Table Of Contents
What is the Check Sheet?
A Check Sheet refers to a document used for recording data at the time and place of the operation of interest. Typically, a blank document is taken to start with. Then it is designed for easy, quick, and effective recording of the required data, which can be either qualitative or quantitative.
This sheet helps identify all possible errors and has the flexibility to add more sources of error based on practical experience. These are then used for recording data about the errors, which are eventually used for analyzing the operational issue. This sheet is an important part of Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa's seven quality control tools.
Key Takeaways
- A check sheet is a document used to capture data at the time and location of the operation of interest.
- Typically, a blank paper is used to begin. Then, it is built for easy, rapid, and successful data recording, whether qualitative or quantitative.
- This sheet gathers information about faults and analyzes them to address operational issues. It is part of Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa's seven quality control tools.
- The check sheet types are Tabular, location, and graphical sheets.
How to Prepare a Check Sheet?
- Select the problem that has to be resolved and then construct the operational definition of the problem.
- Determine when to start and for how long the data has to be collected.
- Take a blank document and design it so data can be recorded quickly. For instance, record the errors using tick marks or similar symbols in checkboxes provided adjacent to the error type.
- Run a short trial to ensure that it appropriately serves the purpose of data collection.
- Once checked and confirmed, this sheet is ready for use.
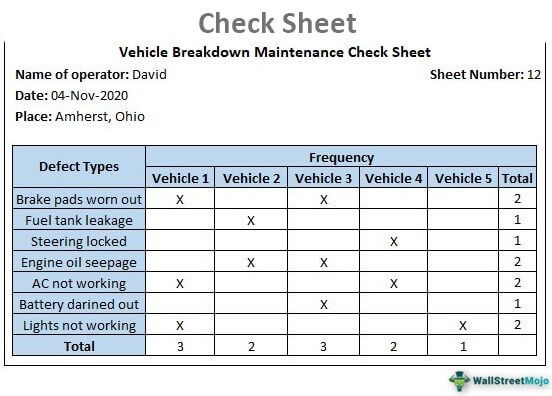
Check Sheet Example
The below example shows the check sheet prepared to understand the major issues underlying the vehicle breakdown.

Check Sheet Types
- Tabular Sheet: This is usually used for collecting data about quality issues and determining the frequency of any event—for instance, the reasons for accidents during laboratory experiments.
- Location Sheet: This usually employs a diagram-based representation of the issues. For instance, one can indicate the damages and dents on a car's body by marking the corresponding location in its picture.
- Graphical Sheet: This uses a graphical form of representation such that the observer can collect data and visualize the distribution of data.
Check Sheet Format
An appropriately designed check sheet covers various points, such as frequency and location of defect events, whether or not inspections have been completed, etc. Some of the common points that are usually included in the format of a check sheet are as follows:
- Name of the operator
- Type of the data being collected
- A location where the data is being a collection
- Schedule of data collection
- The objective of data collection
The following is one of the common formats used for the check sheet.

When to Use?
- The data can be continuously observed and collected at the same location by the same person.
- The data is collected to capture the frequency or patterns of problem events.
- The data is collected from a production process.
Applications
These are usually associated with menial tasks of recording defect events; it can be beneficial for recording expected items in the process, displaying the performance of the process, identifying causes of the defect event, and revealing trends or patterns in the defect events.
Replacement
Over the period, check sheets have become archaic as they have been gradually substituted by various modern-day business process management software. Now the data can be recorded automatically and organized, and presented in whatever way required in a few clicks. Some of the available business process management software produces the output in a ready-to-use graphical format which is more convenient for the users. This new set of software enables automatic recording of more complex data, and it practically eliminates the dependence on human intelligence and the reliability of check sheets.
Tips
- Ensure that all the operators involved in the process are properly trained and clearly understand every section of the check sheet.
- Run a short pilot exercise to validate that the sheet captures the required data appropriately and, if required, make the necessary improvements.
- As far as possible, try to make use of quantitative data instead of qualitative data, as the former results in more conclusive evidence.
- As far as possible, try to make use of quantitative data instead of qualitative data, as the former results in more conclusive evidence.
