Table Of Contents
Consumer Cyclical Definition
Consumer cyclicals are stocks of companies producing non-essential commodities. Their performance is directly related to any changes in the economy. Investing in cyclical stocks during an economic upturn may yield promising returns to investors.
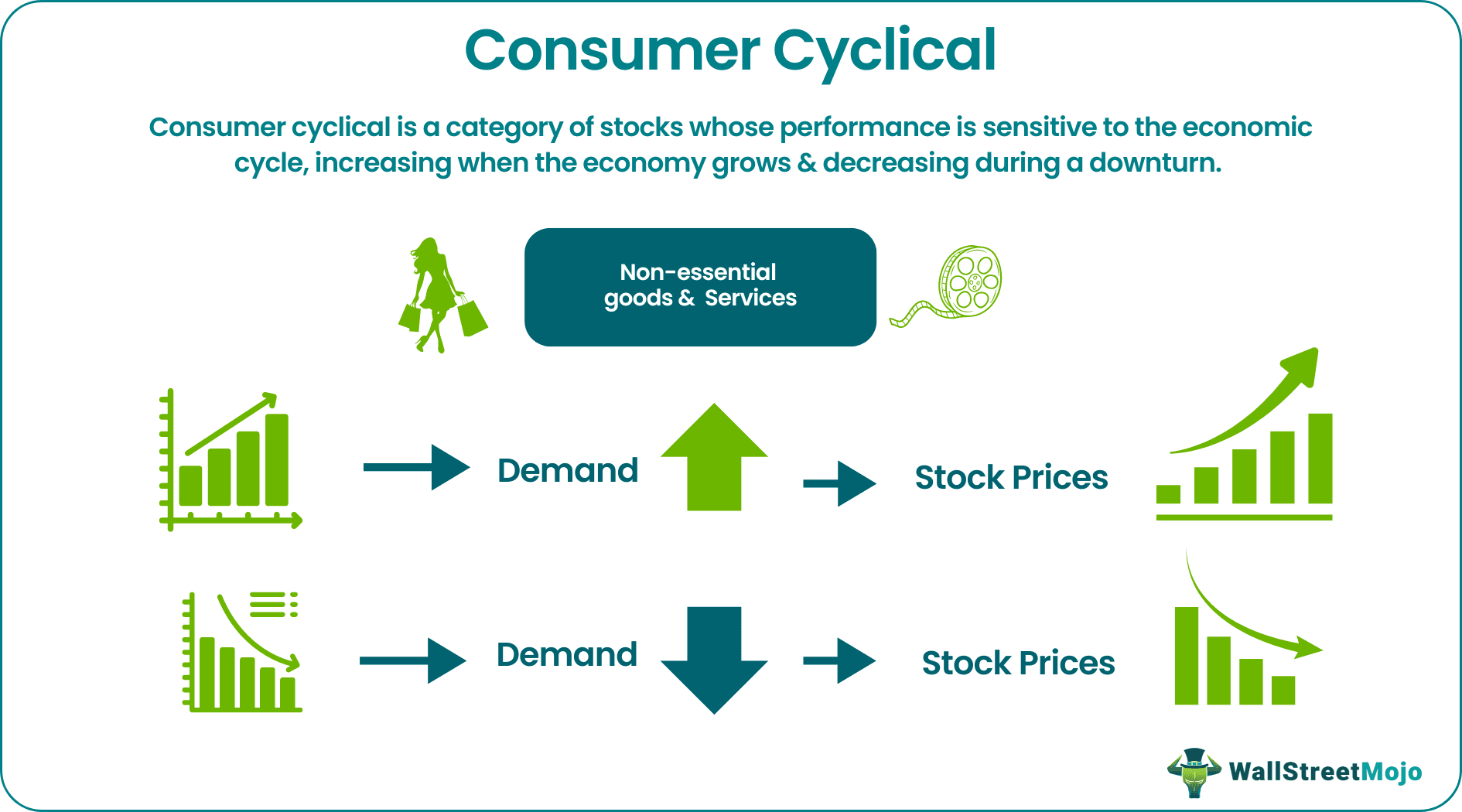
Also called “consumer discretionary,” it encompasses businesses that sell dispensable goods and services like designer clothing, automobile, eateries, and entertainment. The stocks of such companies are referred to as cyclical stocks. This is because their movement is usually synchronized with the market. Thus, the risks and benefits of investing in them depend on the investment timing.
Key Takeaways
- Consumer cyclical is a category of stocks whose performance is sensitive to the economic cycle, increasing when it boosts and decreasing during a downturn.
- It usually represents stocks of companies selling non-essential products or services like entertainment, high-end gadgets, sports cars, and expensive clothing.
- Investment in cyclical stocks ensures maximum profitability during an economic upturn and portfolio diversification.
- It contrasts with “consumer staples,” including basic commodities like food and medicine, which remain unaffected by market shifts.
Consumer Cyclical Explained
The term consumer cyclical denotes stocks of companies that offer products that are affected by economic cycles. Cyclicals flourish when the market is up, and consumers have more spending potential. Nevertheless, it declines when the market is down, and consumers have less spending potential. So, let’s see how it works.
A growing economy results in higher disposable income with its people, enhancing their buying power. People with rising income are more likely to buy a fancy car, eat out at an expensive restaurant, or take a vacation. This translates into profit for companies offering such goods and services, reflected in their rising stock price.
Conversely, when an economy takes a downturn, demand for these items recedes, reducing the earnings and stock prices of companies producing them. However, people are not likely to curtail their spending on food and medicines even during a slowdown as they are essential for their survival. Such essential commodities are called non-cyclical or consumer staples. They remain unaffected by market changes and enjoy an inelastic demand.
Unlike staples, cyclicals suffer a maximum loss during an economic recession. This is because people prefer to spend money on consumer staples rather than investing in non-essential items. As a result, the prices of cyclical stocks nosedive.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Consumer Cyclical vs Consumer Staple
| Particulars | Consumer cyclical | Consumer staple |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-essential items affected by market variations | Essential items unaffected by market variations |
| Stock market approach | Offensive | Defensive |
| Increased performance | When the market is up | When the market is down |
| Related products | Hotels, restaurants, high-end electronics, entertainment, & luxury items | Grocery, apparel, medicine, & petrol |
| Why invest? | High profit during market ascent | Security during market descent |
Examples
The economic downturn due to the COVID 19 pandemic resulted in several cyclical stocks being affected. One such stock is of global fast-food retailer McDonald's. With people staying at home and spending on consumer staples during the pandemic, the company's fortunes took a beating.
The pandemic-imposed restrictions and economic recession led to a fall in its revenue from $21.4 billion in 2019 to $19.2 billion in 2020. As a result, stock prices declined from $186 in December 2020 to $140 in March 2020.
However, with the pandemic receding and economic upturn, the company is seeing a revival in its revenue. The company's earnings have witnessed positive growth and are likely to ride high in the coming months.
A recent Forbes article discusses the ten best consumer cyclical stocks as of March 2022. It also mentions four sub-sectors of consumer cyclical stocks: retailers, automobile and automobile parts, durable household items, and hotels, restaurants, & entertainment.
Here is the list.
| Cyclical stocks | Market cap | 10-year trailing return |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN) | $1.6 trillion | 30.9% |
| Tesla Inc. (TSLA) | $929 billion | 64.3% |
| LVMH Moet Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE (LVMHF) | $408 trillion | 17.7% |
| The Home Depot Inc. (HD) | $375 billion | 24.4% |
| Toyota Motor Corp ™ | $271 billion | 11.7% |
| Nike Inc. (NKE) | $230 billion | 19.4% |
| McDonald’s Corp. (MCD) | $195 billion | 11.6% |
| Hermes International SA (HESAY) | $158 billion | 15.6% |
| Lowe’s Companies Inc. (LOW) | $155 billion | 24.8% |
| Volkswagen AG (VWAGY) | $142 billion | 6.8% |
Role of Consumer Cyclical in Investments
Cyclical stocks provide the highest gains in a bull market and endure the biggest losses in a bear market. This is because it comprises stocks of industries that are highly dependent upon consumer demand for business sustenance and growth. Consequently, their prices surge in a booming economy and fall when it slows down.
Since cyclical stocks move in tandem with the markets, their performance is based on market timing. Therefore, investors must know how to trade cyclical stocks at the right time to obtain the utmost benefits. Nonetheless, it is tough to interpret the right market timing due to an unexpected rebound in certain cyclical before the end of the downturn.
Hence, investors must target cyclical stocks with high dividends
to diminish the possible drawbacks. The best time to buy cyclical stocks is when they possess high valuation ratios. With perfect investment timing, the volatile consumer cyclical sector provides impressive growth potential. Needlessly, cyclical stocks are suitable for experienced investors with professional insight.
Investors may purchase cyclical stocks via individual stock investments in companies like Adidas, Amazon, Tesla, McDonald's, etc. To reduce risk and diversify investment in consumer cyclicals, investors can choose exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or index funds. Also, they can choose any of the accessible consumer discretionary ETFs.
Moreover, a judicious mix of both cyclical and non-cyclical stocks leads to sustained long-term returns with minimum risk.
When to invest in cyclical stocks?
The investor must buy cyclical stocks when the economy is growing. This growth happens when:
- Metals witness the beginning of a supercycle
- Government pushes its capital investment cycle
- Frenzied business expansion occurs
- A significant external investment happens in the economy
Why invest in cyclical stocks?
Investment in cyclical stocks aids in:
- Ensuring excellent performance in a thriving economy
- Portfolio diversification
Investment in cyclical stocks requires thorough financial knowledge with a backup plan to limit the damage caused by a possible economic slump.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs)
A – Consumer cyclical industries include:
· Automakers
· Airlines
· Construction
· Durable goods like industrial equipment
· Discretionary goods like home appliances
· Luxury goods like designer clothing, jewelry, etc.
· Mining
· Finance
A – Consumer cyclical and non-cyclical stocks are two types of stock categories. Cyclical stocks depict companies selling inessential goods and services whose demand is sensitive to market fluctuations. At the same time, non-cyclical stocks portray firms selling basic goods and services whose demand remains unaffected by market changes.
A – Investors must buy consumer cyclical stocks during an economic upturn. When the economy is expanding, people have more money to spend on discretionary items, which is likely to drive their demand up. This increases the profitability of companies producing them, surging their stock prices. As a result, investors can expect a handsome return on their investment.
A – Yes, consumer cyclical is also often known as “consumer discretionary.” Both terms represent companies generating non-essential items whose demand and supply are directly related to the economic cycles.

