Table Of Contents
Core Competencies Meaning
The core competencies in business refer to its resources and unique fundamental capabilities that distinguish it from market competitors. It is an essential component of marketing strategy leading to brand recognition and business growth. The concept serves to be useful for companies focusing on multiple product lines and operating more than one business unit at a time.
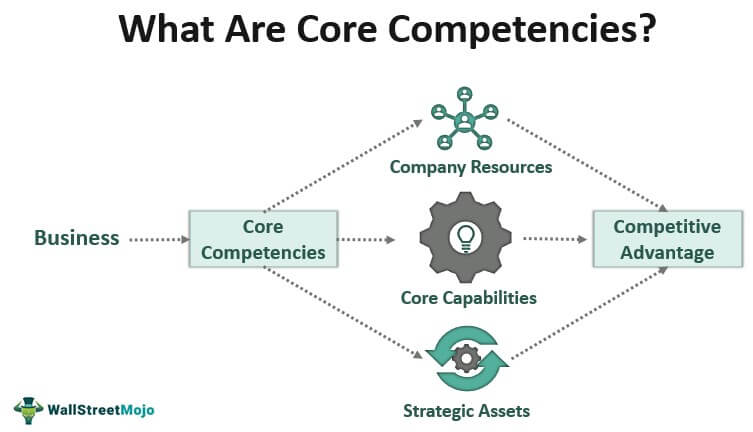
Also known as distinctive competencies, these include human resources, capital, and brand equity. As part of the modern management theory, these core capabilities entail providing unique products, processes, and services. Other characteristics like innovation, quality control, and brand advertising can also help businesses gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Key Takeaways
- The core competencies in business are its unique and fundamental capabilities, setting it apart from the competitors and making it the best in the market.
- It advocates the collaboration of diverse teams having unique skills to achieve one goal, i.e., producing the best end product.
- The term got its first appearance in the 1990 Harvard Business Review article "The Core Competence of the Corporation" by C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel.
- Brands like Apple, Amazon, Starbucks, Nike, etc., have established themselves as the best in their respective field by identifying their core capabilities and introducing innovative core or end products.
Understanding Core Competencies
The concept of distinctive competencies revolves around making a collective effort to achieve one goal, i.e., delivering the best output. People in an organization with diversified skills collaborate to manufacture or produce the desired end product. The business can then use this end product for its separate units and individual product lines.
The idea was first introduced by C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel in their article "The Core Competence of the Corporation," published in Harvard Business Review in 1990. It clearly stated the significance of the core competencies in business in developing core products to be used in its other products.
The writers used the analogy of a large tree as a diversified business to illustrate their point. They considered the smaller branches as business units, the roots system as distinctive competencies, the trunk as the core product, and the leaves, flowers, and fruits as end products.
According to the core competencies definition provided by Prahalad and Hamel, the existence of the tree, i.e., business and its end products, would be affected if the root system, i.e., core capabilities, is weak. Therefore, when consumers prefer products of a particular brand, the competitors must figure out its distinctive competencies.
While allowing a business to expand in different markets, these unique traits add value to the customer service. Since each industry functions differently, the core capabilities might vary for companies based on their operation.
Real World Business Examples
Here are some core competencies examples to provide a better understanding of the concept. However, the more common distinctive competencies of a successful business are:
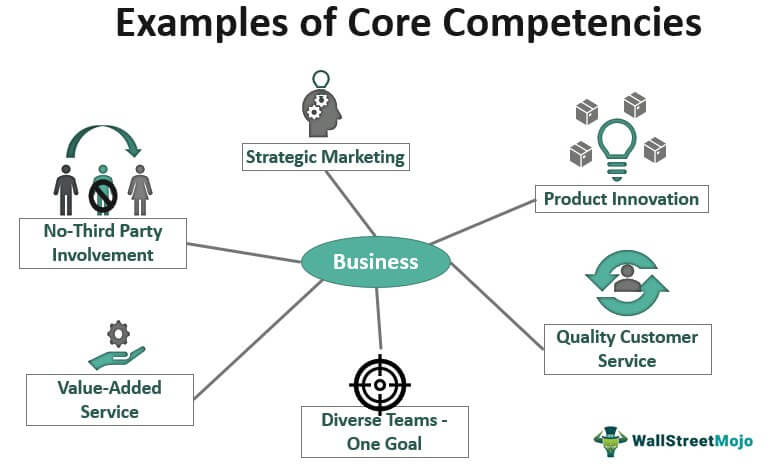
- Value-Added Service
- Excellent Customer Service
- Product Innovation
- Strategic Marketing
- Unmatched Quality
#1 - Apple
While any software and device manufacturing business would claim to be innovative, Apple has other characteristics that distinguish it from the competition. This American conglomerate handles everything from product design to sales of innovative products and services. As a result, when consumers invest in its products, they know they are investing in a brand that never compromises customer benefits by outsourcing production and sales to a third party.
The core competencies of Apple include:
- Unique, innovative, and creative technology
- Integration of software and devices
- User-friendly interface
- Ergonomic and eye-catchy product designs
- Premium electronics brand
- Access to user data
- Artificial intelligence-enabled devices
- Worldwide sales and distribution channel
#2 - Amazon
Amazon has successfully established itself as the first choice of consumers with products and services catering to various niches. The company has thrived in every field it has entered, be it e-commerce or software development, or media streaming. Some of its services that consumers, sellers, content creators, and distribution channels rely on include AWS (cloud computing service), Twitch (video game streaming), Whole Foods (supermarket chain), etc.
The core competencies of Amazon include:
- Brand-consumer relation
- Customer-centric approach
- Innovative services
- Self-suffice shopping and media streaming platforms
- No third-party involvement
- Independent product distribution
- Well-organized logistics
- Premier customer service
- Fast product delivery
- Wide range of low-cost products
#3 - Nike
Nike has never had to look back after becoming the number one global brand of athletic footwear, leisure clothing, and accessories. With time, the company has grown to become one of the most trusted providers for sports shoes and other apparel.
The distinctive competencies that led to the stability of Nike include:
- Innovative design and durable products
- Consumer-focused approach
- Diverse teams, one focus, one goal
- Efficient sales and distribution channels
- Effective marketing strategies
- Global brand recognition
- Strong research and development
- High manufacturing standards
#4 - Starbucks
The coffeehouse chain Starbucks is hardly unknown to anyone. Its roastery reserves make them one of their kind. When people think of having beverages and snacks or hanging out with friends, Starbucks is the name that strikes their minds instantly. By forging a personal connection with consumers and offering quality coffee products, the brand has turned itself into a community and a symbol of social status.
The distinctive competencies that helped the coffee chain have an ideal business arrangement to produce the best coffee include:
- Localized customer experience
- Expert in coffee roasting
- Secret coffee menu
- High-quality coffee beans
- Affordable coffee products
- Global brand reputation and equity
- Aesthetic store concept
- Personalized customer service
- Continuous product development
- Manually processed beverages
- Introducing the U.S. coffee culture across the globe
How To Identify Core Competencies?
No matter what size or how old a business is, it must identify its distinctive competencies to sustain and stay ahead of the market competition. Understanding core products and capabilities will help companies deliver value to customers. Eventually, it will drive their growth and reputation.
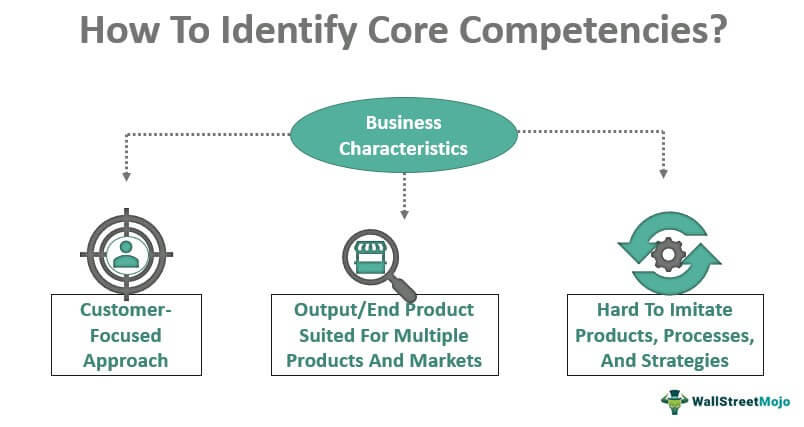
Businesses can determine which of their characteristics qualify as distinct fundamental capabilities. Prahalad and Hamel suggested that the strengths of a business meeting the requirements below can be considered core competencies in strategic management if:
- The initiative or end product offers consumer benefits.
- An end product can be used in its variety of products and markets.
- The strategies, processes, and results are rare and hard to imitate.
Aside from the duties and processes that serve as their unique selling propositions, businesses can outsource part of their duties and processes.
Businesses with a strong focus on developing a specific product type can utilize their core capabilities to produce innovative products. For example, Google, Inc., an Internet company, has little exposure in the hardware segment. But by exploiting the distinctive competencies of artificial intelligence and mobile-first ads, it achieved success with its Pixel smartphones.
