Table Of Contents
Competitive Bidding Definition
Competitive bidding can be referred to as a formal process of solicitation through which goods and services can be procured. The main purpose of such a system is to encourage transparency and provide equal and fair participation to eligible parties. Another objective is to increase the competitiveness of the bids.
Competitive bidding involves inviting potential vendors and conducting a fair auction or bidding for the commodity. The subsequent offer is granted to the person who places the winning bid. The winning bid depends on factors like the bid amount, qualifications reliability of the vendors, etc. The process of international competitive bidding improves transparency and competition among suppliers.
Key Takeaways
- Competitive bidding is a commercial activity in which an entity, like a business organization, government institution, or bank, solicits the procurement of certain goods and services.
- The competitive bidding process begins with the soliciting entity issuing a Request for Proposal (RFP), which contains the required good or services and other relevant details of the bid.
- It works similarly to a tender, except that a tender is an invitation to quote competitive prices, whereas bidding is the process of quoting an actual value.
Competitive Bidding Explained
Competitive bidding is a type of solicitation or a request by an organization to various parties to submit bids to procure some commodity. Interested vendors make bids considering costs, profit, and other factors like time. The organization finds the best bid for them. More often than not, the lowest bid wins. The entity also considers parameters like vendor reliability, quality of work, etc.
The entity mostly solicits by issuing the Request for Proposal (RFP). However, an organization that has to often solicit for procurement of goods or services need not always issue an RFP. Instead, they can identify the regular bidders from the past who they think are suitable for the bid and invite them.
Interested suppliers then prepare and submit their bids, which typically include detailed information on pricing, proposed timeline, qualifications, and any other relevant factors. These bids are usually sealed to maintain confidentiality until the specified deadline for submission.
Once the deadline passes, the organization evaluates the bids based on predetermined criteria such as cost-effectiveness, technical expertise, compliance with specifications, and past performance. The evaluation process aims to select the bid that offers the best overall value to the organization.
A competitive bidding strategy promotes transparency, encourages competition among suppliers, and helps organizations secure the best value for their procurement needs. It also allows for cost savings and ensures that projects are awarded to qualified and capable vendors. However, the process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive for both the organization and participating suppliers.
Additionally, there's a risk of bid rigging or collusion among suppliers, which could undermine the integrity of the process. Therefore, organizations must implement robust controls and oversight mechanisms to mitigate these risks and ensure a fair and competitive bidding environment.
Process
Let us understand the step-by-step process of competitive bidding strategy through the points below.
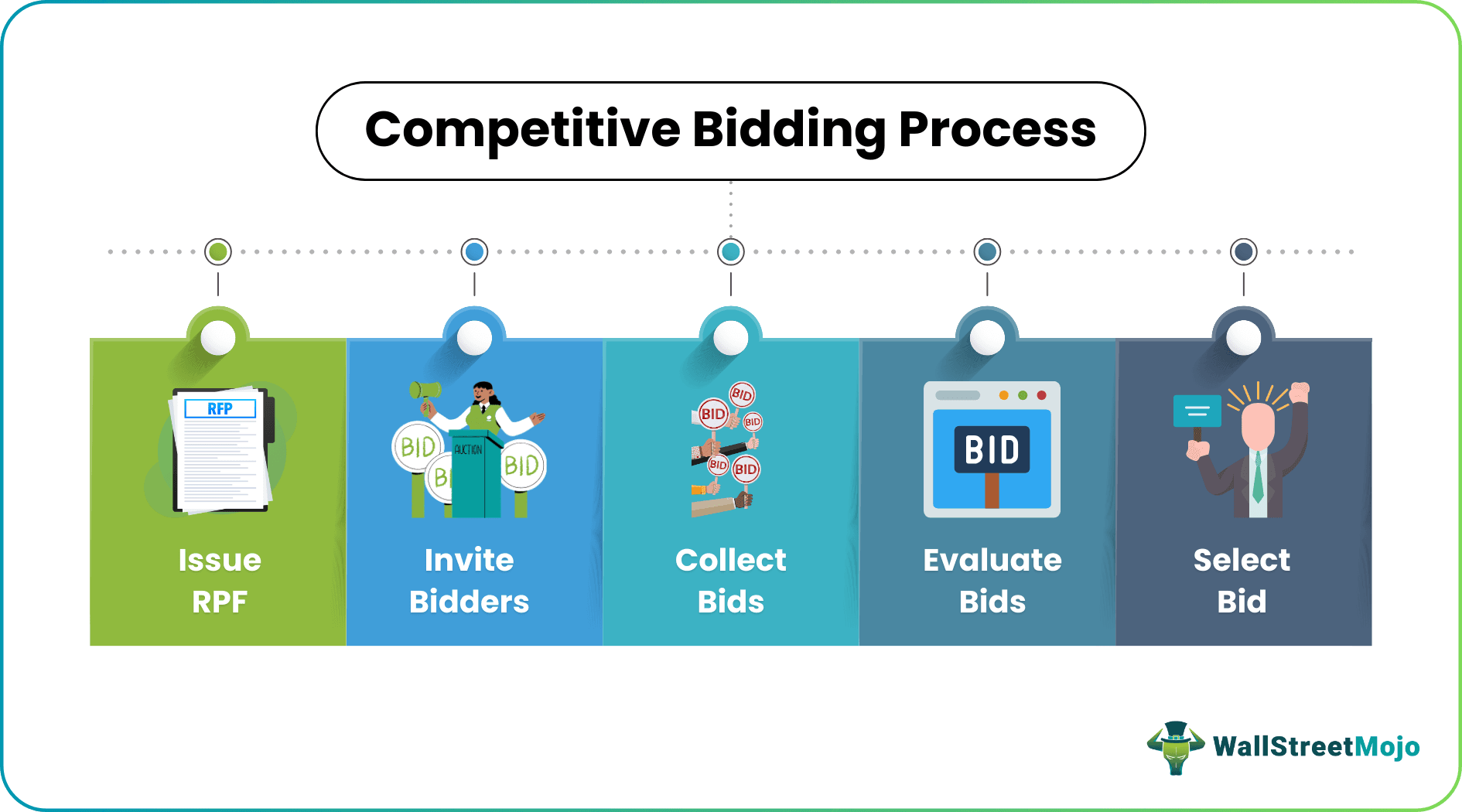
- The competitive bidding process begins with the concerned entity issuing an RFP containing the details of the bid.
- Then, vendors are invited to participate in the bid. The invitation is not personal but is often published in newspapers or on the organization's website.
- Interested vendors submit their bids by considering the costs, required time for completion of the project, etc.
- Once a satisfactory number of bids are received, the acceptance of bids is closed.
- Then comes the essential part of the process – evaluating the bids.
- Bids are evaluated primarily based on the costs, i.e., a lower bid is considered profitable to the bid-issuing organization. However, considering various supporting factors is a pragmatic approach. Hence, parameters like the vendors' history, reliability, contract terms, estimated completion time, etc., are also accounted for.
- After evaluating the bids, the suitable bid is identified, and the project is handed over to the winner. Usually, some entities often conduct interviews, meetings, and background checks on the bidders who place attractive offers.
- Finally, sending the results of the bid to all participants is an important step, as it increases the reputation of a firm and safeguards its future interests.
Types
There is no clear-cut or universal classification of domestic or international competitive bidding. However, based on certain characteristics, it is possible to classify them. For instance, the first classification can be based on geography, and the second classification can be based on the selection mode.
Based on geography, bidding can be two types:
#1 - National Competitive Bidding
In national competitive bidding, the entity invites bidders from within the country. Usually, governments and, to some extent, commercial banks confine their range to the domestic borders of a country. Especially the government should opt for this type, as it should encourage commercial activities within the nation and function in its best interests.
#2 - International Competitive Bidding
On the other hand, international competitive bidding means outsourcing contracts to other countries for better offers. But it doesn't mean that local bidders cannot take part. It us businesses and manufacturing industries who mainly adopt this practice. It can increase competition and present deals at cheaper rates. Also, it is possible to experiment with newer technologies or innovations. Globalization and digitization in recent years have promoted this type of bidding.
Based on the selection mode, bidding can be classified into:
- Open bidding - Open bidding implies that all the participants can see the bids placed by others throughout the selection process.
- Closed bidding - In closed bidding, there is no disclosure of the identity of the participants or the bids placed. In most cases, however, there is open announcement of the bid winner, despite the closed selection.
Further, other types of minor classifications can be based on the channel – online or physical. Nevertheless, most bids now take place in real-time. Sometimes offline mediums like newspapers publish the news or the invitations.
Guidelines
In competitive bidding strategy, adhering to clear guidelines is crucial to ensure fairness, transparency, and efficiency throughout the procurement process. Below are some essential guidelines for competitive bidding.
- Transparency: All procurement requirements, evaluation criteria, and bid submission procedures should be clearly communicated to all potential bidders.
- Equal Opportunity: Ensure that all qualified suppliers have equal access to bid opportunities and information without favoritism or discrimination.
- Compliance: Bidders must comply with all relevant regulations, standards, and contractual terms specified in the bidding documents.
- Confidentiality: Maintain confidentiality of bids until the specified deadline for submission to prevent unfair advantage or bias.
- Evaluation Criteria: Clearly define evaluation criteria and weighting factors to assess bids objectively based on factors such as price, quality, and technical specifications.
- Bid Opening: Conduct bid openings publicly and promptly after the submission deadline to demonstrate transparency and allow for immediate review.
- Documentation: Maintain accurate records of the bidding process, including bid submissions, evaluations, and contract awards, for audit and accountability purposes.
Examples
Now that we understand the basics and intricacies of the concept of domestic and international competitive bidding, let us understand the practicality of the situation through the examples below.
Example #1
Allon Art Museum decides to auction off a renowned painting from its collection. The museum announces that it will use a competitive bidding process to determine the new owner of the artwork. Interested buyers, including private collectors, art dealers, and galleries, are invited to submit their bids for the painting.
During the bidding process, each participant submits their offer, and the bids are evaluated based on factors such as the amount offered, the bidder's reputation, and their intended use for the painting. The bidding continues until a predetermined deadline, at which point the highest bidder wins the auction and becomes the new owner of the painting.
Example #2
In May 2023, regulators seized control of First Republic Bank, marking the third bank failure in the United States since March 2023. Despite efforts to secure support from other banks, the struggling institution could not be saved. Following a competitive bidding process, JPMorgan Chase, already the nation's largest bank, emerged as the successful bidder for First Republic.
The acquisition includes all of the troubled bank's deposits and a "significant majority" of its assets, according to JPMorgan. As part of the deal, JPMorgan is absorbing approximately $92 billion in deposits, including the $30 billion injected by several large banks the previous month. Additionally, the acquisition involves assuming $173 billion in loans and $30 billion in securities. This event marked the most substantial bank failure since the 2008 financial crisis when Washington Mutual collapsed, with JPMorgan also acquiring its assets that time around as well.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Domestic and international competitive bidding is mostly advantageous. However, like any system, it has its drawbacks. Let's understand them briefly.
Advantages
Competitive bids are usually conducted by considering the parties' best interests. For example, rather than an entity entering into a contract with the same party time and again, looking for other parties with better deals at better rates can be beneficial.
Also, it ensures equal opportunities and representation for eligible vendors. Hence, it is supposed to be a win-win situation for the issuing entity and the vendor.
Disadvantages
Some of the demerits of the system of competitive bids are that in the race to place the lowest bid and win the project. The vendors might use cheap quality materials or resources, which can affect the project result. And sometimes, to secure a bid, the vendors might be left with little or no profits.
Also, there might be some communication gaps or barriers between the entity and the vendor. It might lead to the entity losing out on a vendor with more to offer, and the selected vendor might have some other demands that can later tax the entity.
Competitive Bidding Vs Sole Source
Let us understand the distinctions between a competitive bidding strategy and sole source through the comparison below.
Competitive Bidding
- Involves inviting multiple vendors to submit bids for a particular project, product, or service.
- Promotes competition among vendors, leading to potentially lower prices and better quality.
- Requires clear specifications, evaluation criteria, and bid submission procedures.
- Typically used for large-scale procurement projects where multiple vendors can fulfill the requirements.
Sole Source
- Occurs when only one vendor is capable of meeting the specific requirements of a project or providing a unique product or service.
- May be justified by factors such as proprietary technology, specialized expertise, or a longstanding relationship.
- Often results in a direct negotiation between the buyer and the sole source vendor.
- Generally used for urgent or specialized procurement needs where alternative vendors are not feasible or practical.
