Table Of Contents
What Is A Contingent Beneficiary?
A contingent beneficiary for any financial account is the person who has been designated as a secondary beneficiary. The benefits of the associated proceeds are to be realized if the primary beneficiary for the said financial account cannot learn the same, which may happen due to the primary beneficiary's death.
Any individual, organization, charitable, or another trust may be chosen as the contingent beneficiary by the financial account holder. However, the selected person must be of legal age and capacity. Thus, if a minor is selected, one must ensure that a legal guardian is appointed to manage the assets until the minor attains maturity age.
Key Takeaways
- A contingent beneficiary is a secondary beneficiary designated to receive the benefits or earnings of a financial account if the primary beneficiary cannot receive them, typically due to their death.
- The financial account holder can choose an individual, organization, charity, or trust as their contingent beneficiary if they are of legal age and capacity.
- If a minor is chosen as the contingent beneficiary, a legal guardian must be assigned to manage the assets until the minor reaches the age of majority.
How Does Contingent Beneficiary Work?
Contingent beneficiary refers to the position given to an individual, organization, or a trust as a receiver of the proceeds after the primary beneficiary cannot use the funds due to their unsound mind or death.
In the case of any contract for financial accounts, such as an insurance contract or a will, certain conditions might exist that define the terms relating to the beneficiary’s benefits.
The contingent beneficiary designation require them to adhere to such conditions to get the benefits under the contract. However, in any case, their rights are secondary and conditional upon the inability of the primary beneficiary to present his claim for these reasons.
If the primary beneficiary accepts the benefits, the contingent beneficiary no longer remains eligible for any benefits under the contract.
Features
Let us understand the features of a contingent or a secondary beneficiary through the discussion below.
- The claim of the contingent beneficiary over the benefits of the financial account is conditional.
- One can claim benefits only without a claim by the primary beneficiary.
- It may further limit the rights as per the contract. The claims can only be made up to the contingent beneficiary percentage.
- There may be multiple beneficiaries in a contract, which will mention their proportionate share in the agreement.
Examples
Let us understand the concept of contingent beneficiary percentage with the help of a couple of examples.
Example #1
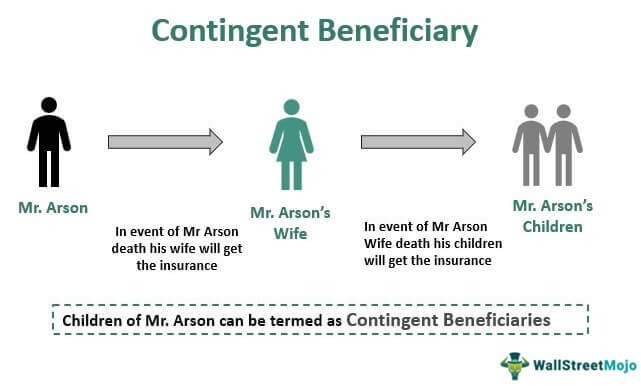
Mr. Arson mentions in his life insurance policy that upon his death, his spouse shall be the one who shall get the insurance proceeds in the event of his death. It is also mentioned that if the spouse is deceased or of unsound mind as on the date of his death, the proceeds shall flow to the couple's children.
In this example, Mr. Arson's children can be termed contingent beneficiaries as their benefits are secondary to that of the primary beneficiary, Mr. Arson's wife.
Example #2
In January 2023, a citizen of the United States claimed that the IRA amount in his mom’s account were not being transferred to him and his sister who held contingent beneficiary percentage.
Their mom had mentioned her husband as the primary beneficiary, who also passed away shortly after the former’s death. Since the latter had mentioned his spouse as the primary beneficiary and no contingent or secondary beneficiaries were mentioned the funds were transferred to his estate instead of his children.
Will Contingent Beneficiaries Have Rights?
The rights of the contingent beneficiary designation are secondary to that of the primary beneficiary. Thus, they can establish their rights over the benefits under a contract only in case of the following events: -
- The primary beneficiary dies or goes missing.
- The primary beneficiary refuses to accept the contract's rights when it becomes due.
However, the rights may be subjected to certain other conditions, the fulfillment required to claim possession.
Advantages
Let us understand the advantages of declaring a contingent beneficiary designation through the explanation below.
- It is always beneficial for account holders to add primary and secondary beneficiaries for their accounts.
- That is because the assets will flow to the legal heirs' named beneficiaries without any unnecessary delay.
- Counting only the primary beneficiaries is not sufficient. As a backup strategy, contingent beneficiaries should be added so that resources can flow to them in the account holder's death.
Contingent Beneficiary Vs Primary Beneficiary
Let us clarify a common confusion of the hierarchy of beneficiaries by the comparison below.
The difference is that the primary beneficiary is the first person entitled to the benefits and the proceeds under the contract. On the other hand, contingent beneficiary designation is given to someone who can claim their rights only when the primary beneficiary cannot present their claim or such conditions are met as prescribed.
