Table Of Contents
What is Cross-Border Payments?
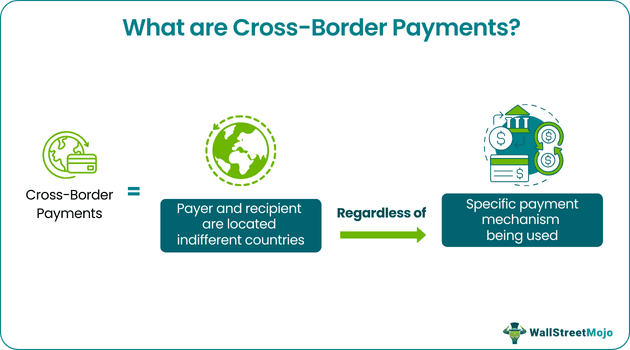
Cross-border payments refer to the movement of funds or execution of financial transactions between individuals, businesses, or financial entities in two different nations. Such transfers are initiated through a channelized system and supported by banks or other financial institutions in sender and recipient countries.
International transactions or payments involve different currencies and are essential for global trade, investments, remittances, travel and tourism, or any other financial activity that requires transferring funds from one nation to another. The process often includes currency conversion, adherence to international regulations, and intervention of banks, payment processors, or digital platforms.
Key Takeaways
- Cross-border payments send funds by individuals and firms from one country to another via a bank, financial intermediary, or a third party.
- The various methods of such payments are international wire transfers, cryptocurrencies, credit and debit card payments, international payment platforms, electronic funds transfers, and international money orders.
- It facilitates global trade, foreign investment, foreign remittance, abroad tours, and other international financial activities.
- Cross-border transfers are often expensive, time-consuming, and risky. Also, such exchanges are performed under regulatory compliance and involve currency exchange.
How Do Cross-Border Payments Work?
Cross-border payments are financial transactions between individuals or entities in different countries. Such transactions occur in international trade, foreign investments, cross-border remittances, and travel. However, understanding potential fees, exchange rates, and processing times is crucial when making cross-border payments. The emergence of fintech services has led to innovations in this area, offering faster, more transparent, and often more cost-effective cross-border payment options for individuals and businesses.
Let us now have a look at the basic steps involved in the cross-border payment process flow:
- Initiation: The sender (payer) begins the payment process, providing the necessary details, like the recipient's information, the amount, and the purpose of the payment.
- Bank or Payment Service: The sender's bank or a specialized payment service handles the transfer. International payment systems like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) are often employed to establish communication between the sender's and recipient's banks.
- Currency Conversion: If the sender and recipient use different currencies, the payment needs to be converted into the recipient country's currency at the prevailing exchange rate, which may include fees or a margin.
- Intermediary Banks: In some cases, the transactions are processed through intermediaries that facilitate the transfer across borders, potentially increasing the processing time and cost.
- Recipient's Bank: The recipient's bank receives the funds, converts the currency if needed, and credits the recipient's account. They might deduct fees associated with obtaining such cross-border payments.
- Processing Time and Fees: The entire process can take several business days, depending on the banks, payment systems, and the complexity of the transfer. Fees can vary based on the institutions involved, the amount transferred, and the urgency of the transfer.
Types
Below are the multiple ways the payer can send money to a payee from a different country through cross-border payments.
- International Wire Transfers: Such payments involve transferring funds from one bank account in a specific country to another in a different country.
- International Payment Platforms: Utilizing digital payment platforms and services like PayPal, TransferWise (now Wise), and others facilitate international money transfers to individuals or businesses located in other countries. This mode is appropriate for transferring small amounts and has low transfer charges and exchange rates.
- Card Transactions: International credit and debit cards are globally recognized payment methods used by customers who purchase foreign products to make payments in different currencies. However, banks apply certain currency conversion fee charges on such transfers.
- Cryptocurrencies: The decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Ethereum to immediately make payments for international retail transactions. It is a widely accepted payment mode by many retailers worldwide. However, some countries still need to recognize it as a legal tender.
- International Money Orders: It is an old-school method suitable for small transactions whereby the payer buys an international money order from the bank or other financial institution by depositing money and sending it through mail or via a third party to the payee in another nation.
- Electronic Funds Transfers (EFTs): E-checks or electronic bank transfers are digital payment modes that allow sending money from one bank account to another. In contrast, both banks are located in different nations. It is one of the fastest, easiest, and hassle-free modes of cross-border payments.
Examples
Let us understand cross-border payments through the following hypothetical and real-world examples.
Example #1
Consider a craft business based in the US. A customer from France wants to purchase goods. An online payment platform is used to streamline the process, allowing the customer to pay in Euros while the business receives US Dollars. The platform manages currency conversion and ensures secure transactions. Following the payment receipt, the products are shipped to France. This case illustrates how cross-border payments aid global sales by handling currencies and providing a seamless experience for all parties involved.
Example #2
Through a strategic partnership with Cashfree Payments, a prominent payments and API banking company in India, Tazapay strengthens its ability to offer streamlined cross-border payment solutions to Indian exporters. This collaboration empowers Tazapay to establish a frictionless platform, facilitating hassle-free international transactions for Indian exporters.
This collaboration has the additional advantage of expediting cross-border payment settlements for Indian exporters. Tazapay can now efficiently transfer funds to the local bank accounts of Indian exporters in Indian rupees within a single day, a notable improvement from the previous process, which often took 2-3 weeks and required multiple follow-ups.
Benefits
Imagining globalization in the absence of cross-border payments is difficult. Such transfers are inevitable for individuals and businesses engaged in international financial transactions. Cross-border payments have various advantages, which are as follows:
- Facilitates Global Trade: Cross-border payments are crucial in international trade, enabling businesses to exchange goods and services across national boundaries.
- Boosts Economic Growth: These transactions contribute to economic growth by granting countries access to foreign markets and the ability to attract foreign investments.
- Enhances Financial Inclusion: International payments can help foster financial inclusion by linking individuals and businesses in less advanced or underdeveloped regions to the broader global economy.
- Encourages Diversification: Businesses can diversify their customer base, reducing dependence on domestic markets and mitigating risks while fostering stability.
- Drives Innovation: Cross-border payment solutions often contribute to fintech development and innovation, developing improved technologies and services.
- Initiates Remittances: Many people working in foreign nations rely on such payments to send remittances for financial support to their family members in their home towns or countries.
- Competitive Advantage: Efficient management of cross-border payments gives firms a competitive edge in the international marketplace.
- Access to Global Resources: Cross-border payment systems aid the companies to avail global resources such as raw materials or specialized services that may not be available domestically.
- Promotes Cultural Exchange: International payments encourage cultural exchange and collaboration between countries, fostering a better understanding of diverse cultures and societies.
Challenges
Cross-border payments involve banks or other financial institutions and currencies of different nations. Hence, it encounters the following obstacles:
- Complexity: The intricacies of managing diverse currencies, adhering to various regulations, and navigating different financial systems complicate cross-border payments.
- Costly Affair: Elevated fees, exchange rate fluctuations, and involvement of intermediary banks contribute to the high cost of international transactions for individuals and enterprises.
- Delays: These transactions often experience prolonged processing due to intermediary entities, time zone disparities, and mandatory regulatory checks.
- Excessive Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations like anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) rules, posing a challenge to the parties engaged in the transaction.
- Fraud and Security Issues: The global nature of cross-border transactions exposes them to vulnerabilities such as fraud, cyberattacks, and security breaches, necessitating robust measures to safeguard sensitive financial information.
- Foreign Exchange Risk: The instability of exchange rates exposes participants to unanticipated foreign exchange risk, affecting the ultimate amount received or disbursed.
- Lacks Transparency: Tracking the progress of cross-border transactions can be challenging, resulting in uncertainties for both senders and recipients.
- Limited Accessibility: Certain regions may lack access to modern financial infrastructure and payment facilities, hampering their participation in cross-border transactions.
- Prone to Inefficiencies: Multiple financial intermediaries contribute to inefficiencies, raising costs and increasing the possibilities of errors.
Innovative solutions such as blockchain technology, fintech advancements, and enhanced international collaboration on financial regulations are undertaken by nations to tackle the drawbacks mentioned above of such payments.
