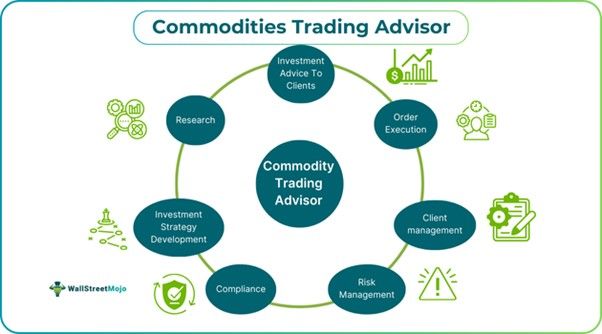
While both these professionals deal with similar underlying assets, the main distinction is the structure of their investments and the nature of accumulating funds for trading. However, if we look closely, there are minute differences at different levels. The distinctions between a commodity trading advisor (CTA) job and a commodity pool operator (CPO) are:
Table Of Contents
What Is A Commodity Trading Advisor (CTA)?
A commodity trading advisor (CTA) is a firm or individual who provides customized advice to clients concerning the buying and selling of off-exchange forex swaps or contracts, options on futures, and futures contracts. To practice as a CTA, these professionals must have a commodity trading advisor license from the National Futures Association (NFA).
CTA definitions can also apply to mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, and hedge funds. These professionals adopt one of three major trading styles: quantitative, technical, or fundamental. CTAs receive their remuneration through management fees, which are calculated as a certain percentage of the trading profits. Typically, CTAs get no incentive fees if they are unable to generate profits for that period.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Key Takeaways
- Commodity trading advisors are organizations or individuals who provide advice on commodities trading. They are registered with the Commodity Future Trading Commission (CFTC) and regulated by the National Futures Association (NFA).
- These professionals are remunerated through management and profit-generation fees. However, they might not be paid for a specific period if they do not generate any profits.
- Apart from a handful of situations, there are set requirements for CTAs to fulfill before they get certified by the NFA.
- Most CTAs have a minimum investment requirement of $10,000 to manage a client’s portfolio.
Commodity Trading Advisor Explained
Commodity trading advisors are organizations or individuals who provide services and advice regarding commodity options, futures contracts, and commodity swaps. They are responsible for trading within a managed futures account.
Commodity trading advisor jobs are most commonly found in hedge funds and other private funds, such as exchange-traded funds and mutual funds. Otherwise, certified professionals start their firm and practice.
They use a wide array of trading techniques and investment strategies, including futures and options contracts on multiple physical goods such as metals, energy, forest products, and agricultural products. They also tend to trade derivative contracts on financial instruments like bonds, currencies, and indices.
CTAs have to be members of the National Futures Association (NFA), which is regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), a state-federal government-regulated entity in the United States of America.
Trading in such information-driven, physical underlying assets requires a high level of market expertise. Therefore, these professionals use multiple strategies, such as trend-following systems and automated systems, to meet clients' and investors' investment goals.
These professionals are slightly different from commodity pool operators, who pool investor money and trade it, treating it as a single investment vehicle. CTAs address each client's requirements and invest according to their objectives and risk appetite. However, most CTAs set a minimum investment amount of $10,000.
A CTA's remuneration pattern is similar to that of most traders and advisors. They are compensated through a management fee, which is calculated based on the percentage of profits generated. They receive no compensation if they fail to generate a profit in a particular period.
Role And Responsibilities
A few of the most vital roles and responsibilities of a CTA after attaining their commodity trading advisor certification are:
- Providing trading/investment-related advice to clients on currency and commodity products
- Generating brokerage
- Executing orders on clients’ behalf
- Conducting extensive research
- Communicating research findings to clients for further actions
- Client management
- Onboarding new clients for commodity trading
- Developing investment strategies
- Risk management
- Compliance and regulation
- Implementing investment strategies
How To Become?
The foremost part of any profession is education. To obtain a commodity trading advisor license, an aspirant first needs a bachelor's degree in economics, finance, or a complementary field.
Given the domain's high intensity and competitiveness, it is also advisable to secure a relevant certification, such as the Series 3 license or the more challenging Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA).
With these qualifications, the individual shall be equipped with the knowledge to handle client affairs and the challenges of the commodity market. Therefore, they can proceed to apply for membership with the National Futures Association (NFA).
These are just the technical aspects of becoming a CTA. The ideal way to ensure success is to ensure that the professional is constantly on a learning trajectory, on top of current affairs, and has fantastic fundamental and technical skills to execute trades.
In addition to these skills, the ability to manage clients and communicate complicated findings and reports has helped these professionals advance in the industry.
Registration Requirements
To land a gratifying commodity trading advisor job, a CTA is expected to meet specific criteria set by the NFA. They include:
- CTAs must appoint a security manager to get access to NFA’s ORS (Online Registration System)
- Fill out online Form 7-R
- Fill out the Annual Questionnaire
- Pay CTA membership dues (non-refundable)
- Pay an application fee of $200 (non-refundable)
- Fill out the NFA membership application
Exemptions From Registration
The registration criteria mentioned above must be met by all commodities trading advisor certification holders as per the National Futures Association unless:
- The individual has advised only 15 clients or fewer in the past year, and the firm or individual needs to portray themselves to their clients as a full-time CTA.
- It is exempted if the advice is provided to a client without directly targeting their trading account or their trading/investing interests.
- The firm or individual is registered with the CFTC, and their advice regarding commodities is incidental to the firm's business or the individual's profession.
For professional-grade stock and crypto charts, we recommend TradingView – one of the most trusted platforms among traders.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Commodity Trading Advisor vs Commodity Pool Operator
| Basis | CTA | CPO |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | CTA refers to an individual or an organization that advises or manages client portfolios regarding commodity futures and options. | A CPO is an individual who invests in commodity futures and options through funds pooled from various investors. |
| 2. Client Relationship | Works directly with clients. Provides customized trading strategies. | Their role is similar to that of a mutual fund’s fund manager. They do not handle individual client accounts. |
| 3. Role | Based on client objectives, they advise trades or investment strategies. | They manage a collective pool of funds from different investors and trade in commodity markets. |
| 4. Regulatory Body | CTAs are registered with CFTC but are regulated by NFA | Registered with CFTC and regulated with NFA. |
| 5. Structure | Offers advise client-by-client basis. | Operates as a common investment vehicle. All investors share the risks and returns. |