Following are the differences between collecting and paying banks in general. Let us look at them:
Table of Contents
Collecting Bank Meaning
Collecting bank refers to the bank assigned on behalf of the customers to collect cheques (payments) from third parties. They act as an intermediary between the customer and the other party's bank. Their sole purpose is to undertake the work of the customers and receive payments drawn from the customer's bank.
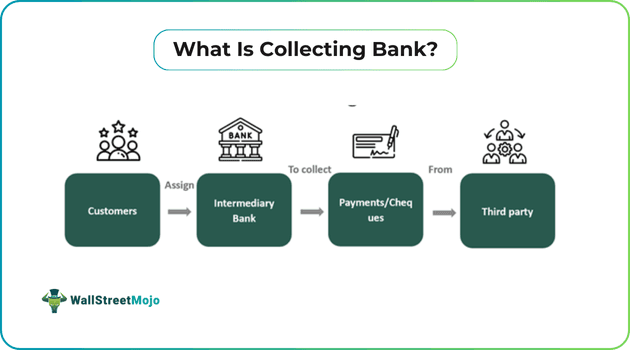
The primary role of this banker is to act as an agent and holder of value for items received. They ensure that there is a safe and secure transfer of funds from debtor to customer. Also, this bank verifies and authenticates the related documents on their behalf.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Key Takeaways
- A collecting bank is a commercial bank appointed by the payee (exporter or seller) to collect payments on their behalf.
- They charge a fee or remuneration for this service.
- They ensure the authenticity and security of the payments made by the debtor. Also, on cheque honor or dishonor, they must report to the payee as well.
- It differs from paying banks in that the former collects cheques, whereas the latter pays on the customer's behalf.
- However, drawee is a bank that processes the cheques.
How Does A Collecting Bank Work?
Collecting banks function as financial institutions that collect payments and cheques on behalf of their customers. They act as agents to facilitate the payments of the exporters and sellers. Also, they play a crucial role in ensuring authenticity in trades, thus reducing the chances of fraudulent payments and defaults. Thus, the presence of these banks is more prevalent in international trade. However, there are specific duties associated with collecting banks that ease the process.
In most trades, banks are a prime destination for accessing and depositing funds. However, they have certain duties and liabilities. Let us understand them in brief:
- Right To Collect Payment - One of the prime duties of such banks includes payment collection. They have the right to demand payment for the services or goods supplied by the customer to the buyer. However, it must be done as an agent to the customer.
- Right To Presentation - Such banks should also present the cheque to the customer within a reasonable time. In case of any delay, the bank may fail to obtain payment from the concerned party, and they may lose the right to collect the payment from the collecting party.
- Right To Remuneration - This banker also owns the right to charge its customers fees for the service provided.
- Right To Disclosure - Furthermore, the banker must also disclose all the details and information about the collection process. Plus, it is vital to cross the cheque before collection and inform in case of dishonor.
- Right To Set Off - It includes setting off any outstanding debt or liability of the customer against the payment they collect.
- Right To Indemnity - Likewise, the right to indemnity allows the banker to claim any losses or damages that occurred while collecting the payment. It mostly happens at times of dishonor of cheques or payments.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept in a much better way:
Example #1
Suppose James owns a plant that manufactures Android phones and related accessories. In the past few years, he has also started exporting orders to other nations. However, in this process, James always fears default payments from importers. Also, if he accepts the payments in advance, the customer (the importer) is doubtful on his end. Therefore, to solve this issue, James hired a collecting banker. At the same time, Kevin (importer) applied for collecting bank in documentary collection. It means that James's bank will try to collect payment from the importer. Kevin's bank will receive the documents from James. As a result, both parties are satisfied with their items.
However, at the time of collection, Kevin made a late payment. As a result, his bank expected a similar delay in the documentary collection process. But soon, the process speeded up, and Kevin could receive the goods on time.
Example #2
According to the news update, as of September 2023, the Oman-based Bank Nizwa announced its role as a collecting bank for OQ Gas Networks IPO (initial public offering). With this move, the banker made a wide impact on a larger audience. Also, customers and depositors of Bank Nizwa could easily apply for an IPO with their user-friendly application or by submitting their bids at physical branches. As a result, the issuer announced a float of around 49% capital with this IPO, making it the country's largest IPO to date.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Collecting Bank vs Paying Bank
| Parameters | Collecting Bank | Paying Bank |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Meaning | A bank that collects payments on behalf of their customers. | The paying bank is the one making payments on the customer's request with the available funds in the account. |
| 2. Role | The bank collects cheques from exporters or sellers and deposits them in the drawer's account. | They release payments to the seller or creditor when requested. |
| 3. Initiated by | It is initiated by exporters, sellers, or creditors to collect payments from other parties. | Here, the customer (or debtor) appoints a financial institution to act as a paying bank for them. |
Collecting Bank vs Drawee Bank
Thus, the collecting bank functions as a collector on the customer's behalf. However, it differs from drawee bank. Let us look at their differences:
| Parameters | Collecting Bank | Drawee Bank |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Meaning | It refers to a financial institution or bank that collects cheques on a customer's behalf. | Drawee Bank is the one on which the cheque is mostly drawn. |
| 2. Purpose | To collect payments from the concerned party within the stipulated time. | It is responsible to pay the full drawn amount and honor the check. |
| 3. Parties involved | The payor, payee, banker, and drawee bank. | Drawer, drawee, and payee. |

