Table Of Contents
What Is Cash with Order (CWO)?
Cash with order (CWO) refers to a B2B payment method utilized in the supply chain sector where the purchaser makes full payment for products when placing their order with no further payment required at the time of delivery. It encourages buyers and sellers to honor trade agreements while protecting purchasers from receiving substandard products.
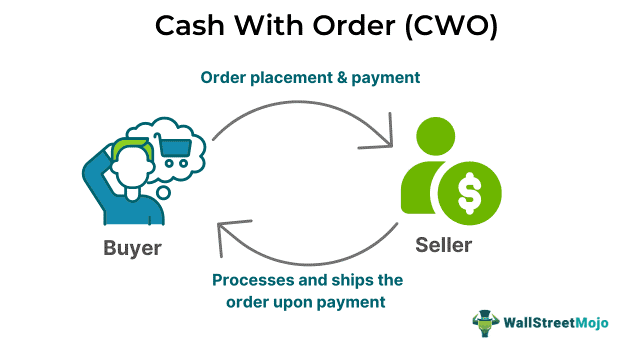
This method is often used by buyers and sellers with established trade relationships because the buyer has confidence in the seller and their offerings. Sellers start processing, fulfilling, and shipping the order only after the buyer makes the full payment upfront. It is similar to prepayment or payment in advance of trade.
Key Takeaways
- The cash with order (CWO) is a B2B payment option used in the supply chain industry where the buyer pays the full amount at the time of placing the order.
- It protects the seller and buyer from payment-related issues.
- It benefits sellers and purchasers through improved financial management, reduced fraud risk, increased satisfaction, easy B2B commerce, manufacturer control, refund protection, and project cost determination.
- It has risks like limited cash flow, risk of check return, limited flexibility, and potentially fraudulent activity due to non-delivery or lack of payment confirmation.
Cash with Order Explained
Cash with Order (CWO) or Cash in Advance (CIA) is a payment term where the exchange of cash occurs while placing an order, forming a binding agreement between the buyer and the manufacturer. Such an approach mandates commitment and immediate payment from the buyer to complete the agreement. It has become an important mode of transaction in various industries like retail, manufacturing, and construction.
CWO is often used when:
- The order placement is for high-value products or,
- The seller wishes to minimize the risk related to non-payment or,
- The buyer seeks to minimize the risk of poor quality or non-delivery of goods.
The CWO model comes with several implications in high-value transactions. Once the CWO payment is made, the seller is bound to deliver goods corresponding to the order, and the buyer must receive the order without any objection. CWO does not allow the buyer to make part payment of the order upfront and the rest upon receipt; the full payment is necessary during the order placement.
Payment before delivery improves the cash flow position and liquidity of the seller, manufacturer or service provider. As a result, the seller can manage its working capital in a better manner. It has great usability in businesses because of its simplicity and straightforwardness. Hence, it has become the best option for businesses wanting to systematize their payment systems and decrease the time taken to fulfill the order. Furthermore, sellers benefit by securing upfront payments by reducing their bad debt risk.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
Let us assume that a clothing boutique – Kara Corp., decides to order a tailored batch of shirts from a manufacturer for the first time. The value of the order runs into millions of dollars, and the boutique has never before worked with the manufacturer. As such, it secures the order and protects itself from fraud; it decides to pay using CWO for the entire batch.
As a result, the manufacturer starts producing the shirts after receiving the upfront payment. Hence, the boutique's risk of placing unfulfilled orders is reduced to a great extent, and it gets the order fulfilled on time using CWO.
Example #2
Let us assume client A, having a stationary retail shop in Old York City, needs pens in bulk from its manufacturer urgently. Understanding the gravity and emergency, manufacturer B in ancient York city requests CWO arrangement from the buyer to get immediate payment prior to shipping the pens. Client A approves the demand and makes the payment to B's account.
As a result, B ships the bulk pen orders to A store in Old York City swiftly so that A is able to restock the penstocks quickly. Hence, CWO saves the day for retailer A and increases its reputation amongst the customers.
Benefits
CWO model offers multiple benefits to sellers and purchasers, as listed below:
- CWO offers systematic cash payment to the seller, improving its financial management and cash flow.
- This model reduces the risk of fraud by receiving payment before delivering the goods.
- It increases the satisfaction and trust between the manufacturer and the buyer.
- It facilitates easy trading in B2B commerce.
- It gives the upper hand to the manufacturer over the buyer or retailer.
- It eliminates the need to chase after payments from the buyer.
- The customer gets protection from substandard services or goods by requesting a refund for the advance made.
- Manufacturers and businesses determine a project's total earnings and cost through automated invoices.
Risks
The risk associated with the CWO model includes:
- Buyers' cash flow becomes limited as they are made to pay for goods before their delivery, potentially disrupting their operations.
- It becomes risky for buyers as it does not guarantee delivery or quality.
- In case the transaction utilizes the cheque mode of payment, then there is a risk of the cheque being returned due to insufficient funds in the buyer's account.
- It has less flexibility than other modes of payment.
- It may become a means of fraudulent activity where the manufacturer declines to deliver the goods or fails to acknowledge the receipt of payment.

