Table Of Contents
Co-Operatives Meaning
Co-operatives or co-ops are associations of people with common social, cultural, and economic goals and needs. They are autonomous organizations that function democratically. The common types of co-ops present worldwide include housing, consumer, and agricultural co-operatives. Most co-ops are business enterprises, and the rest are people-centered organizations.
Co-operatives are more productive and often have more success than other businesses. This is because they form by bringing together people, especially those who belong to the same profession. Also, most co-operatives address social concerns and become more inclusive – they encourage women's participation, support LGBTQIA+ communities – and are overall progressive.
Key Takeaways
- Co-operatives are self-governing institutions formed by people with common social, cultural, and economic interests, often intending to address a specific issue.
- It brings together people, functions like a normal legal entity, and even conducts business.
- Most co-ops follow the seven Rochdale principles in their due course. The principles are laid down by the Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers, England.
- Co-ops are extremely democratic organizations. The members exercise their voting rights to elect their leaders and make important decisions.
How Do Co-operatives Work?
Co-operatives' history can be traced back to the first ever established, the Mondragon Corporation, a worker co-op founded by José María Arizmendiarietta, a Catholic priest, in 1956. It is still in operation.
Co-operatives are simple associations of people who either have similar interests or face similar problems. Mostly, their objective is to resolve the issue and help everyone benefit. Unlike other types of enterprises or business organizations, they are not motivated by profits. The agricultural co-operatives are best examples of the same.
Hence, co-ops are more productive. Surveys suggest that 80% of co-operatives are likelier to succeed in the first five years of establishment than 41% of other business enterprises.
Nowadays, many co-ops even have an online presence. Further, they have a global base and accept membership from eligible candidates worldwide. This gives them a good level of influence and global reach. Moreover, one can easily identify co-op websites by the .coop domain.
Characteristics
Let us study the characteristics of the system of agricultural or housing co-operatives or any others in details.
- The are voluntary in nature. Anyone can become a member of the society and remain a member. There is no differentiation based on any criteria.
- The co-operative follows a structure that is similar to democracy, which means that every member is equal within the system and has equal voting rights.
- Every member gets equal opportunity and access to the products and services provided by the co-operatives as it happens in agricultural co-operatives. There is an equal and completely fair distribution of facility that benefits all members.
- The members work with independence and have to face less rules and regulations.
- The main aim of the organization is to concentrate on community welfare, not earning profits. However, any profit earned is reinvested into the group for future use and social development.
Thus, the above are some important characteristics of this concept.
Principles
Co-operatives are usually governed by the seven Rochdale principles put forth by the Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers, England, in 1844.
- Voluntary and open organizations - Volunteers form co-ops with membership open to all considered eligible. It functions beyond gender, racial, and social stereotypes.
- Democratic member control - Co-ops are extremely democratic organizations that elect members to govern. Therefore, they make most decisions by considering the opinion of all the members.
- Member economic participation - Since co-ops are autonomous organizations, they are funded internally by the members. Therefore, members contribute to financing the co-op activities of agricultural or housing co-operatives or any others. Any profit made by the co-op is first set aside for its operations and then divided between the members.
- Autonomy and independence - The very word 'autonomy' defines co-ops. They are self-governed and not answerable to other associations except the law.
- Education, Training, and Information - Co-ops offer education and training to their members to enhance their overall capability and skills. They also disseminate information within and with their partner organizations.
- Co-operation among co-operatives - Co-ops work in partnership with other co-ops locally, nationally, and internationally with similar or complementary interests. This can present a win-win situation for all the co-ops involved.
- Concern for the community - Co-ops usually address important social and economic issues like unemployment, racial or gender discrimination, environmental and sustainability concerns, etc.
Types
Now, let's discuss the prominent types of co-operatives around the world.
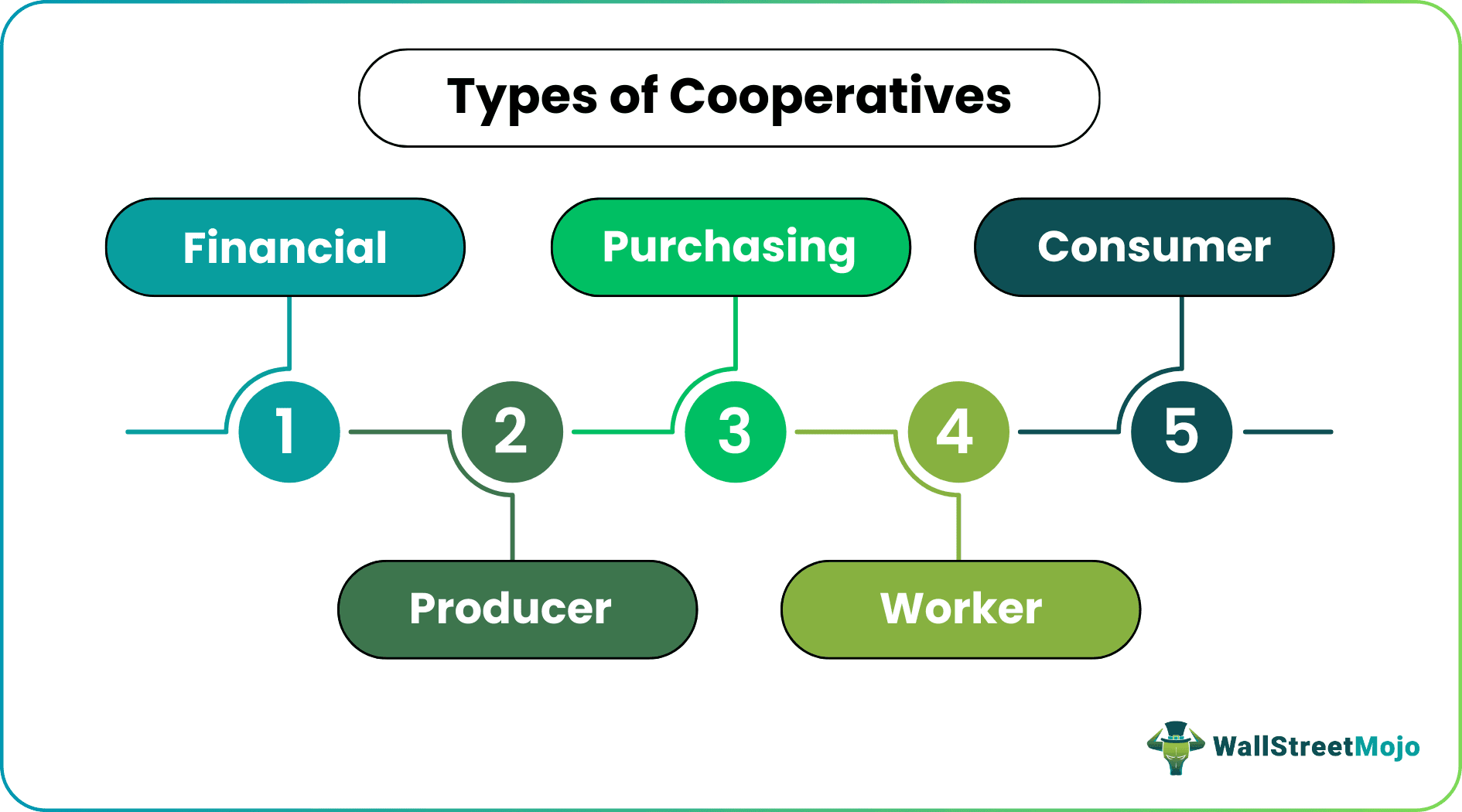
- Consumer co-operatives – These are co-ops that consumers themselves own. Examples include retail co-ops, housing co-ops, etc. These help the management address the needs of the consumers and tailor their offerings accordingly.
- Worker co-operatives – These associations of co-operatives business form by people who often belong to the same profession. They train, educate, and prepare the members to get employment. Occasionally, they also address some issues faced by the people working in the same field.
- Purchasing co-operatives – Those co-ops form by businesses that partner for common buying interests and requirements. For example, firms that sell flour can demand a wheat price reduction.
- Producer co-operatives – Producers of similar goods and services, form associations known as producer co-ops. Agricultural co-operatives are an excellent example of this category. For instance, sellers of wheat can together demand that its price be increased.
- Financial co-operatives – In this type, associations of people provide financial services like banking and insurance. Credit unions are a good example. There are a large number of co-operative banks worldwide, providing critical financial assistance to those who need it.
These are the most common types of co-ops. Some other less common types include multi-stakeholder co-ops, which consist of the different stakeholders of an organization, like employees, shareholders, partners, etc. Another type is the federal co-op, in which many co-ops form a secondary association.
Examples
Let's discuss co-operatives in detail with the help of a real-life and hypothetical example of of co-operatives business.
Example #1
Here is a hypothetical example of a worker co-op X in the United States. It was formed by graduates who could not land a job due to outsourcing. Over the years, the co-op partnered with many organizations to specialize in members' training.
The association expanded to Canada and now focuses on jobs lost due to automation. The main objective of the co-op is to enable the members to get jobs that are less liable to be lost by external factors.
Example #2
Consider this recent example of energy co-ops in Belgium. Unfortunately, the present electricity situation in Europe is not pleasant. The Russia-Ukraine war has contributed to soaring electricity prices, and the demand is only increasing.
Enter energy co-operatives, which can power their members for half of what the commercial provider would ask. But the condition isn't great here either. The demand for energy co-op memberships has also increased, and these associations have had to stop taking new admissions temporarily.
In Belgium, there are 40 co-ops, currently supplying power to 2% of households. The market leader is Ecopower, which alone powers 55,000 homes and produced about 80 kWh last year. However, a more supportive legal framework could benefit the citizens with the demand-supply situation.
Importance
Co-operatives are one of the increasingly popular enterprise types in the world. So let's look at the key factors that make them important.
- Co-ops are formed mostly due to social and economic concerns. For example, women in business can together form an association and work for equitable pay and job representation.
- Co-ops are generally considered more productive than other types of organizations. This is probably because they have other objectives rather than just making profits.
- Co-ops promote democracy within organizations. In the era of many management techniques, bureaucratic and flat organizations, productivity through democracy can be a convincing reason for the popularity of a co-operative.
- Co-ops can provide quality. Since they are formed by identifying gaps or addressing the needs of a section of society, their personal needs are often associated with their goals. Hence, they strive to benefit by providing quality.
Benefits
Some benefits of the system of community co-operatives are as follows:
- In any co-operative model, be it relate to business, or society or agriculture, etc, all members will get equal opportunity and status in the unit. The power of decision and control in various matters remain same for all, even though their monetary contribution may differ.
- The system does not differentiate any member based on class religion, social status or financial ability. Therefore, anyone can join the group and take benefit of the services provided and ideally there is no minimum or maximum limit to the number of members.
- The groups are mainly focussed towards providing best level of products or services to the members. Their profit motive is not so prominent. Sometimes that arrange for goods or services that may not be normally available in the market and the profits earned are usually reinvested for upgradation and development.
- The main purpose is community service and enhancement of the lives of the people. The members believe in good and ethical business practices so as to make community people stronger, well informed and closely connected to each other.
- It is a very stable and strong system that leads to sustainability and typically, due to very low profit motive, the typical business-related problems can be avoided. There are more people who bring in ttheir knowledge and experiences and control any negative deviations to achieve the aim.
- It is a system that can be formed and maintained very easily, without many rules and legal documentations. Therefore, it is commonly preferred for many purposes.
Co-operatives Vs Corporations
Both the above refer to formation of groups of people with the aim of providing products and services to its members. But there are some differences between them as follows:
- The community co-operatives is a type of corporation but formed with less complexity and legal hassles. But the latter is formed after the members meet many general and legal criteria.
- The former is not very focussed on profit motive. Rather they are more interested in providing the best level of products and services to its members. The latter may be profit earning or non-profit earning. It depends on the purpose of their formation.
- The members in case of the former, is liable for any action and financial liability of the group. Thus, the owners are not separate from the entity. But in case of the latter, the owners are typically the shareholders of investors who are not liable for any financial burden that the organization may suffer. The owners are completely separate from the entity.
- In case of the former, all members are given equal status and possess the same right to vote. But in case of the latter, the members may have different voting rights, which depends on the type of shares they hold or their position in the company affairs.
- The former is commonly found in fields like agriculture, education, housing, healthcare, insurance, groceries, labor, etc. But the latter is commonly in industrial products, technological innovation, research, etc.
- In terms of taxation, the former gets many tax-related facility that are not normally available to the latter.
Thus, the above are some important differences between the two concepts.
