Table Of Contents
Crowdsourcing Meaning
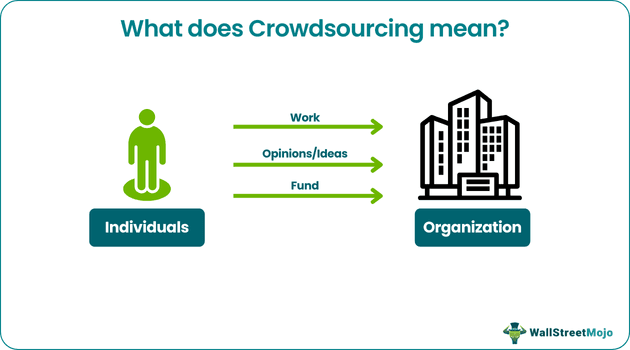
Crowdsourcing refers to the practice of soliciting ideas, contributions, or services from a large group of people, typically via an online platform. Crowdsourcing aims to leverage a group of individuals' or organizations' collective knowledge, skills, and resources to accomplish a specific task or goal.
Crowdsourcing enables individuals and organizations to harness the collective power of the crowd to accomplish tasks more efficiently while also providing freelancers, gig workers, and part-time professionals with opportunities to showcase their skills, gain experience, and grow their careers. In addition, this collaborative approach can foster innovation, drive progress, and create value for contributors and beneficiaries.
Key Takeaways
- Crowdsourcing refers to distributing work, obtaining information, receiving suggestions, and collecting funds from a group of people.
- Websites, apps, and social media are excellent platforms for crowdsourcing talents and ideas.
- Crowdsourcing is a great way for individuals to contribute to higher causes or make extra income by spending time on other projects. At the same time, organizations benefit from the ability to hire people without making them regular employees
- Google's use of crowdsourcing is a prime example of the practice.
Crowdsourcing Explained
Crowdsourcing platforms have gained immense popularity in recent years. As the term suggests, these platforms bring together individuals from different or similar backgrounds for a common purpose. The nature of the task or project requirements determines the type of individuals required for the job.
The digital era of the 21st century has led to the rise of crowdsourcing websites. With people seeking multiple sources of income, crowdsourcing platforms have become a preferred option for individuals to offer their experience and expertise. One of the significant advantages of crowdsourcing is the flexibility it offers. Individuals can work from the comfort of their homes, with flexible deadlines and timings, making it an ideal option for those seeking work-life balance.
For companies, crowdsourcing offers a cost-effective solution. They do not have to keep additional labor on their payroll and can only benefit from the individuals' expertise when required. Moreover, companies can also crowdsource from their target audience, bringing them closer to their customers and increasing brand loyalty. Crowdsourcing is especially beneficial in product or service pre-launch. It provides valuable feedback from the target audience, enabling companies to make necessary changes and improvements before launching the product or service in the market.
Types
Now, let's classify crowdsourcing.
- Crowdfunding – In this type of crowdsourcing, a group of people contributes a small amount towards a large funding project with commercial or charitable purposes. This is usually done via the Internet, and often the participants do not even know each other or the host personally but only know the goal/ project. The individual or company hosting the project will present their case with facts, videos, and testimonials. Example: A crowdfunding project with a target of $10,000 to increase the book count in the public library of City X.
- Crowd Voting – In crowd voting, a group is chosen to select the winners in a competition. Also, crowd voting can be used to understand the demographics of the sample population or identify their preferences in platforms where people can vote. This is especially helpful in surveys and market research. Example: Do you prefer online shopping? (Yes, No, Can't say)
- Crowd Wisdom – This model believes in the wisdom and potential of the crowd to offer solutions and observations concerning certain business processes and products or services. This can be considered a focus group that companies use in studying market behavior. Example: What do you think about product Y of our company, price, positioning, functionality, etc., and what changes do you propose?
- Crowd Jobbing/Creation – This method is known by different terms in different sources. But the essence of this method is that people from the same profession or background complete a task, typically outsourced from a company. This helps the company to finish its tasks faster and receive inputs from multiple participants. Example: Company Z crowdsources 50 content creators to develop a mass social media campaign on its biggest sale of the year.
Examples
Refer to the following examples to understand crowdsourcing better.
Example #1
One of the best examples of the concept is Google crowdsourcing. The platform by Google enables people to answer certain questions, identify web content, and read charts that will help the search engine to develop artificial intelligence abilities. This machine learning can be extended to Google Translate, Search, Maps, etc. Anyone with a Google account can contribute to this initiative from anywhere.
Example #2
Let's study the example of a recent Fortune survey involving 347 companies in 45 countries and around 6 million employees. The pandemic has changed the paradigm of work. With the complete dependence of businesses and organizations on the Internet, 'talent' has become an important factor.
Ninety-one percent of the respondents in the survey have prioritized 'new and diverse talent models' that include crowdsourcing, project-based staffing, gig cadres, etc. Such models are considered future-of-work initiatives that carry huge advantages for the company. However, only 7% indicated it was on their organization's agenda.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Here's a comparative study of the pros and cons of crowdsourcing.
#1 - Advantages
- The wisdom and talent of the crowd improve quality.
- Faster task accomplishment with a larger group.
- Higher reachability and engagement.
- Understand the preferences and behavior of diverse populations.
- Build customer loyalty.
#2 - Disadvantages
- The trust factor is a big issue.
- Personal bias leading to skewed results cannot be ruled out.
- The probability that the task or project comes out with net zero results exists.
- The group selected might not have the best minds and talents.
Crowdsourcing vs Crowdfunding vs Outsourcing
- Crowdfunding is a type of crowdsourcing where people contribute money to a cause rather than ideas, opinions, services, etc.
- Outsourcing means hiring people outside the organization to complete certain tasks at a lower cost and faster pace.
- In crowdsourcing and outsourcing, companies can expand the talent pool without hiring employees and paying them monthly salaries with other benefits.
- In crowdfunding, money flows from the people to the project or organization. In crowdsourcing (other than crowdfunding) and outsourcing, money flows from the latter to the former.
- When organizations outsource, they do so to get additional labor for faster task completion. But crowdsourcing can be for labor, ideas, observations, suggestions, and preferences.

