Table Of Contents
What Is Corporate Profit
Corporate profit or the profit after tax, is the income received from the business after deducting direct expenses (i.e., cost of materials, direct wages, etc.), Indirect expenses (i.e., salary, rent expenses, professional charges, electricity expenses, other expenses, etc.) and all the applicable taxes from the Total Income generated by the company (i.e., Revenue from the operation, interest income, rental income, other income, etc.) during the year.
It shows the financial condition of the company and is extensively used bu investors, analysts and various other stakeholders to asses whether investment is such an entity is profitable or not. The US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) publishes this data quarterly for the benefit of the investors.
Corporate Profit Explained
'Corporate Profit' in simpler terms is the Profit after Tax of a company for a particular financial period or year. Depending upon the requirements, it is calculated for a month, a quarter, half-yearly, or yearly. It shows the company's earnings over & above the expenditure incurred by the company during the given financial period. In case the earnings of the company fall short of the total expenditure incurred during the period, then that amount is termed a Corporate Loss.
Corporate profits over time is profit received by a company from its business. All organizations need to sustain the expenses of the business. A company can consider expanding the business if it earns a good profit. Suppose the company's revenue covers all the expenses related to a company's business. In that case, the company is in good condition and can continue its business. It can stand in the market in the long run.
The concepts of corporate profit and inflation is very important in this context. This income can be seriously affected by inflation in which the price level of goods and services rise. This increases the cost of raw materials, transportation etc and erode the income. On the other hand, the consumers purchase less due to reduction in their affordability. Thus the overall profit of the company comes down. The business is not able to survive the competition leading to fall in market share. So, it is important to understand both the concepts of corporate profit and inflation in this case.
Structure
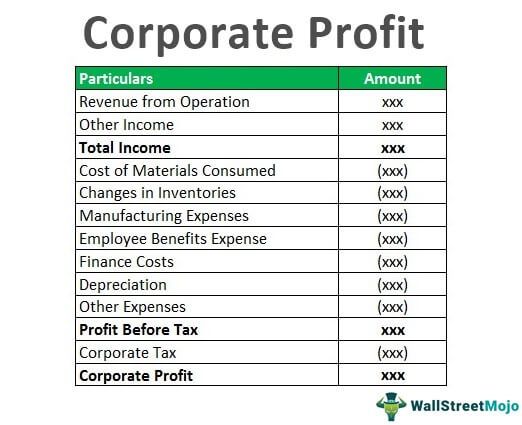
Let us understand the basic structure of this kind of profit as computed by any business.
| Particulars | Notes | For FY xxx |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue from Operations | - | |
| Other Income | - | |
| Total Income | - | |
| Expenses | - | |
| Cost of Materials Consumed | - | |
| Changes in Inventories of Finished goods, Work-in-progress and Stock in-trade | - | |
| Excise Duty on Sale of Goods | - | |
| Manufacturing Expenses | - | |
| Employee Benefits Expense | - | |
| Finance Costs | - | |
| Depreciation and Amortization Expense | - | |
| Other Expenses | - | |
| Total Expenses | - | |
| Profit / (loss) Before Tax | - | |
| Tax Expenses | ||
| Current Tax | - | |
| Deferred Tax | - | |
| Profit / Loss (Corporate Profit) | - |
How To Calculate?
The following are the steps of calculating the corporate profits over time.
- For calculation of profit, all the Journal Entries related to that period should be booked in the books of accounts & the ledgers should be updated. After doing the following step, the Trial Balance of the company will be considered final & the profit calculation will be done for the period based on the balances present in the trial balance.
- After the Finalization of the Trial Balance for the period, the ledgers mentioned in the trial balance are categorized according to the classifications, i.e., Revenue from an operation, direct expenses, indirect expenses, Taxes, Assets, liabilities, etc.
- After the classification, the revenue from the Operations & other incomes are calculated and are summarized accordingly. After doing so, the company's total income for that period is calculated.
- After the calculation of Total Revenue, the same step is followed to calculate the total expenditure. For the same, firstly, the Direct expenses are calculated, i.e., Direct material consumed, direct wages, etc. and after that, the Indirect Expenses are calculated, i.e., salary, rent expenses, finance cost, depreciation & the other expenses.
- After calculating Total Income & Total Expenditure, the difference between them is calculated. If the Total Income is greater than the Total Expenditure, the profit is termed 'Profit before Tax.'
- After the calculation of ‘Profit before Tax,’ the taxes are adjusted, and the resulting figure is termed ‘Profit after Tax’ or ‘Corporate Profit.’
Example
Let us go through some corporate profits examples to understand the concept.
ABC Ltd is a manufacturing company. The company's accountant is calculating profit for the period 31st Dec 2019. He is calculating profit by considering the following figures- Sales value – 3300 lac, other income is 65 lac, cost of material consumed- 1400 lac, change in inventory- (100) lac, manufacturing expenses- 1000 lac, employee benefit expenses- 400 lac, finance cost- 150 lac, depreciation- 100 lac, other expenses- 70 lac, current tax 65 lac, deferred tax- 50 lac. Calculate corporate profit-
Solution
The first step is for all the transactions to be entered into the system, and after that, all those transactions will be posted to the respective ledger; after posting in ledger all the ledgers will be summarized in the trial balance.
Then the accountant will extract the trial balance from the system. After extraction of trial balance grouping, he will do a grouping of all ledger like sales will be grouped in revenue from the operation, any income from interest will be grouped in other income, and so on. After these grouping, profit and loss will be prepared-
Calculation of Corporate Profit

- =345.00 - 115.00
- Profit =230.00
From the above corporate profits examples, the concept of this kind of profit is very clear.
Importance
The following are the importance of such a profit.
- Expansion - Earning profit in the business is one of the key reasons for which manufacturers, entrepreneurs, or owners start the business. Earning profit helps the organization to expand its business, even expanding the business globally.
- Cover Expenses - In the initial stage of the business, the company focuses on earning. It expects that earning at least can cover the Fixed expenditure and as much as possible covering the variable expenditure. Earning more than that is what is termed profit for the company.
- Hire more employees- Those excess corporate profit sharing help the company hire as many employees as the business needs. It also keeps the motivational value for the employees working in the organization.
- Get Funding - As the company's profit gets bigger, it becomes easy for the sanctioning of Loans or funds for the business from the financial institutions because they provide the funds based on the company's financials.
- Sustain Competition - Strong financials of a company helps the company to do the CSR (corporate social responsibility) work. In addition, it maintains its public image, which allows the company to maintain its position in the competitive market through corporate profit sharing.
Limitations
Let us look at the various limitations of this kind of profit.
- Inequality – Profits may benefit the shareholders and some executives but not everyone always. Employees may not always benefit from it if a part of the profit is not passed on to them in the form of compensation.
- Impact on environment – The environment may be impacted in a negative way because companies may induge in over consumption of resources, especially the non-renewable ones, or aim for ramping up production leading to emission of harmful gases or environmentally harmful waste materials.
- Lack of social responsibility – Organizations may aim for profits at the cost of sacrificing their social responsibilities to the society. They might lose their reputation in the process.
- Focus on short term gain – Companies may focus on short term profits.This may not be sustainable and may hinder the long term growth and expansion.
- Volatility – The fluctuations in the market may affect the prices of stocks and company performance. This will lead to a negative effect on the profits causing financial distress and instability.
It is important for every business to consider the limitations along with the benefits while using the profit figures to make any decisions. Companies should try to maintain ethical and sustainable corporate practices.
Corporate Profit Vs Wages
The following are the differences between corporate profit vs. wages.
Corporate Profit
Corporate profit, also called after-tax or net income, is calculated by deducting expenses from sales or revenue from the operation. Expenses include material expenses, manufacturing expenses, salary and wages, rent, depreciation, interest expenses. After deducting all these expenses, it comes to profit before tax; then, it needs to calculate corporate tax as per income tax law. After calculation of corporate tax, it deducts from profit before tax; then it comes corporate profit.
Wages
Wages are a manufacturing expense directly related to the manufacturing of a product. It is deducted from sales/revenue from operation while calculating corporate profit. It is a part of the profit calculation. Wages are the amount paid to workers.