Futures | Crypto Options | Crypto Spot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It allows users to trade crypto tokens at a predetermined price and time. | Crypto options are derivative contracts where traders have the right to buy or sell the crypto token but are not compelled (obligated) to do so. | Unlike futures contracts, these trades enable traders to settle crypto transactions on the spot. |
| Purpose | To take advantage of the price movements and make gains. | Its purpose is to reduce the loss risk associated with the expiration. | It allows parties to make transactions on the current market price. |
| Types | It includes standard futures contracts, physical delivery, and perpetual contracts. | The options are call (right to buy) and put (right to sell). | It consists of crypto exchanges and over-the-counter (OTC) trading. |
| Expiry date | It has a fixed expiry date and is decided in advance. | These options can expire before (American options) or on maturity (European options). | They expire on the same day when executed. |
| Ownership | There is no ownership of tokens available. | Here, the parties have total control of their tokens. | Traders own crypto assets in spot trading. |
| Additional requirements | Users must maintain an amount as a margin or collateral in future accounts. | Buyers are likely to pay a premium or initial fee. | There is no margin or premium required for this trading. |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.