Table Of Contents
COUNTIF Not Blank Function
The COUNTIF not blank function counts non-blank cells within a range. The universal formula is “COUNTIF(range,"<>"&"")” or “COUNTIF(range,"<>")”. This formula works with numbers, text, and date values. It also works with the logical operators like “<,” “>,” “=,” and so on.
Note: Alternatively, the COUNTA function can be used to count the non-blank cells.
- The COUNTIF not blank function counts the non-blank cells within a given range.
- The generic formula of the COUNTIF not blank function is stated as–“COUNTIF (range,“<>”&””).”
- The criteria (condition) must be specified within a pair of inverted commas to avoid errors.
- The COUNTIF function works for data that consists of numbers, text, and date values.
- The COUNTIF formula gives the same output irrespective of whether the formula is entered in uppercase or lowercase.
How to Use COUNTIF Non-Blank Function?
#1–Numerical Values
The steps to count non-empty cells with the help of the COUNTIF function are listed as follows:
In Excel, enter the following data containing both, the data cells and the empty cells.

Enter the following formula to count the data cells.
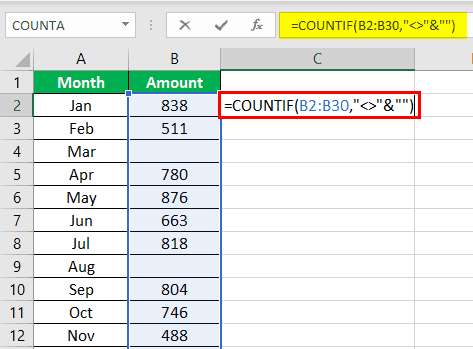
"=COUNTIF(range,"<>"&"")"
In the range argument, type B2:B30. Alternatively, select the range B2:B30 in the formula, as shown in the following image.
Press the “Enter” key. The number of non-blank cells in the range B2:B30 appear in cell C2. The output is 26, as shown in the succeeding image.
This implies that there are 26 cells in the given range that contain a data value. This data can be a number, text, or any other value.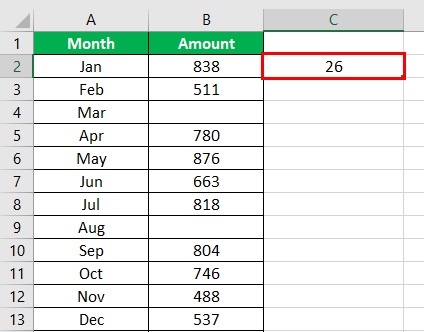
#2–Text Values
The steps to count non-empty cells within text values are listed as follows:
- Step 1: In Excel, enter the data as shown in the following image.
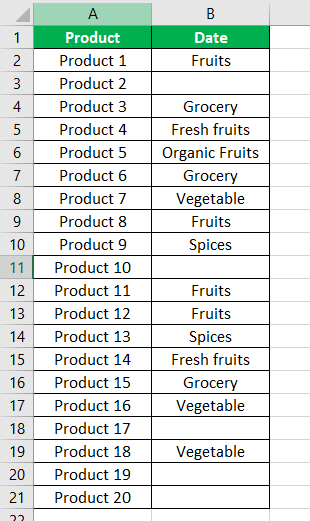
- Step 2: Select the range within which data needs to be checked for non-blank values. Enter the formula shown in the succeeding image.
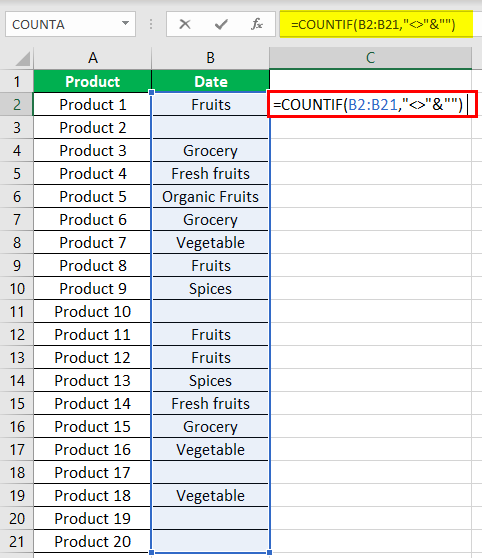
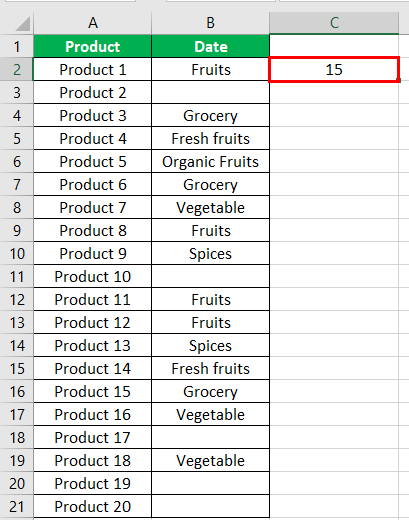
- Step 3: Press the “Enter” key. The number of non-blank cells in the range B2:B21 appear in cell C2. The output is 15, as shown in the succeeding image.
Hence, the COUNTIF not blank formula works with text values.
#3–Date Values
The steps to count non-empty cells, when the data consists of dates, are listed as follows:
- Step 1: In Excel, enter the data as shown in the following image. Select the range whose data needs to be checked for non-blank values. Enter the following formula.
“=COUNTIF(B2:B21,"<>"&"")”

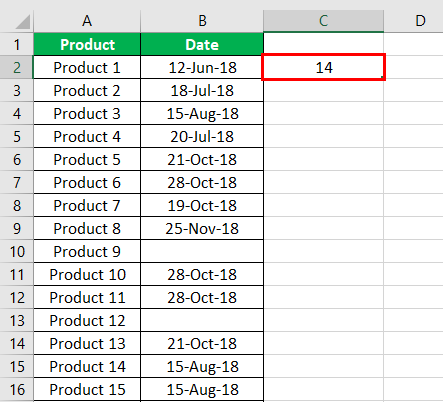
- Step 2: Press the “Enter” key. The number of non-blank cells in the range B2:B21 appear in cell C2. The output is 14, as shown in the succeeding image.
Hence, the COUNTIF not blank formula works with data that consists of date values. If your data is in another format, you can convert PDF to MS excel to easily manipulate and analyze the information using this formula.
Video Explanation of COUNTIF Function in Excel
The Characteristics of COUNTIF Not Blank Function
- It is case insensitive, implying that the output remains the same irrespective of whether the formula is entered in uppercase or lowercase.
- It works for data that consists of numbers, text, and date values.
- It works with greater than (>) and less than (<) operators.
- It is difficult to use the formula with long strings.
- The criteria (condition) must be specified within a pair of inverted commas to avoid errors. If you're struggling with applying this function in spreadsheets, you might consider seeking Excel assignment help to better understand its usage.