Table of Contents
What Are Corporate Governance Best Practices?
Corporate governance best practices are a set of guidelines that direct the actions of a company's management and board so that they efficiently serve the best interests of stakeholders. These stakeholders comprise shareholders, investors, suppliers, creditors, senior management, government, and society.
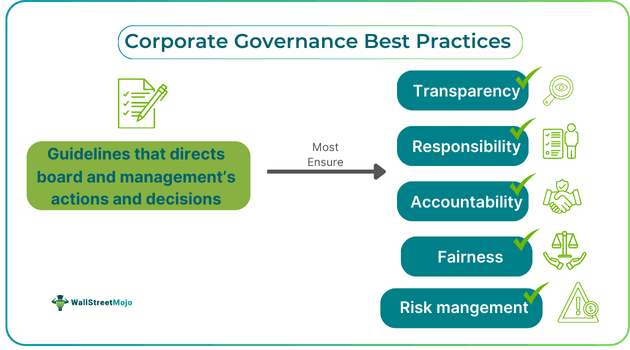
In other words, good governance practices emphasize shaping the decision-making process and actions so that the fundamental principles of corporate governance, i.e., transparency, fairness, accountability, responsibility, and risk management, are not compromised. Some of its fundamental aspects are diversifying and maintaining independence in boards, aligning executive compensation with performance, and safeguarding shareholder rights.
Key Takeaways
- Corporate governance best practices refer to the guidelines that facilitate ethical and effective corporate management while ensuring the best interests of stakeholders.
- These good governance practices incorporate the five principles of corporate governance into an organization's functioning: transparency, responsibility, accountability, fairness, and risk management.
- Some of these best practices include board diversity, board independence, legal and regulatory compliance, ethical conduct, sustainable approach, transparent disclosure of financial and non-financial affairs, and clear roles and responsibilities.
- Such practices pay off in the long run as they build brand reputation, shareholders' trust, customer confidence, and business ethics.
Corporate Governance Best Practices Explained
Corporate governance best practices have undergone a historical evolution, initially prioritizing shareholder protection and financial oversight. In the mid-20th century, the companies emphasized transparency. In 2002, reforms like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act were formed to safeguard investors from financial fraud and false reporting after the financial scandals, including Enron, WorldCom, and Tyco International PLC in the early 2000s. Further, the financial crisis in 2008 prompted the need for robust risk management systems in businesses. The International Corporate Governance Network (ICGN) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) have played pivotal roles in shaping global governance principles.
Hence, the current best practices fostering board independence, diversity, ethical conduct, and a commitment to social and environmental responsibility have been shaped over the years for prominent governance of corporations. Moreover, corporate governance is an ever-evolving subject for developing policies, codes, and practices that adapt to the changing business scenario. However, the corporate governance guidelines have a one-size-fits-all approach, which makes it irrelevant in diverse organizations. Also, it prioritizes board diversity, which is challenging to achieve and maintain in the real world. Indeed, small and medium-sized enterprises may need help to allocate sufficient resources for comprehensive governance practices. Further, the impact of current actions is visible in the long term.
The best practices for corporate governance are nurtured and developed in the long term. Before adopting good governance practices, the company must analyze its unique characteristics, such as size, structure, industry, and specific needs. Also, the board should take care of legal and regulatory compliance in this context. It is even better to involve the stakeholders to understand their expectations and concerns. Further, the management can assess the existing practices against the industry standards to identify areas for improvement. Notably, corporate governance principles must align with the firm's goals, values, and vision. Moreover, every organization is unique, and therefore, governance practices should be tailored to specific needs and business models while adhering to general guidelines.
List of Corporate Governance Best Practices
Good corporate governance requires constant implementation and improvement of the board's actions. Following are some of the prominent best practices that companies of all sizes and sectors should consider:
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities: State the roles and responsibilities of board members and executives clearly to ensure better accountability.
- Stakeholder engagement: Engage with and consider the interests of various stakeholders, including employees, customers, and the community.
- Transparency and disclosure: Provide clear and comprehensive information to stakeholders, fostering trust. Such disclosures should be in writing for better communication.
- Ethical conduct and accountability: Cultivate a corporate culture of integrity and ethical behavior led by top management.
- Risk management: Develop and implement effective strategies for identifying and mitigating risks.
- Board composition and diversity: Promote diversity in skills, backgrounds, and perspectives during board composition to ensure well-rounded decision-making.
- Board independence: Ensure a majority of directors are independent to uphold impartial decision-making.
- Regular and accurate reporting: Provide timely and accurate financial and non-financial information to stakeholders.
- Technology governance: Keep pace with technological advancements and establish effective technology governance.
- Effective communication: Emphasize transparent communication of the corporate affairs to the shareholders, investors, and other stakeholders.
- Fair Compensation: Ensure executive compensation aligns with company performance and shareholder interests.
- Independent audit committee: Maintain independence of the audit committee to enhance the credibility of financial analysis and reporting.
- Protection of shareholder rights: Safeguard and uphold shareholders' rights, enabling their active participation in critical decisions.
- Sustainability practices: Integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into business strategies.
- Compliance and legal obligations: Adhere to all applicable laws, regulations, and ethical standards in all disciplines of corporate governance.
- Aligned strategies with corporate goals: The companies should design and improve their governance practices to match their long-term goals.
Examples
Some examples to demonstrate a robust corporate governance system are as follows:
Example #1
Suppose the board of directors of XY Ltd. strictly adheres to the industry's best practices in corporate governance. Regular and transparent board meetings are held, ensuring collective decision-making while considering diverse perspectives. The company upholds a comprehensive Code of Ethics that fosters a culture of integrity and accountability across all levels of employees and leadership.
Emphasizing shareholder rights, XY Ltd. actively engages with investors by providing regular updates on the company's performance and strategic plans to maintain transparency. The board is composed of independent directors, ensuring impartiality and expertise in strategic discussions, which fosters a well-rounded decision-making process.
To reinforce accountability, the company conducts periodic audits and risk assessments, engaging an external auditing firm to ensure financial transparency. Additionally, XY Ltd. demonstrates a genuine commitment to sustainability through its sustainability reporting, integrating environmental and social considerations into its business strategy.
Example #2
In 2020, Ethisphere recognized General Motors (GM) as one of the World's Most Ethical Companies, standing out in the automotive sector for its strong commitment to ethical business practices. This acknowledgment is based on Ethisphere's Ethics Quotient® framework, which evaluates critical categories such as ethics and compliance, corporate citizenship, the culture of ethics, governance, and leadership.
Mary Barra, GM's CEO, emphasized the company's determination to lead the automotive industry with integrity, aiming for zero crashes, zero emissions, and zero congestion. GM has set ambitious sustainability goals, including sourcing 100% of its global electricity from renewable sources by 2040 and increasing the use of sustainable materials in its vehicles. Additionally, GM was included in the Bloomberg Gender Equality Index in January 2020.
Benefits
As more and more companies are going global, the urgency to adopt fair corporate governance practices has become a necessity for small businesses and large organizations. Discussed below are some of the critical advantages of adopting such ways:
- Better decision-making: Well-structured governance encourages informed and strategic decision-making by the board, leading to better organizational outcomes.
- Enhanced stakeholder trust: Adhering to best practices in corporate governance cultivates trust among stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees, fostering a positive and authentic reputation.
- Risk mitigation: Effective governance structures help identify and manage risks, reducing the likelihood of financial and operational setbacks.
- Access to capital: Companies with robust governance structures are often more appealing to investors, facilitating more accessible access to capital through equity or debt.
- Long-term succession planning: Robust governance structures facilitate smooth leadership transitions, ensuring the continuity and stability of the organization.
- Innovation and adaptability: Boards that embrace diverse perspectives and adapt to evolving business scenarios are better positioned to foster innovation and navigate change.
- Financial transparency: Transparency in financial reporting enhances credibility, attracting investors and maintaining stakeholders' confidence.
- Ethical business culture: Top management's commitment to ethical conduct sets the tone for the entire organization, promoting a culture of integrity.
- Effective communication: Clear communication channels between the board, management, and stakeholders help in disseminating information effectively, reducing the risk of misinformation.
- Customer confidence: Transparent and ethical business practices instill confidence in customers, leading to stronger brand loyalty.
- Global competitiveness: Companies that adhere to international governance standards enhance their competitiveness on a global scale.
- Brand reputation: Good governance contributes to a positive public image and builds the brand reputation, which is crucial for long-term success.
