Table Of Contents
Catastrophic Risk Meaning
Catastrophic risk refers to a situation where a large number of individuals become exposed to large loss-making risks due to a catastrophic event. To deal with the high impacts of large-scale risks, it identifies critical system functionalities, quantifies consequences and vulnerabilities, develops mitigation solutions, and creates crisis response guidelines.
Its assessment helps governments and organizations recognize main strengths, conduct horizon scans related to top risks, evaluate fresh designs, and highlight international events concerning such risks. It aids in threat mitigation, conveys policy decisions, and minimizes lifecycle costs. Sometimes, the government comes forward to provide coverage against these risks.
Key Takeaways
- Catastrophic risk occurs when a large group of people becomes exposed to a significant risk of monetary loss as a result of a catastrophic event.
- It defines crucial system operations, measures the implications and vulnerabilities, formulates mitigation strategies, and sets crisis response protocols to address the significant effects of large-scale hazards.
- It can be managed by facilitating risk mitigation decisions, developing detailed risk financing solutions,
- exploring alternative insurance risk transfer using catastrophe bonds, designing risk management strategies, setting up business sustainability plans, involving directors in risk oversight, and coordinating with public sector leaders.
Catastrophic Risk In Insurance Explained
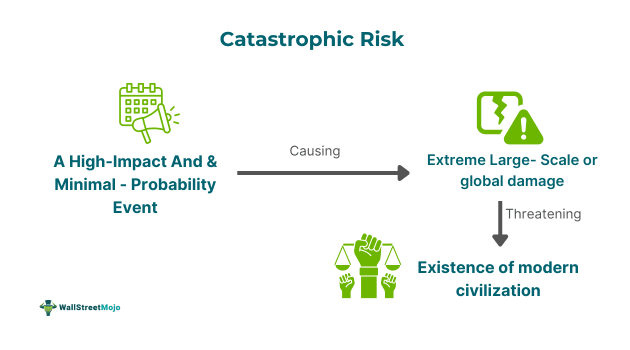
Catastrophic risk means a high-impact and minimal-probability event that might cause extreme damage on a global or large scale, threatening the very existence of human life and modern civilization. It represents a risk that businesses face out of human causes or natural events. These may include asteroid impacts, gamma-ray bursts, super-volcanic eruptions, new technology, climate change, governance, engineered pandemics, nuclear war, and floods.
It has wider implications that can result in irreparable and irrecoverable harm, which makes it the most critical concern. It becomes quite challenging to accurately assess its impact and probable occurrence because of non-existent historical precedence and data. Also, its place and time of occurrence cannot be ascertained in the dynamic geopolitical landscape and technological changes.
Organizations like the Global Catastrophic Risk Institute, insurers, and governments examine catastrophe risk to find vulnerabilities in mitigation strategies and quantify risk exposures. They do this using various techniques, such as stress testing, alternative risk transfer systems like catastrophe bonds, and catastrophic risk modeling. This has become a great challenge for the financial sector.
It is because they cause damages on a widespread and large scale that breach the capacity of containment or coverage by conventional reinsurance or catastrophic risk in insurance markets. Moreover, such impact has resulted in the creation of new innovative risk management methodologies like capital market solutions and public-private partnerships.
Therefore, such devastating risks pose a high degree of complex and significant challenges in the current time, as pointed out in Nick Bostrom's book on global catastrophic risks. Hence, it requires a multipronged approach to evaluation, reduction, and response across different domains like technology, insurance, and finance.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
An online article published on 14 May 2024 discusses the effect of recent floods in Rio Grande do Sul of Brazil related to the demand for catastrophic coverage. Also, heavy rains started falling on 28 April and continued until the first week of May, totaling 400 millimeters, which caused significant disruptions, including 147 deaths and hundreds of thousands of displacements. Hence, an estimated loss of 7.5 billion BRL took place, consisting of 2 billion BRL public losses and 1.1 billion losses pertaining to the private sector.
As a result, the demand for coverage of the risk of catastrophe has been seen on the rise, as reported by S&P Global Ratings, leading to increased premiums and insurance prices. Further, the impact of floods has the potential to affect all other sectors, including public infrastructure, the agricultural sector, and the private property and services industry.
Example #2
Let us assume that in the year 2024, the old York City will have to face a catastrophic risk. This risk stems from an impending hit by asteroid Thanos on Earth and specifically on the said city. A data scientist studied the asteroid and found that it has a 10 km width and a 90% chance of impacting the city in the coming six months.
The devastation that Thanos would cause could destroy 60% of the city, including human losses, infrastructure elimination, animal extinction, and destruction of arable land. Hence, governments and organizations have tried very hard to develop sound mechanisms to avert the danger and safeguard human losses and animal lives. Hence, many reinsurers who had earlier covered such losses due to catastrophe failed to respond, transferring the whole obligation to the government.
How To Manage?
It can be managed by implementing the following:
- Designing strategies for risk management while recognizing interdependence concerning sophisticated system interactions.
- Helps to set up sound business sustainability plans to enable operational resilience during disruption.
- It makes risk management an integral part of the business and encourages directors' proactive participation in risk oversight.
- It also engages with leaders of public sectors to coordinate crisis-thwarting efforts and leveraging resources.
- Facilitates risk mitigation decisions through geographical information procedures and catastrophic modeling.
- Develops detailed risk financing solutions and enhances insurance penetration, thereby strengthening public-private partnerships.
- It allows the exploration of alternative insurance risk transfer using catastrophe bonds.
