Table of Contents
What Is A Compliance Management System (CMS)?
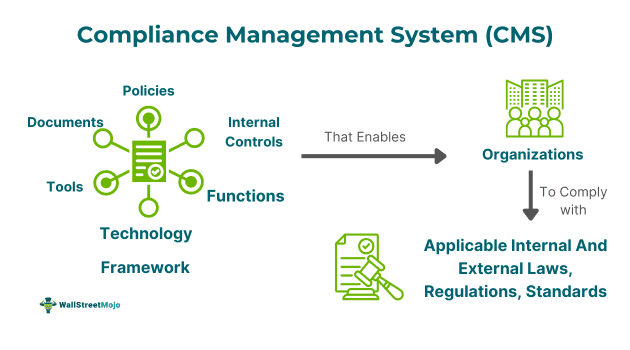
A compliance management system (CMS) refers to a framework comprising processes, internal controls, documents, tools, technology, and functions. This system helps organizations track, monitor, and enforce their adherence to applicable standards, regulations, and laws. Management ensures the integration of this system into their business processes.
Companies need to design an effective CMS to avoid the adverse consequences and risks of non-compliance. These consequences include fines, penalties, a shattered reputation, lost business, and breach of stakeholders' trust. Further, organizations that fulfill every compliance requirement tend to maintain a superior brand reputation and trust among their stakeholders. This includes shareholders, investors, creditors, clients, and employees.
Key Takeaways
- Compliance management software (CMS) is an internal mechanism that aids organizations in meeting legal, audit, regulatory, and reporting compliance requirements.
- It includes various policies, internal controls, procedures, tools, functions, documents, and technology.
- These elements ensure the compliance of the firm's processes, products, and services with laws, regulations, and standards.
- Companies need to track, monitor, review, enforce, and improve their CMS periodically.
- The primary components of CMS include senior management and board of directors, compliance program, and compliance audit.
Compliance Management System Explained
The compliance management system (CMS) is an integrated framework that encompasses various policies, internal controls, procedures, functions, tools, documents, and technology. This framework assists the organization in adhering to all legal, audit, reporting, and regulatory compliance requirements. Notably, sometimes non-compliance can cost a company's reputation and stakeholders' trust, with various legal charges and consequences. However, a constant upgrade of the CMS is essential to ensure that the firms' compliance status adapts to the changing regulatory environment.
For instance, the ISO compliance management system is widely adopted by firms to promote ethical business practices and comply with corporate governance laws. It also increases operational efficiency and builds trust and confidence among stakeholders. Similarly, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) compliance management system focuses on companies' compliance with consumer protection laws.
However, developing a CMS alone is not sufficient to strengthen compliance status. A significant challenge lies in its proper implementation and integration with business activities and practices. Also, the evolving regulatory and legal requirements require frequent revisions of the CMS.
Components
Every CMS comprises the following three critical elements:
- Senior Management and Board of Directors: Compliance begins with disciplining an organization’s top level. The senior executives and the Board of Directors decide on a compliance vision. They integrate their business activities with the CMS, make their subordinates follow the compliance standards, and ensure that the framework remains relevant.
- Compliance Program: It includes all the internal controls, procedures, policies, standards, documents, tools, and technology that the leaders aim to enforce. Further, it lays out a blueprint for employee training and education on the compliance process, customer complaint redressal, and other compliance issues.
- Compliance Audit: This is the most essential element of a CMS. It helps gauge whether the organization meets all regulatory requirements and follows internal policies in its processes.
How to Build?
Given below are the fundamental steps in CMS creation:
- Identify Compliance Needs: The first step is to gauge the internal compliance requirements, i.e., industry standards, regulations, and laws, as well as other external compliance needs.
- Ascertain Compliance Risk: The next step is to determine the potential compliance issues and risks that may cause the organization trouble.
- Allocate Responsibilities Among Compliance Teams: Divide the responsibilities, tasks, and functions between the different members of the compliance team to establish proper accountability.
- Design and Implement Procedures, Policies, Controls, and Reporting Structures: The team can now devise effective internal controls, policies, procedures, tools, and reporting structures. These measures are designed to meet all regulatory, legal, reporting, and audit compliance requirements.
- Make Use of Technology: Companies need to implement suitable compliance management system software. It automates the compliance management process, such as monitoring, tracking, auditing, updating, and reporting compliance status.
How to Implement?
Some of the relevant best practices for CMS implementation are discussed below:
- The firms can appoint someone to monitor and report the compliance practices in business activities constantly.
- The compliance policies, procedures, guidelines, and standards should be in writing. In addition, it should be circulated among all departments to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
- Management should be open to two-way communication with the stakeholders. They should welcome suggestions, discuss compliance issues, and report any type of non-compliance.
- Organizations should run employee training and education programs to help employees realize the significance of compliance with laws, standards, and regulations.
- Businesses should have an auditing team to review their internal and external compliance.
Examples
Some examples to highlight the significance of ensuring proper compliance management are discussed below:
Example #1
Suppose ABC Textiles has a tax compliance management system whereby each transaction needs to be accurately recorded in the accounting software. However, the company still has some vendors who don't provide a proper bill for the raw materials procured by the company. Also, some of the finished products are sold out without an invoice, which leaves the company with a scope for tax evasion. After the compliance audit, this issue was identified, and management was advised to maintain proper invoices for all its transactions.
Example #2
Discover Financial Services shares surged 7% on October 02, 2023. This surge followed its commitment to enhance its corporate governance and consumer compliance under the FDIC consent order. This rise in the bank's stocks made it a leading gainer on the S&P 500.
Notably, the Discover bank has been constantly making efforts to improve its compliance management system, as mentioned in a recent SEC filing. According to the bank, in July 2023, it was handed a proposed consent order from the FDIC. Meanwhile, during the regulatory review, the bank found some misclassified credit card accounts dating back to mid-2007, due to which it halted the share repurchases.
Benefits
Let us explore some of the advantages of CMS:
- Secure Stakeholders' Trust: A business entity with a robust CMS can efficiently gain the confidence and trust of its investors, shareholders, creditors, clients, employees, and other stakeholders.
- Improve and Maintain Brand Reputation: When companies integrate the CMS with their business processes, they eliminate the chances of non-compliance with the legal and regulatory frameworks. This builds a solid brand value and reputation.
- Fend Off Legal Risks: This initiative helps organizations ward off possible legal charges that arise from not following laws, regulatory requirements, and standards.
- Avoid Other Non-compliance Consequences: The adverse outcomes of compliance failure can be severe, extending to penalties, fines, business loss, fall in brand reputation, etc. Thus, CMS serves as a savior from such adversities.
- Ensure Compliance Process Traceability and Transparency: The compliance team should have a written format of the compliance requirements, including the process, internal policies, tools, controls, and others. It helps them easily track non-compliance and ensure transparency in adherence to the compliance guidelines across all departments.
