Table Of Contents
What Is A Challenger Bank?
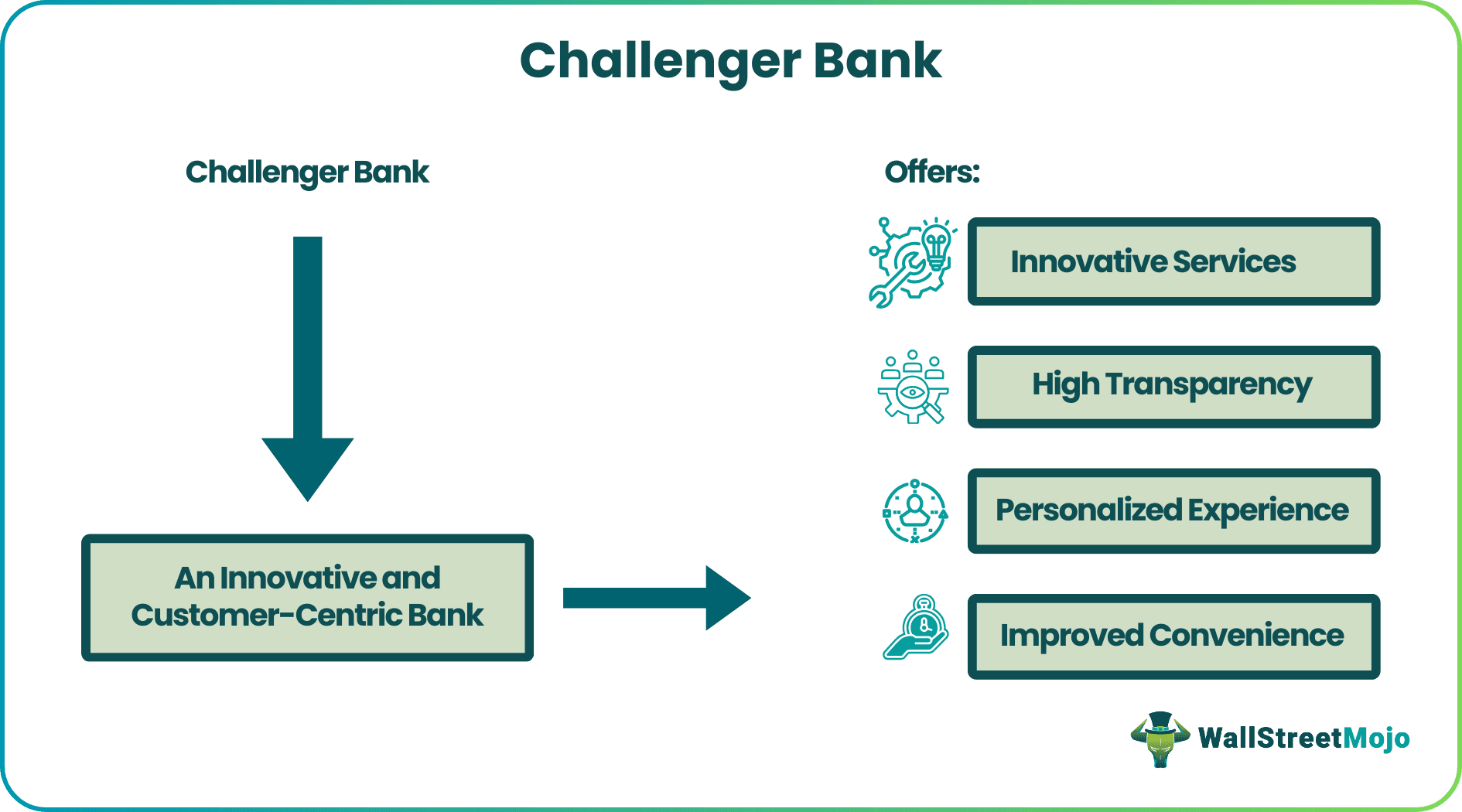
Challenger Bank refers to modern banking entities that primarily operate online and typically focus on providing digital and mobile-based financial services. These banks challenge traditional banking models by offering innovative, customer-centric, and often more cost-effective solutions. However, they may also have physical presence.
These banks play a key role in boosting financial inclusion, especially in regions or among populations that remain underserved by traditional banks. Their online and mobile-based services make banking more accessible to people who may have limited access to physical branches of banks. Challenger banks prioritize user-friendly interfaces, easy account setup, and 24/7 customer support.
Table of contents
- What Is A Challenger Bank?
- Challenger banks emerged after the 2008 financial crisis, aiming to revolutionize traditional banking with innovative digital solutions.
- They prioritize user-friendly mobile apps, transparent fees, and robust customer service. These banks enhance financial inclusion by providing services primarily through online platforms.
- The advantages of these banks include technological innovation and improved customer experiences, but limitations involve service restrictions, cybersecurity concerns, and potential stability issues due to their relative newness compared to established banks.
Challenger Bank Explained
Challenger bank evolution was a bigger milestone after the 2008 financial crisis. The Global Financial Crisis of 2008 had a profound impact on the public's trust in traditional banking institutions. Many traditional banks were implicated in risky lending practices and financial misconduct, leading to a loss of confidence in the industry. They were believed to have been key contributors to the economic turmoil that ensued. This loss of trust created an opportunity for alternative banking models to gain ground.
In response to the public's disillusionment with traditional banks, challenger banks emerged with a focus on transparency and customer-centric approaches. They aimed to address the shortcomings and negative perceptions associated with traditional banking.
In Europe, the deregulation of the financial sector following the crisis reduced the barriers to entry for new banking institutions. This deregulation made it easier for startups and fintech companies to enter the banking industry without facing the same level of regulatory hurdles that had previously characterized the sector.
Rapid technological advancements, particularly in the domain of digital infrastructure and mobile technology, provided the essential tools for online banking. The availability of smartphones and the growth of the internet created a conducive environment for online banking to thrive.
Furthermore, banks integrated their online banking platforms with third-party applications, such as budgeting tools and personal finance management apps, using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). It proved to be a major step in advancing online banking, which offered a more holistic banking experience.
A market study report focuses on a new assessment of the Neo and Challenger Bank market, providing a comprehensive analysis of the factors shaping its size and growth. In 2022, the global Neo and Challenger Bank market share was estimated at approximately $6.57 billion and is anticipated to reach around $8000.47997710596 million by 2028, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 3.33% over this period. The report examines the regional landscape and the competitive environment and explores existing and upcoming trends expected to steer the growth of this industry.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Characteristics
Challenger banks have certain unique characteristics that distinguish them from traditional banks. Let us study these characteristics.
- Exceptional mobile banking services: Challenger banks prioritize user-friendly mobile apps and websites, enabling customers to easily manage their finances, deposit checks, transfer funds, and pay bills with minimal effort. Additionally, they streamline the account opening process and offer swift loan approvals, enhancing customer convenience.
- Transparent fee structures: They prioritize fee transparency, prominently displaying fees on their websites and apps. Many banks keep fees to a minimum or eliminate charges altogether, sparing customers from unexpected costs like overdrafts or monthly maintenance fees.
- Customer-centric approach: These banks invest in robust customer service teams and deliver an all-encompassing customer experience. Many of them offer easy access to human customer support alongside digital services, which contributes to enhanced overall customer satisfaction.
- Branchless banking model: These banks operate as branchless banks, resulting in low overhead costs. This cost-effective model enables them to deploy more resources towards activities that focus on customer convenience and satisfaction while offering competitive interest rates.
Examples
Let us study some challenger bank examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose SmartSavings Bank is a forward-thinking challenger bank designed for the digital age. SmartSavings takes banking convenience to a whole new level with its intuitive mobile app, allowing customers to effortlessly manage their finances from a device in the palm of their hands. What sets the bank apart is its highly competitive savings account, offering an Annual Percentage Yield (APY) that outpaces traditional banks.
This is made possible by their agile, branchless model that reduces overhead costs. To further enhance the customer experience, SmartSavings proudly promotes fee transparency, ensuring customers can easily access information on any applicable charges. Most notably, SmartSavings is fully chartered and Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insured, assuring its customers that their hard earned money is safe and secure.
SmartSavings Bank exemplifies the hallmark features of a challenger bank, combining digital convenience, competitive savings opportunities, transparency, and financial protection, all while maintaining a strong focus on customer satisfaction.
Example #2
Revolut, launched in the UK in 2015 by founders Nikolay Storonksy and Vlad Yatsenko, was one of the pioneering challenger banks. It began with free currency exchange and ATM withdrawals, making international spending and money transfers easy.
Expanding globally, it offers services like currency exchange, debit and virtual cards, Apple Pay, stock trading, and cryptocurrency. In 2020, Revolut entered the Japanese and US markets and achieved a $5.3 billion valuation, becoming the UK's most valuable fintech company.
As of 2021, it boasts over 30 million users, but its UK banking license application is pending, meaning it is currently an e-money institution without Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) protection. Revolut secured substantial equity funding and aims to further develop products and expand its presence in the US, India, and Latin America. In 2021, it acquired Wanted and Nobly.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of challenger banks are listed below.
Advantages
- Challenger banks are at the forefront of technological innovation, providing customers with user-friendly mobile apps, real-time notifications, and other advanced features that traditional banks may lack.
- These banks prioritize customer experience and often offer 24/7 customer support, transparent fee structures, and user-friendly interfaces.
- Challenger banks often cater to underserved populations and regions by providing banking services through mobile apps and websites, increasing financial inclusion. The importance these banks give to mobile-first platforms and digital banking enables them to reach customers, particularly in geographical areas where traditional banks have limited physical presence.
- Some challenger banks offer favorable exchange rates and reduced fees for international transactions, making them ideal for travelers or individuals with global financial needs. The hefty charges for currency conversions and international transfers of traditional banks make availing of global financial services an expensive affair for customers.
Disadvantages
- Some challenger banks focus on specific services, like savings or payments, rather than offering a full suite of traditional banking services. This can be limiting for customers with diverse financial needs.
- As digital institutions, challenger banks may be susceptible to cyber threats, and there can be apprehensions about the safety of digital banking. Customers need to ensure they use strong security practices.
- Some challenger banks are relatively new and may lack the experience and stability of long-established traditional banks. Customers may be concerned about the bank's long-term viability and ability to handle financial downturns.
- While online banking is convenient, the absence of physical branches can be a drawback for customers who prefer in-person interactions or need services that require a physical presence, like safe deposit boxes.
Challenger Bank vs Digital Bank
The differences between challenger banks and digital banks are enumerated in the table below.
| Basis | Challenger Bank | Digital Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition and scope | Challenger banks are a subset of digital banks that specifically challenge traditional banking models by offering innovative and customer-centric financial services. | Digital banks are financial institutions that primarily operate online, providing services through websites and mobile apps. |
| Focus | They often prioritize ease of use, transparency, and competitive pricing. | They leverage technology to offer digital banking experiences. |
| Objective | They aim to disrupt the traditional banking sector and target specific pain points or areas of inefficiency in traditional banking, such as high fees, complex account management, and outdated technology. | These are banks with a disruptive approach, where they encompass a broader category that includes both traditional banks with online services and challenger banks. |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, challenger banks are regulated financial institutions, just like traditional banks. They are subject to the same regulatory standards and consumer protection measures as traditional banks. These regulations may vary by country or region but typically include requirements related to capital adequacy, consumer protection, anti-money laundering, and more.
Challenger banks are financial institutions, often digital, that challenge traditional banking practices with a strong emphasis on innovation and customer-centric services. On the other hand, Neobanks are a subset of challenger banks that operate exclusively in the digital space, without physical branches, and typically partner with traditional banks for core banking services.
Metro Bank is categorized as a challenger bank since it takes an innovative approach to banking and emphasizes customer experience. It also follows a digital-first strategy. It was one of the first challenger banks in the United Kingdom and has played a key role in altering the traditional banking landscape.
The emergence of challenger banks as a significant force in the banking industry gained momentum in the years following the Global Financial Crisis of 2008. This period saw a surge in dissatisfaction with traditional banks, which led to an opportune environment for more customer-centric and technologically innovative financial service providers. Challenger banks, particularly in Europe, began to proliferate in the mid-2010s. Their disruptive impact continues to reshape the banking landscape globally.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is a Challenger Bank. We explain it with its examples, comparison with digital bank, advantages, & disadvantages. You may also find some useful articles here -

