Table Of Contents
What Are Corporate Bylaws?
Corporate bylaws are foundational regulations that govern a company. It comprises company structure, procedures, laws, and guidelines. Therefore, every employee, staff, manager, and organization member has to comply with company bylaws.
Right at the inception of a firm, the board of directors formulates company bylaws. Bylaws are mandatory for all kinds of businesses, and institutions, be it a school, a college, a hospital, or society. In addition, every new member receives a bylaw orientation.
Table of contents
- What are Corporate Bylaws?
- Corporate bylaws are rules and regulations that govern a company; every firm employee and member abides by them.
- Company bylaws outline a firm's management structure, chain of command, meeting procedures, board of directors, and shareholders.
- Firms are mandated to report bylaws to the IRS and the secretary of state.
- The board of directors can process, propose, accept, or reject bylaw amendments.
Corporate Bylaws Explained
Corporate bylaws are foundational regulations that govern a company. Therefore, every new member receives a bylaw orientation. The bylaws outline a company's objectives, mindset, and approach.
Right at the beginning, the bylaws are drafted by a committee of board members. Before finalizing, the bylaws need the approval of the entire board—via voting or other methods.
Most bylaws are easy to comprehend, and every employee is acquainted with them. But some bylaws are dictated by IRS norms. Depending on the size and structure, firms either have a dedicated team of lawyers, accountants, and compliance analysts or outsource them. In addition, businesses must share documents with the government and regulatory bodies—corporate records.
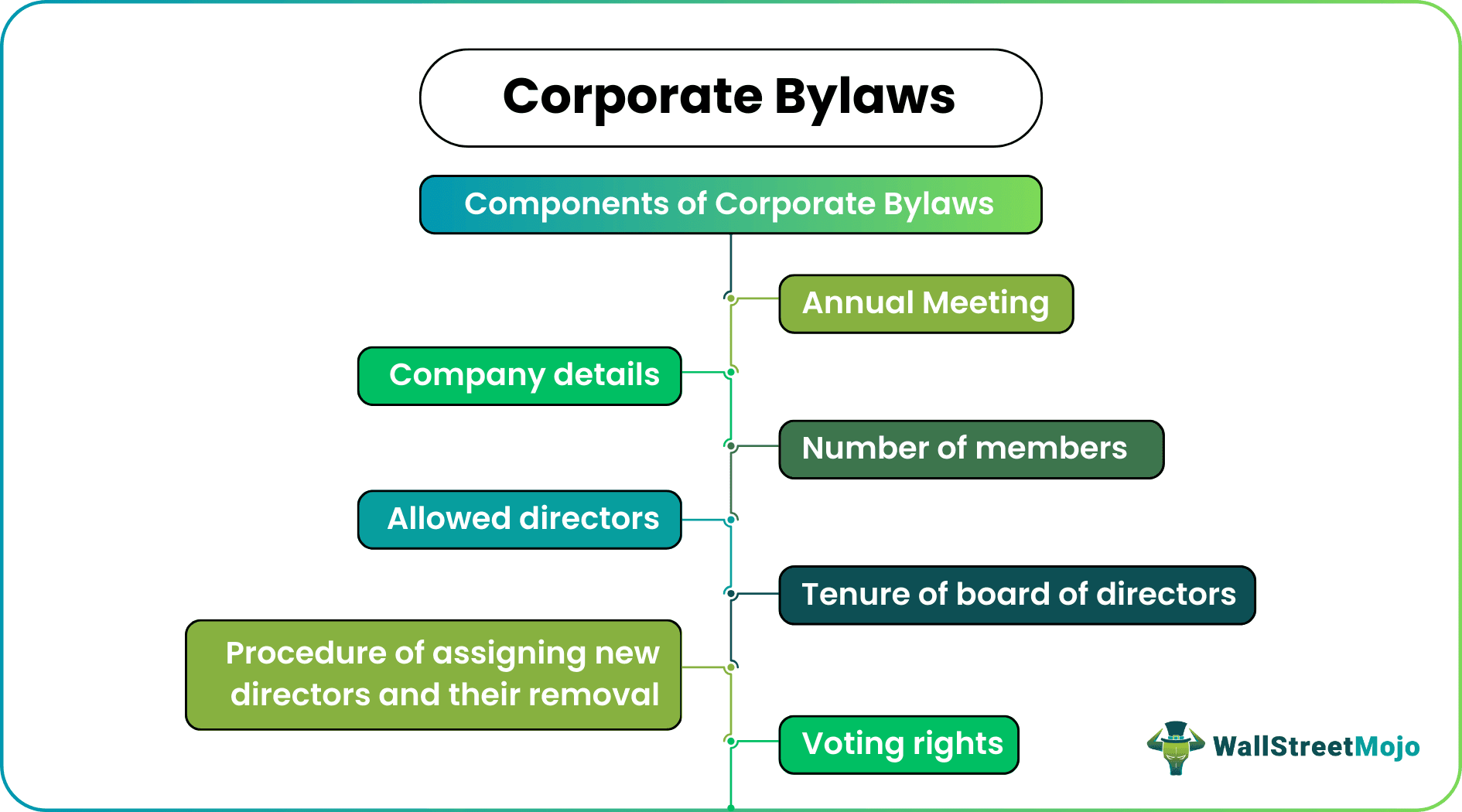
Company bylaws are formal documents containing guidelines and regulations about the employee code of conduct, organizational structure, type of shares, meeting procedures, and member elections. At least one meeting per year is mandatory for every firm.
Corporations adhere to stringent regulation and compliance standards. But this is not suitable for all institutions. Therefore, some institutions register themselves as non-profit company. Non-profit organizations focus more on their vision and mission—at the cost of losing business opportunities.
Company bylaws are not entirely rigid or inflexible. Over time a company grows in size, the governing structure evolves, and the objectives need to be altered. Therefore, company bylaws contain information about amendments. The board of directors plays a vital role in this. Company bylaws authorize the board to process, propose, accept, or reject bylaw amendments. This could be a specific change in a rule or policy.
Examples
Let us look at corporate bylaws examples to understand their application.
Example #1
Let us assume four friends started a social media platform and registered it as a company. The objective of this new firm is to advertise job vacancies. The firm empowers economically challenged sections of society by providing job opportunities. In return,n the firm charges fees from employers and successful job seekers.
The firm grows steadily and makes a profit. As core members, the four friends constitute the board of directors. Then, keeping their vision intact, the founders draft the company bylaws.
Every recruit receives instructions about the bylaws (outlining firm objectives). Employee performance appraisal also depends on the firm's core principles. This y vital for employees to be sure of what is expected of them.
In the future, if an employee is to be promoted to a board member, their selection, role, and responsibility will be dictated by the company bylaws. Since this is a startup, the bylaws are flexible—the four founding members can amend existing bylaws upon mutual consent. So to do that, board members need to call an official meeting and conduct voting.
Example #2
Due to the rise of class action suits, US companies have started including a clause preventing shareholders from suing the firm. This clause is mentioned in the company bylaws.
For example, Imperial Holdings does not allow investors with less than 3% to sue the firm.
For large corporations, brand perception and reputation are paramount. Mere speculation and rumors can cause substantial losses. Even if the firm is found not guilty, lawsuits create unnecessary negative publicity for the firm. Therefore, many companies mention in their bylaw that if a shareholder sues the firm, the legal fees and the plaintiff will bear the cost of defending. This way, frivolous suits are eliminated.
Template
Following is a sample of a corporate bylaws template.

Primarily, a corporate bylaws template contains the following information:
- Registration Details.
- Permanent Address/Place of Business.
- Board of Directors List.
- List of Shareholders.
- Committee Details.
- Meeting Schedule.
- Conflicts of Interest.
- Amendment Procedure.
Corporate Bylaws vs Article of Incorporation vs Operating Agreement
Let us look at corporate bylaws vs articles of incorporation vs operating agreement comparisons to distinguish between them.
- Corporate bylaws are structured guidelines about the company, whereas an article of incorporation offers legal identity to a company in the state it is located. In contrast, an operating agreement binds members of a limited liability company to carry out business operations.
- Firms are mandated to report bylaws and articles of incorporation to the IRS and the secretary of state. In contrast, LLCs report only to the filing authority.
- Bylaws and operating agreements are detailed documents outlining plans, voting rights, procedures, etc. In contrast, an article of incorporation is succinct.
- Company bylaws are applied to corporations, whereas operating agreements govern LLCs. In comparison, an article of incorporation is used to establish a corporation; for registering it with the government.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The board writes corporate bylaws of directors. The document establishes core principles, core values, purpose, and vision. This document is formulated right at the inception.
The following are critical functions of corporate bylaws:
- Management structure.
- Establishing a chain of command.
- Meeting procedures.
- General laws, rules, and regulations.
- Introducing hierarchy.
- Orienting employees about the firm's core values.
The main components of company bylaws are as follows:
- Registration details.
- Board of directors list.
- List of shareholders.
- Committee details.
- Conflicts of interest.
- Amendment procedure.
- Management structure.
- Company's purpose.
- Loan and contractual agreements.
- Shareholder meetings.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what are Corporate Bylaws. We explain its template, example, and comparison with the operating agreement & article of incorporation. You can learn more about it from the following articles -
