Table Of Contents
What is Capital Gains Tax?
Capital gains tax (CGT) refers to the tax liability realized by a taxpayer for the profit he made by selling an investment. For example, if an individual sold a property that he owned for more than a year and received a profit, he is liable to pay CGT.
In simple words, it is the tax applied on realized capital gains. A capital gain occurs when the value of a capital asset increases, and it is unrealized until the capital asset is sold. In contrast, if the value of a capital asset decreases, a capital loss occurs, and when it is sold for a decreased value, the capital loss is realized.
Key Takeaways
- Capital gains tax is the tax applicable for the income earned from selling capital assets or investments like stocks, bonds, houses, and collectibles.
- Capital gain is classified into long-term and short-term capital gains (LTCG and STCG) and is taxed differently.
- LTCG tax occurs when the gain is realized from the sale of an asset held for more than a year.
- STCG tax occurs when the gain is realized from the sale of an asset held for less than one year and is taxed as ordinary income.
Capital Gains Tax Explained
Capital gains tax is associated with capital assets owned by the people for personal or investment purposes. Such assets include stocks, bonds, houses, buildings, and collectibles. When people sell these assets, the difference between the selling price and the purchase price (cost basis or adjusted basis) gives the capital gain value, given the selling price is greater than the purchase price. Furthermore, the capital gains are classified into short-term and long-term (STCG and LTCG).
There is no single uniform rate for capital gains realized. It varies with the type of gains (short-term or long-term), taxpayer's category or taxable income, filing status, state's tax laws, etc. There are exceptions also. For example, the LTCG realized corresponding to the sale of collectibles is taxed differently, usually at a high rate compared to the normal range. Also, owning and using the asset sold profitably as a home for a minimum of two years in five years preceding the sale date will give the taxpayer the benefit of subtracting a specified amount from the gain realized while calculating the tax liability.
Long-Term Capital Gains Tax
- It is applied to profit from the sale of assets held for more than a year.
- It is observed that the LTCG tax rate is lower than the tax rate applicable for ordinary income and depends on the taxpayer's taxable income. A lower rate than the ordinary income tax rate makes holding investments for the long term a favorable strategy.
- In the United States, the various LTCG tax rates are 0%, 15%, and 20%, based on the taxable income and corresponding tax bracket.
- The net long-term capital gain is the difference between long-term capital gains and long-term capital losses, including any unused long-term capital loss from previous years.
- Long-term capital losses can offset long-term gains. Also, if the long-term losses exceed long-term capital gains, the remaining amount can offset the short-term capital gains.
Short-Term Capital Gains Tax
- Obtained from the profit from selling an investment held for less than a year.
- Normally, STCG is taxed as ordinary income applying tax rates set for ordinary income. Hence, the STCG tax rate is generally higher than the LTCG tax rate.
- Short-term capital losses can offset short-term capital gains. Also, if there is a balance in the short-term capital loss account, it can offset the long-term capital gains.
Capital Gains Tax Video Explanation
How to Calculate Capital Gains Tax?
Let's look into some of the capital gains tax rates in 2021 and 2022 essential to calculate LTCG taxes. Furthermore, people also use the online capital gains tax calculators to reduce the complexity involved.
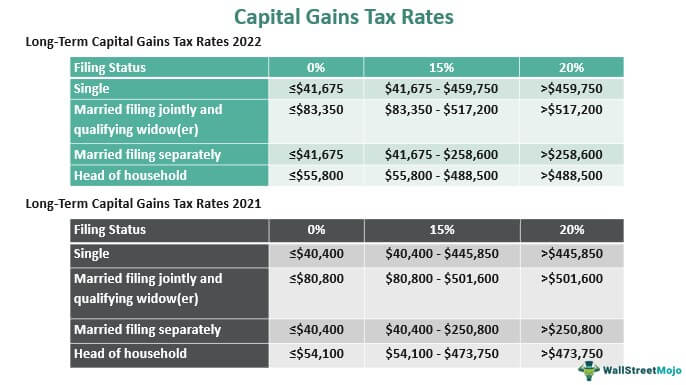
0% (2022):
- Taxable income should be less than or equal to $41,675 for taxpayers under filing status "single."
- If the filing status is "married filing jointly" or "qualifying widow(er)," the taxable income should be less than or equal to $83,350.
- Less than or equal to $41,675 for taxpayers under filing status "married filing separately."
- Less than or equal to $55,800 for taxpayers under filing status "head of household."
15% (2022):
- It applies if the taxable income is between $41,675 - $459,750 for taxpayers under filing status "single."
- For "married filing jointly" or "qualifying widow(er)," taxable income should be between $83,350 - $517,200.
- Taxable income should be between $41,675 - $258,600 for "married filing separately".
- Taxable income should be between $55,800 - $488,500 for taxpayers under filing status head of household.
20% (2022)
- LTCG rate of 20% applies if the taxable income exceeds the limit set for the 15% LTCG rate.
- Maximum 28% rate: The taxable part of a gain from selling "Section 1202 qualified small business stock" and gains from selling collectibles.
- Maximum 25% rate: The portion of any "unrecaptured section 1250 gain" from selling "section 1250 real property".
