Table Of Contents
Corporate Finance Definition
Corporate finance refers to planning, developing and controlling the capital structure of a business. It aims to increase organizational value and profit through optimal decisions on investments, finances as well as dividends. It focusses on capital investments aimed at meeting the funding requirements of a business to attain a favorable capital structure.
Key Takeaways
- Corporate finance is the process of obtaining and managing finances in order to optimize a company's growth and value for its shareholders.
- The concept focusses on investment, financing and dividend principle.
- The main functional areas are capital budgeting, capital structure, working capital management and dividend decisions. For example, judging whether to invest in debt or equity as a medium to raise funds for the business.
- Going over the risk-return aspect of investment alternatives, ensuring working capital management, etc. are some aspects of this branch of finance.
Corporate Finance Explained in Video
How Does Corporate Finance Work?
Corporate finance emphasizes the desire to maximize the financial soundness of a company and its stockholders. The departments working under this branch of finance primarily manage a company’s financial activities. They take crucial decisions regarding organizational budgeting, investments, and capital allocation.
For example, in a real estate investments company, the department computes capital requirements to acquire assets. They will also focus on finding efficient sources of capital for asset acquisition using appropriate calculations. Such decisions determine an organisation's capital structure, i.e., whether to finance by debt or equity or a combination of the two. Another aspect of this segment includes ensuring optimal working capital management.
Decisions around how much profit to retain or distribute amongst the shareholders are also an important element. All these essential decisions have the underlying tone of ensuring profit maximization. Hence, corporate finance jobs are in huge demand, with many institutes offering courses to enhance the required skills. For example, the average annual salary of a corporate finance executive in New York is $1,24,212.
Sometimes, the difference between corporate finance and corporate accounting can be confusing. However, the main distinction between the two is that the finance team focuses on strategy formulation, planning, directing and executing the financial strategies of an organization. Majorly, they provide a blueprint for future performance.
In contrast, the accounting domain typically focuses on analyzing, recording, tabulating and reporting on the business's finances. That is, it measures past performance.
Corporate Finance Principles
Let us take you through some central principles guiding this concept.
- Investment Principle - Investment principle urges on the significance of investing in the suitable options by assessing the risk and return. The evaluation of an investment proposal should be based on a predetermined hurdle rate that serves as a return analysis benchmark. It is important to ensure that cost of acquiring the capital is not offsetting the expected returns.
- Financing Principle - Financing principles influence the selection of financing methods to ensure the extraction of maximum value from the investment. The most crucial question here is whether to use debt financing, equity financing, or a combination of both. Many factors affect the capital structure such as business structure and goals, cost of financing, interest rate and access to the equity market.
- Dividend Principle - The dividend principle of an entity explains whether to streamline surplus towards business growth or shareholders in the form of dividends.
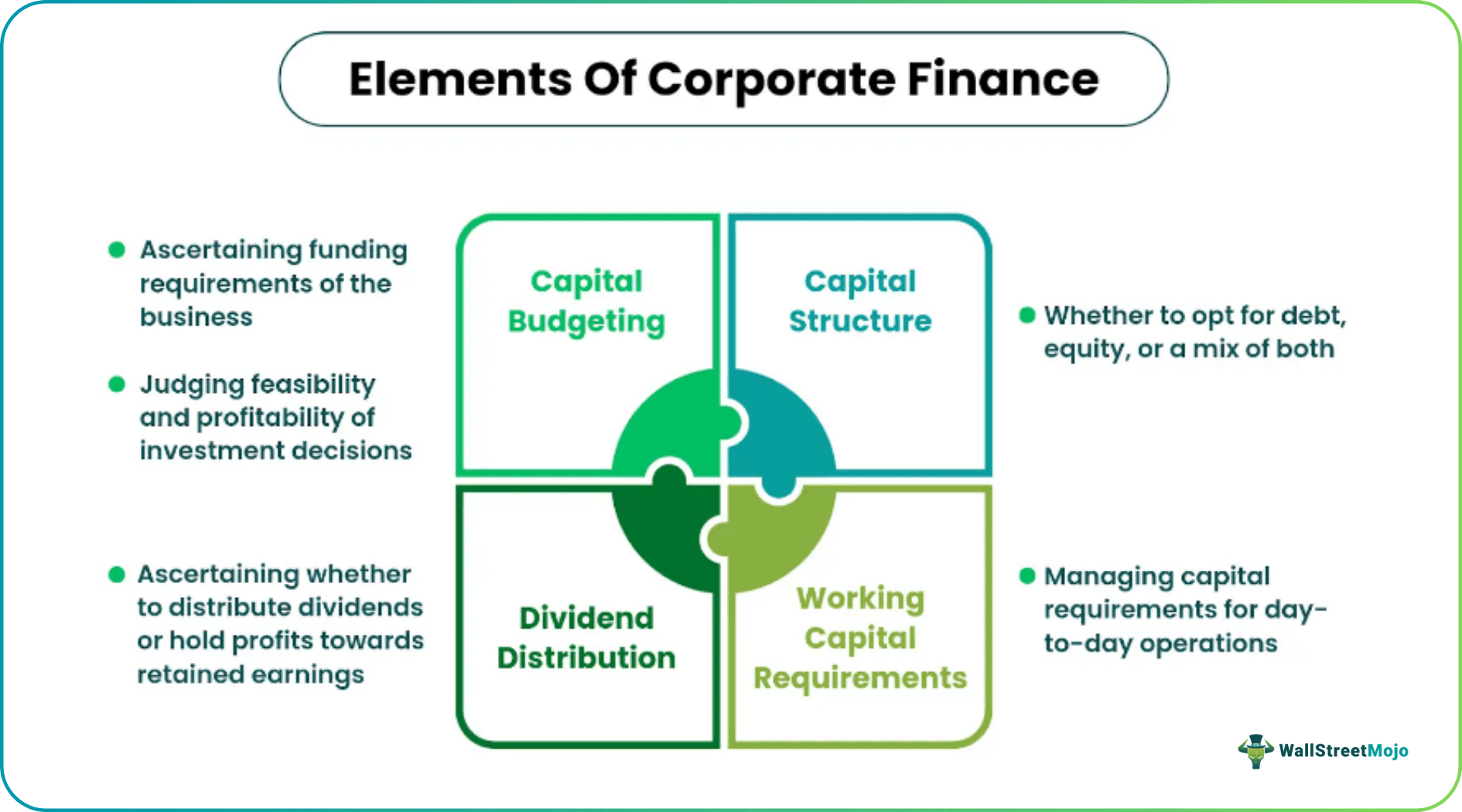
Central Elements
Corporate finance major focus areas include capital budgeting, capital structure, working capital and dividend decisions.
#1 - Capital Budgeting
The capital budgeting process discloses the viability of investment proposals and helps invest in profitable projects. The goal is to maximize the growth and profitability of the business. As part of capital budgeting, financial analysts go over various investment alternatives. They conduct a comparative analysis of investments' present and future value to interpret their risk-return aspects concerning organizational goals. Only the most suitable projects are given a chance.
#2 - Capital Structure
The capital structure tells us the method of financing used by the entity. The capital structure, for example, might include equity, retained earnings, and debts. In the perspective of investors, a combination of too much debt or equity is unappealing. They want a well-balanced combination of debt and equity funding instead. Consequently, the proper financial decision produces an optimum mix of various types of funding and enhances the company's value.
#3 - Working Capital
Working capital refers to the capital for day-to-day business operations. Efficient financial management can ensure an adequate cash flow in line with business policies. In this way, maintaining the liquidity of the organization can save them from going bankrupt.
#4 – Dividend Distribution
Public companies hold answerability to their shareholders. As a result, they often wonder how much of the business profit they should distribute as dividends. If they reinvest surplus as retained earnings, it must be backed with a strong conviction that the sum will generate business growth. At the same time, a certain amount of dividend distribution is also essential for many companies to serve their shareholders better.
Types of Corporate Finance
The two chief types include -
- Equity Financing - Companies can raise finance through equity issuance or obtain from retained earnings. Equity comes in the form of common stock, preference stock etc. A company can sell its shares by getting itself listed on a stock exchange or through over the counter (OTC) exchanges. Too much equity dilutes shareholders’ voting rights and reduces dividend share.
- Debt Financing - Debt financing refers to obtaining the finance required through loans, usually from financial institutions, or through bond issuance, etc. Debt financing attracts the cost of regular interest payments and repayment of the principle at the end of the loan tenure. Too much of debt induces the risk of default or going bankrupt in case of non-repayment of the debt.
Examples of Corporate Finance Activities
Corporate finance jobs entail managing the interaction between corporations, assets, markets, investors, government, financial institutions and intermediaries. Following are some examples of such activities -
- Financial modeling: Financial modeling helps to analyze the value and risk associated with investment options.
- Bank loan: Taking a loan from a bank to meet business needs and associated due diligence to analyze the cost of loan and repayment capacity.
- IPO: Initial public offering (IPO) generally helps to raise capital through equity financing.
- Refinancing and renegotiating all debts and payments: As the market changes, corporations may strategically negotiate to update the terms of loans or other payment agreements.
- Dividend distribution: Dividend distribution depends on the policy set by the management. It can be regular or irregular.
Why is it Important?
Corporate finance aims to obtain finances through the right sources to manage day-to-day and long-term financial activities. It strategizes how a company uses and manages capital to maximize value. Planning appropriate capital budgeting and structures is vital for balancing risk and profitability.
A company’s management evaluates future cash flows from investment through capital budgeting tools. They find the least expensive fund sources or the right mix of debt and equity in the capital structure. For short-term needs, working capital requirements are paid attention to.
Hence, we can say that these strategies ensure the going concern concept of the organization. Moreover, it improves the statistics on financial statements. Consequently, it will maximise value, or more specifically, the maximization of stock price.
