Table Of Contents
What is Cost Per Unit?
Cost Per Unit can be defined as the amount of money spent by the company during a period for producing a single unit of a particular product or the services of the company, which considers two factors for its calculation, i.e., variable cost and the fixed cost and this number helps in determining the selling price of the product or services of the company.
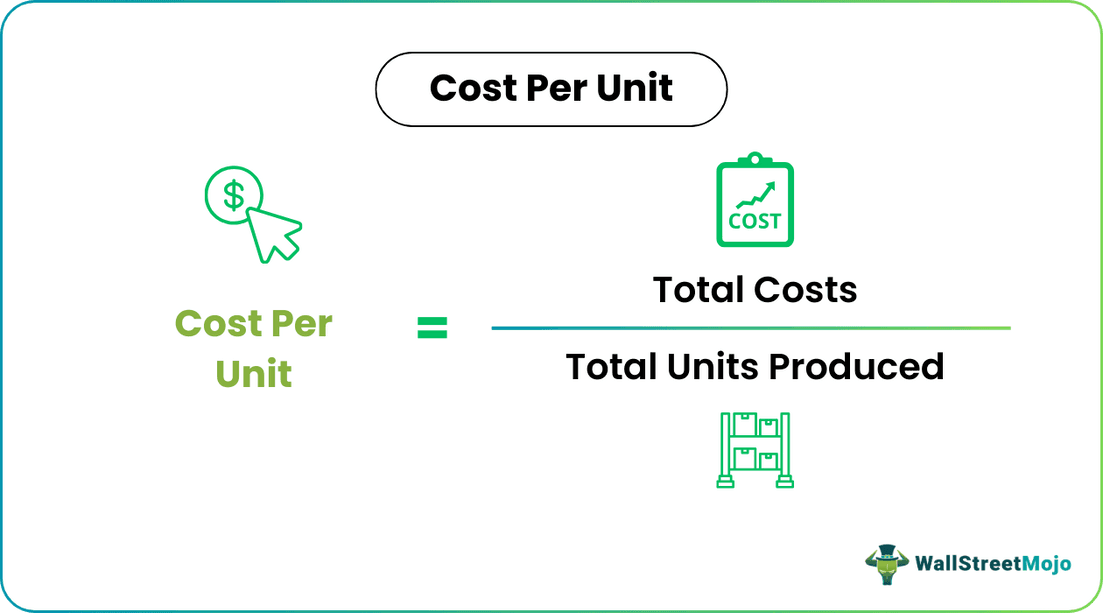
Cost per unit equation is a crucial metric in evaluating financial performance. It provides insights into the efficiency of production or service delivery. By dividing total costs by the number of units produced or services rendered, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about pricing strategies, cost control, and overall profitability. Monitoring cost per unit helps ensure competitiveness and sustainable financial health.
Cost Per Unit Explained
Cost per unit of a company helps measure the cost incurred to create or produce one unit of the product, and it is one of the crucial measures of cost for the company's operation. This accounting measure includes all the types of fixed cost and variable costs associated with the production of goods or provision of the services in the company. It is calculated by adding all the fixed costs related to the product, i.e., costs that do not change when the value of goods or the service produced is changed; and all the variable costs associated with the product, i.e., costs that vary when the value of goods or the service produced is altered and dividing the value with the total of units produced during that period.
Maintaining a vigilant eye on the cost per unit metric is paramount for businesses due to its far-reaching implications on financial health and competitiveness. First and foremost, it directly influences pricing strategies. When a company accurately calculates and manages its cost per unit, it can set competitive yet profitable prices for its products or services. This is vital for attracting customers and maintaining a strong market presence.
Furthermore, a cost per unit calculator serves as a critical indicator of operational efficiency. A consistently high cost per unit can signal inefficiencies in production or service delivery, possibly due to wastage, poor resource allocation, or outdated processes. By keeping this metric in check, a business can identify these inefficiencies and take corrective actions, which can lead to cost savings.
Formula
Let us understand the formula that acts as a basis for attaining an efficient cost per unit equation through the explanation below.
Cost Per Unit = (Total Fixed Cost + Total Variable Cost) / Total Number of the Units Produced
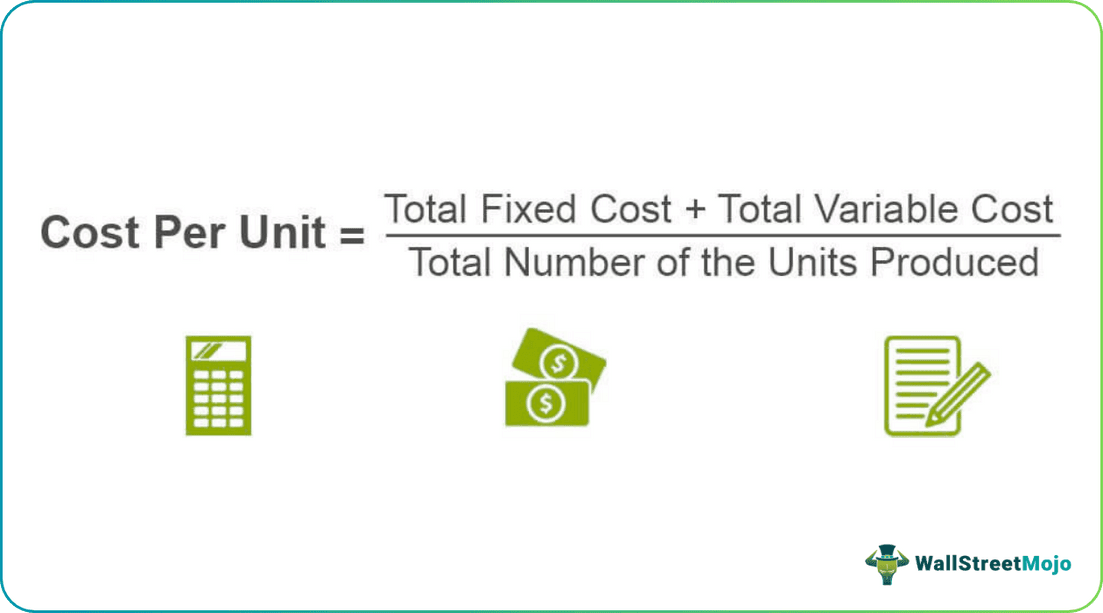
Where,
- Total Fixed Cost: Total of costs which does not change in the company when there is a change in the number or amount of goods or the service produced.
- Total Variable Cost: Total of costs that change in the company when there is a change in the number or amount of goods or the service produced
A total number of the units produced: Quantity of total units produced during a particular period.
How to Calculate?
Below is a step-by-step process on how to calculate using a cost per unit calculator.
- Firstly, the company should calculate the total amount of money spent on the fixed cost during the period by adding all the expenditures incurred on the fixed cost.
- After this, it should calculate the total amount of money spent on the variable cost during the period by adding all the expenditures incurred on the variable cost.
- Then, a value derived in step 1 should be added with the value calculated in step 2, i.e., the sum of total fixed and variable costs.
- After this total number of the units produced during that time is to be derived.
- Lastly, the sum of total fixed cost and total variable cost calculated in step 3 is to be divided by the total number of the units produced during the period as calculated in step 4 to get the figure.
Examples
Now that we understand the basics, formula, and how to calculate cost per unit equation, let us apply the theoretical knowledge to practical application through the examples below.
Example #1
Company A ltd incurred the following expenses during the one month.
Fixed Expenses
- Rent Expenses: $ 15,000
- Insurance expenses: $ 5,000
- Utilities expenses: $ 10,000
- Advertisement Expenses: $6,000
- Other fixed expenses: $ 7,000
Variable Expenses
- Material Expenses: $ 75,000.
- Labor Expenses: $55,000
- Other variable expenses: $ 27,000
During the month the company produced 10,000 units. Calculate Cost Per Unit.
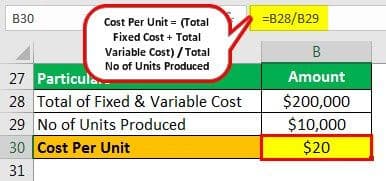
Calculation of Total Fixed Cost

=$15000+$5000+$10000+$6000+$7000
Total Fixed Cost = $43000Calculation of Total Variable Cost

=$75000+$55000+$27000
Total Variable Cost = $157000Total of Fixed Costs and Variable Cost

= $ 43,000 + $ 157,000
Total Fixed and Variable Cost = $ 200,000Calculation of cost per unit

= $ 200,000 / 10,000
=$ 20 per unit
Example #2
At the international conference on green energy in September 2023, India’s Union Minister for Power and New & Renewable Energy, Mr. R.K Singh said that the cost of round-the-clock renewable energy would reduce from Rs. 8 per unit to Rs. 6 per unit if green hydrogen could be used for storage.
The minister also went on to say that green hydrogen is cheaper than gas and battery storage systems and also declared that they have issued a bid for the pilot project of 100 MW. Therefore, the global problem of the availability of lithium-ion batteries would be solved as green hydrogen could be made and stored.
Given the fact that India already has 88,000 MW of renewable energy capacity and aims to add 50,000 MW of renewable energy every year, this project could not only reduce the cost per unit but also make it one of the most attractive hubs for manufacturing renewable energy.
Importance
Let us understand the importance of using a cost per unit calculator through the points below.
- It helps determine the selling price the company should charge to its customers. It is because generally, companies add up the percentage of the profits to derive the selling price.
- It also shows how efficiently the business is running along with providing a dynamic overview of relationships among different essential factors of the company, such as its costs, revenues, and profits.
- Therefore, identifying and analyzing the unit costs in the company is one of the quickest ways to know whether the company is producing its product efficiently or not.
Cost Per Unit Vs Price Per Unit
Let us understand the differences between a cost per unit equation and price per unit through the comparison below.
Cost per Unit
- Definition: Cost per unit represents the average expense incurred by a business to produce one unit of a product or provide one unit of service.
- Components: It includes both fixed and variable costs, such as labor, materials, overhead, and production expenses.
- Focus: Businesses monitor cost per unit to assess operational efficiency and control expenses.
- Purpose: It helps in setting appropriate pricing strategies to ensure profitability while covering costs.
- Impact: A higher cost per unit can erode profit margins, necessitating cost-cutting measures or price adjustments.
- Internal Measure: Typically used for internal decision-making and cost control.
Price per Unit
- Definition: Price per unit represents the amount a business charges customers for each unit of a product or service.
- Components: Determined by market forces, competition, and perceived value, it may not always align with cost per unit.
- Focus: Businesses monitor price per unit to remain competitive and maximize revenue.
- Purpose: It aids in revenue generation and market positioning.
- Impact: A well-calibrated price per unit can boost sales and market share, but setting it too low may lead to losses.
- External Measure: Primarily used for external stakeholders, including customers and investors, as it directly affects sales and profitability.